Interpolation is a powerful method for predicting and estimating data. It helps researchers fill gaps between known data points1. This technique allows for accurate estimations across various fields, from physics to computer science1.
Interpolation is crucial for understanding complex datasets. It estimates values between existing data points. This creates smoother, more complete representations of information1.
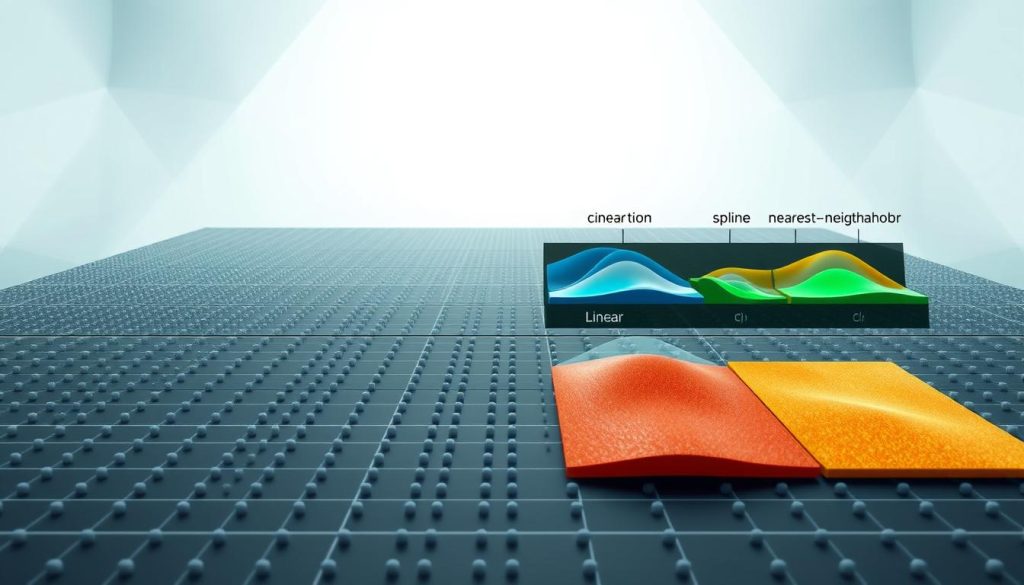
Several interpolation methods exist, each with unique strengths. Linear interpolation connects known points directly1. Advanced techniques like polynomial and spline interpolation offer more precision for complex datasets1.
Data scientists use interpolation in many areas. These include digital signal processing, statistical analysis, and scientific research. It transforms limited datasets into rich, informative visualizations1.
Key Takeaways
- Interpolation enables accurate data prediction between known points
- Multiple interpolation techniques exist for different research needs
- Linear and polynomial methods provide flexible estimation strategies
- Interpolation is crucial in scientific and technological fields
- Advanced numerical methods enhance data understanding
Understanding Interpolation Fundamentals
Interpolation is a powerful math technique for estimating unknown values between known data points. It’s crucial in science and engineering for bridging gaps in discrete datasets. Interpolation uses smart approximation methods to fill in missing information2.
Data scientists use interpolation for tasks like regression analysis and curve fitting. This process helps create smooth, predictive models from incomplete data1.
Linear and Non-linear Interpolation Methods
Interpolation includes several different approaches:
- Linear Interpolation: Connects known points with straight lines2
- Cubic Spline Interpolation: Creates smooth curves between data points1
- Nearest Neighbor Method: Assigns values based on closest existing points2
Mathematical Principles in Practice
The basic linear interpolation formula shows the main idea: y = y1 + ((x – x1)/(x2 – x1) * (y2 – y1)). This equation helps estimate values accurately within known data ranges1.
| Interpolation Method | Key Characteristic | Best Used For |
|---|---|---|
| Linear | Straight line connections | Simple, quick approximations |
| Cubic Spline | Smooth curve fitting | Complex, continuous data |
| Nearest Neighbor | Closest point assignment | Discrete, categorical data |
Interpolation transforms fragmented data into meaningful insights, bridging knowledge gaps with mathematical precision.
Approximation theory is the basis for these techniques. It helps scientists and engineers find useful patterns in limited datasets2.
How to Interpolate Using Different Color Spaces
Color interpolation smooths transitions across color spaces in digital graphics and machine learning. Oklab is the default space for color values. It gives precise and visually consistent results.
Digital designers can pick from various color spaces for interpolation. These include rectangular and polar color spaces.
Understanding hue interpolation methods is key when working with color interpolation. “Shorter hue” is the default method. Developers can also choose increasing, decreasing, or longer options.
A linear gradient using Oklab can create smooth transitions between blue and red. Different color spaces offer unique interpolation features.
RGB represents colors as a 3D cube with red, green, and blue parts. HCL (Hue-Chroma-Luminance) optimizes color perception for machine learning applications.
Interpolation techniques vary in complexity. RGB uses simple linear calculations. HCL gives more visually consistent results but needs complex transformations.
Conclusion
Interpolation techniques are vital in modern data analysis. They help bridge gaps in datasets and create more comprehensive insights4. These methods allow for precise estimation of missing values across various fields4.
Interpolation transforms fragmented information into actionable knowledge5. It’s useful in machine learning, spatial analysis, and other diverse fields5. These techniques help map Earth’s surface and predict material behaviors in engineering5.
Interpolation methods range from simple linear to complex polynomial approaches4. Professionals should learn these strategies to improve their data analysis skills. Applying methods like Lagrange and Newton interpolation can unlock deeper insights4.
Each technique offers unique benefits for specific projects5. As data grows more complex, mastering these skills becomes crucial. The future of data analysis relies on turning raw information into meaningful insights4.
FAQ
What is interpolation and why is it important?
What’s the difference between linear and non-linear interpolation?
How is interpolation used in data science?
What are some practical applications of color interpolation?
Can interpolation be used in machine learning?
What mathematical principles are fundamental to interpolation?
Are there different types of interpolation methods?
How accurate is interpolation?
Source Links
- Interpolation – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Interpolation
- Interpolation | Definition, Formula, Methods & Uses – https://byjus.com/maths/interpolation/
- <color-interpolation-method> – CSS: Cascading Style Sheets | MDN – https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/color-interpolation-method
- Data Interpolation 101: From Novice to Pro Techniques Explained | Airbyte – https://airbyte.com/data-engineering-resources/data-interpolation
- What is Interpolation? Everything You Need To Know | Simplilearn – https://www.simplilearn.com/what-is-interpolation-article