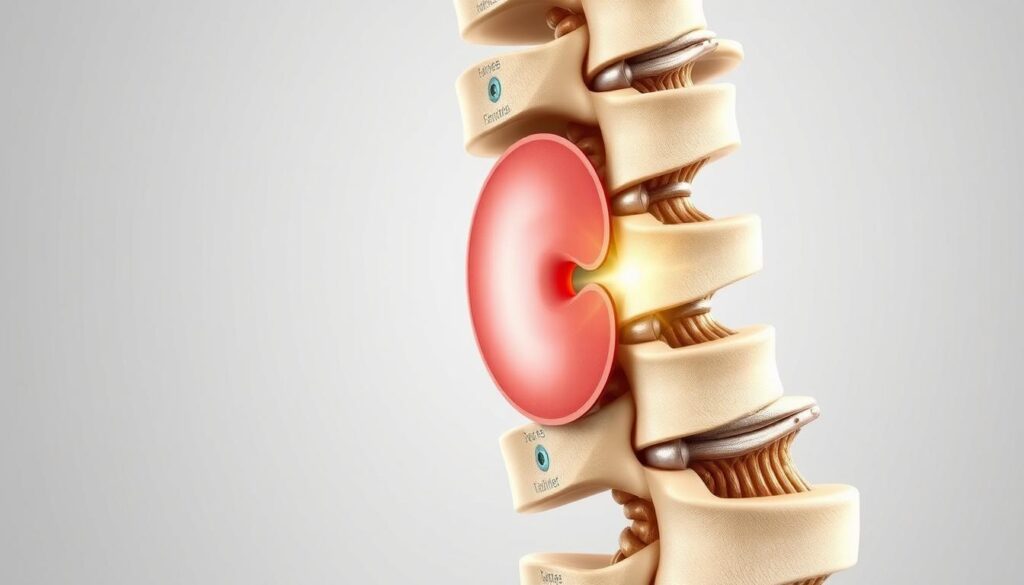
A Herniated Disk can greatly affect your daily life. It happens when a spinal disk’s soft inner part pushes through its tough outer layer. This can cause painful issues that limit your movement12.
Back pain is a common problem for many people. Between 60 and 80% will face it at some point. Herniated disks often cause this pain1.
Men aged 20 to 50 are more likely to get herniated disks12. As we get older, our disks lose water and become less flexible. This makes them easier to injure1.
Smoking can speed up disk damage. It reduces the oxygen supply to your disks1. However, there’s hope for those with herniated disks.
More than 85% of people with this problem get better without surgery2. Most see big improvements within 3 to 4 months1.
Key Takeaways
- Herniated disks are common, especially in men aged 20-50
- Disk flexibility decreases with age, increasing injury risk
- Over 85% of cases improve without surgery
- Lifestyle factors like smoking can worsen disk health
- Symptoms typically resolve within 3-4 months
Understanding Herniated Disks
Spinal health is vital for your overall well-being. Herniated disks can greatly affect your daily life. They may cause discomfort and limit your movement.
What is a Herniated Disk?
A herniated disk happens when the soft inner part pushes through a tear. This can create painful issues, especially when it affects nerve roots.
The disk’s inner material can press on nearby nerves. This leads to various uncomfortable symptoms.
- Occurs most frequently in the lower back
- Can develop in any part of the spine
- Potentially leads to spinal stenosis
Prevalence and Risk Factors
Herniated disks are common, especially among young and middle-aged adults3. Several factors can increase your risk:
- Aging and natural disk degeneration4
- Being overweight, which adds strain to lower back disks4
- Genetic predisposition4
- Physical demanding work environments
“Understanding your body’s signals is the first step in maintaining spinal health.”
Many people might have a herniated disk without noticeable symptoms5. When symptoms appear, they can include pain, numbness, and muscle weakness3.
| Age Group | Herniated Disk Likelihood |
|---|---|
| Young Adults | Higher Risk |
| Middle-Aged Adults | Most Commonly Affected |
| Older Adults | Lower Risk |
Remember, early recognition and professional medical consultation are key to managing potential spinal issues effectively.
Recognizing Symptoms of a Herniated Disk
Spotting signs of a herniated disk helps you get proper medical care. Your body signals when a disk is damaged or pressing on nerves. Pay close attention to these signals.
