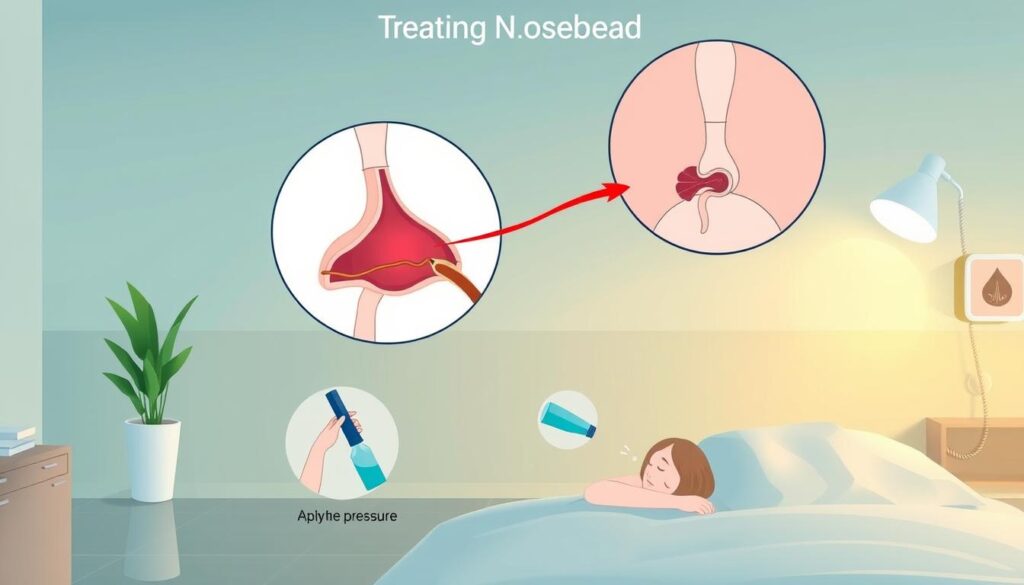
Nosebleeds can be startling, but understanding them helps manage this common issue. Epistaxis occurs when delicate blood vessels inside your nose rupture and bleed1. Though usually not serious, knowing how to handle these situations is crucial.
Many factors can trigger nosebleeds, such as dry air, accidental scratching, and certain medications1. People taking blood thinners might face more severe bleeding episodes1.
Key Takeaways
- Nosebleeds are common and usually manageable at home
- Environmental factors play a significant role in nasal bleeding
- Proper treatment can quickly stop most nosebleeds
- Prevention strategies can reduce bleeding frequency
- Seek medical help for prolonged or severe bleeding
Understanding Common Causes of Nosebleeds
Nosebleeds can happen suddenly. Knowing why they occur helps you manage and prevent them better. Your nose has delicate blood vessels that can easily get irritated or damaged2.
Environmental Factors and Nasal Irritants
Dry air often triggers nosebleeds. Heating systems and low-humidity climates can make your nasal membranes crack and bleed3.
Winter months increase nosebleed chances due to environmental conditions3.
- Low humidity environments
- Heating systems
- Seasonal temperature changes
- Allergic reactions
- Frequent colds
Physical Triggers and Medical Conditions
Some actions and health issues can cause nosebleeds. Nasal congestion, nose picking, and hard blowing can break fragile blood vessels2.
People taking blood thinners are more likely to experience nosebleeds3.
| Trigger Category | Specific Causes |
|---|---|
| Physical Triggers | Nose picking, trauma, high altitudes |
| Medical Conditions | Blood disorders, high blood pressure |
| Medication Risks | Anticoagulants, aspirin, blood thinners |
Understanding these triggers can help you take proactive steps to minimize nosebleed occurrences.
Most nosebleeds are harmless and easy to handle. Recognizing potential causes empowers you to prevent and address them effectively2.
Essential Treatment Steps for Nasal Bleeding
Nosebleeds can be scary, but most are manageable with quick action. Knowing how to handle nasal trauma helps prevent long-lasting bleeding4.
Here’s what to do when a nosebleed happens:
- Sit upright and lean slightly forward
- Breathe through your mouth
- Pinch the soft part of your nose just below the nasal bone
- Apply steady pressure for 5-10 minutes
“Remain calm and act quickly to control nasal bleeding effectively”
To manage nosebleeds at home, try these tips. Put a cool, damp washcloth on your nose and cheeks. This helps shrink blood vessels5.
Don’t lie down or tilt your head back. This can make blood flow down your throat.
| Bleeding Type | Treatment Approach |
|---|---|
| Anterior Nosebleed | Direct pressure and home treatment |
| Posterior Nosebleed | Requires medical intervention |
Warning signs that require immediate medical attention include:
- Bleeding lasting more than 20 minutes
- Excessive blood loss
- Difficulty breathing
- Signs of nasal trauma
Doctors might use cauterization or nasal packing for stubborn nosebleeds5. The American Red Cross suggests learning first aid for such emergencies6.
Conclusion
Nosebleeds are common and happen to almost everyone at least once7. Understanding causes and using prevention strategies can reduce nasal bleeding8. Focus on keeping your nose moist and avoiding irritants9.
Use a humidifier and saline sprays to prevent nosebleeds7. Don’t pick your nose. If nosebleeds happen often, see a doctor. They can find potential medical issues causing repeated nasal bleeding.
Some medicines, environments, and health issues can cause more nosebleeds8. Most nosebleeds are harmless, but severe cases need medical help. Stay proactive about nasal care to reduce nosebleeds.
Keep your nails short and use nasal sprays carefully9. Create a moist environment for better nasal health. These steps can help you avoid nosebleeds and maintain a healthy nose.
FAQ
What causes nosebleeds?
How do I stop a nosebleed?
When should I seek medical attention for a nosebleed?
How can I prevent nosebleeds?
Are nosebleeds dangerous?
Can certain medications cause nosebleeds?
Are nosebleeds more common in children?
Source Links
- Nosebleeds: First aid – https://www.mayoclinic.org/first-aid/first-aid-nosebleeds/basics/art-20056683
- Nosebleeds (Epistaxis): Causes, Prevention and How to Treat – https://www.nationwidechildrens.org/conditions/nosebleeds
- Nosebleed Information | Mount Sinai – https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/symptoms/nosebleed
- Management of Epistaxis – https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2005/0115/p305.html
- Nose Bleed Management and Epistaxis Control – https://medicine.uiowa.edu/iowaprotocols/nose-bleed-management-and-epistaxis-control
- Nosebleeds: Causes and How To Stop | Red Cross – https://www.redcross.org/take-a-class/resources/learn-first-aid/nosebleeds?srsltid=AfmBOoqDrU6jagId0LiihLpT4VtiHs2UIw8X2qxfvBss8To31ntiDI1d
- Patient education: Nosebleeds (epistaxis) (Beyond the Basics) – https://www.uptodate.com/contents/nosebleeds-epistaxis-beyond-the-basics/print
- Epistaxis: A Common Problem – PMC – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3096213/
- Nosebleed : MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia – https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003106.htm