Common Symptoms to Look For
Herniated disks show various symptoms based on their location. Look out for these common signs:
- Sharp or burning pain radiating through buttocks and legs (sciatica)6
- Numbness or tingling in extremities6
- Muscle weakness affecting specific muscle groups
- Pain that worsens with certain movements
Radiculopathy symptoms vary depending on the disk’s location. Lower back issues might cause leg pain. Neck problems could lead to shoulder and arm pain7.
When to See a Doctor
Some symptoms require immediate medical attention. See a doctor if you experience:
- Persistent pain lasting more than a few weeks
- Significant muscle weakness
- Loss of bladder or bowel control
- Severe pain preventing daily activities
“Early diagnosis can prevent long-term complications and improve treatment outcomes.”
Most herniated disk cases heal within weeks or months with proper care6. Your doctor may recommend MRI or CT scans to confirm the condition6.
Approximately 2-3% of adults will experience herniated disk symptoms7. You’re not alone in dealing with this condition.
Causes and Risk Factors
Disc degeneration is a key factor in herniated disks. As you age, your spinal disks become less flexible. This makes them more prone to damage89.
Why Disks Become Herniated
Genetic predisposition plays a significant role in disk herniation. Certain gene variations can speed up spinal disc degeneration8.
Herniated disks often affect middle-aged men. They usually occur in the lower back and neck areas9.
Key Risk Factors to Consider
- Physical job demands
- Excess body weight
- Smoking
- Inactive lifestyle
- Repetitive bending or twisting
Spinal stenosis can make you more vulnerable to disk problems9. Lifting heavy objects incorrectly or having poor posture can harm your disks9.
The Stanford Health Care advises learning about these risk factors. This knowledge can help prevent potential complications.
“Prevention is always better than cure when it comes to spinal health.”
About 30% of 20-year-olds have disc bulges. This number rises to 84% by age 808.
Some disk changes are natural. However, taking proactive steps can help reduce your risk9.
Treatment Options for Herniated Disks
Herniated disk management offers various treatment options. Most patients find relief through non-invasive methods that focus on healing. About 70% to 80% of people with herniated disks can manage their condition without surgery10.
Non-surgical treatments often include physical therapy techniques. These may involve deep tissue massage, traction therapy, and electrical nerve stimulation10. Epidural Steroid Injections have success rates between 76% and 88% for easing disk herniation pain10.
Your doctor might suggest alternative therapies like acupuncture or chiropractic care. These can complement traditional treatments10. If conservative methods fail, surgery options such as discectomy or laminectomy may be considered11.
Surgery becomes more likely if symptoms last beyond four weeks. This may require talking to a neurosurgeon11. About 90% of patients see improvement within 4 to 6 weeks through rest and targeted treatments12.
Self-care strategies are key to recovery. Maintain good posture and use proper lifting techniques. Stay active with low-impact exercises and avoid long periods of bed rest12.
Each treatment plan is unique. Work closely with your healthcare team to find the best approach for your condition.
FAQ
What exactly is a herniated disk?
How common are herniated disks?
What are the main symptoms of a herniated disk?
What causes a herniated disk?
When should I see a doctor about a potentially herniated disk?
What treatment options are available for a herniated disk?
Can I prevent a herniated disk?
How long does recovery from a herniated disk typically take?
Source Links
- Herniated Disk in the Lower Back – OrthoInfo – AAOS – https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/herniated-disk-in-the-lower-back/
- Herniated disk: Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment – https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/191979
- A Patient’s Guide to Lumbar Herniated Disc – https://www.umms.org/ummc/health-services/orthopedics/services/spine/patient-guides/lumbar-herniated-disc
- Herniated disk – Symptoms and causes – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/herniated-disk/symptoms-causes/syc-20354095
- Understanding Herniated Discs: Symptoms and Treatments – https://totalspineortho.com/understanding-herniated-discs-symptoms-treatment-and-recovery/
- Do I Have a Herniated Disk? – https://www.webmd.com/pain-management/do-i-have-a-herniated-disk
- Herniated Disc – https://www.barrowneuro.org/condition/disc-herniation/
- Risk Factors of Intervertebral Disc Pathology—A Point of View Formerly and Today—A Review – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7865549/
- Herniated disk: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia – https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000442.htm
- 11 Various Treatment Options to Help with a Herniated Disk – https://www.sciatica.com/blog/11-treatment-options-for-herniated-discs/
- Herniated Disc – https://www.aans.org/patients/conditions-treatments/herniated-disc/
- What Are the Treatments for a Herniated Disk? – https://www.webmd.com/pain-management/treatments-for-herniated-disk