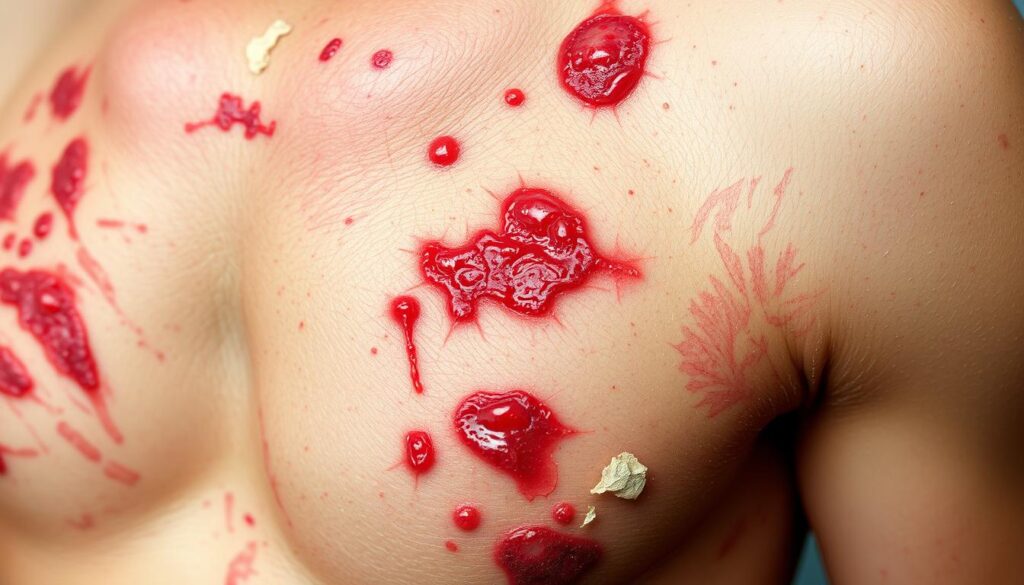
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS) is a rare but serious skin rash. It can become life-threatening, affecting your skin and mucous membranes. SJS often occurs as an unexpected reaction to medications1.
Your immune system can trigger a severe response. This leads to extensive skin and membrane problems2. Understanding SJS is key to spotting risks and getting quick medical help.
Some drugs can spark a chain reaction in your body. This results in painful blistering and skin breakdown1. Spotting early signs can greatly improve treatment outcomes.
SJS is rare but needs serious attention. People with HIV, weak immune systems, or certain genes are at higher risk1. Being aware and proactive can help manage potential issues.
Key Takeaways
- Stevens-Johnson Syndrome is a rare but serious skin reaction
- Medication interactions can trigger this life-threatening condition
- Early recognition of symptoms is critical for treatment
- Certain health conditions increase the risk of developing SJS
- Immediate medical intervention is essential
Overview of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS) is a rare and serious disease affecting skin and mucous membranes. It can lead to life-threatening complications3. Knowing its basics helps spot early warning signs for quick medical help.
What is Stevens-Johnson Syndrome?
SJS is a severe inflammatory disorder causing painful mucosal erosions and skin reactions. It starts with flu-like symptoms and quickly progresses to a widespread, painful rash4.
The condition creates circular patches that become very uncomfortable. Blisters can develop on many body surfaces.
Symptoms to Watch For
- Fever and general malaise
- Painful skin rash
- Blisters on mouth, eyes, and genitals
- Skin shedding
- Painful mucosal erosions
“Early recognition of SJS symptoms can be crucial for patient survival and treatment outcomes.”
Who is at Risk?
Some groups have a higher chance of getting Stevens-Johnson Syndrome. Your risk goes up with certain factors:
| Risk Factor | Details |
|---|---|
| Genetic Predisposition | Variations in HLA-B gene3 |
| Medical Conditions | HIV, systemic lupus erythematosus3 |
| Medication Use | Antibiotics, anticonvulsants, anti-inflammatory drugs4 |
This rare disease affects about 1-2 people per million each year3. Know your risk factors and watch for medication reactions.
Causes of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS) is a serious condition with many possible triggers. It can cause severe reactions to medications. Knowing these causes helps you avoid risks and stay healthy.
SJS may require hospital care. Recognizing early signs is crucial for quick treatment.
Medication Triggers
Some medicines are the main cause of SJS. The most common types include:
- Anti-epileptic drugs
- Antibacterial sulfonamides
- Pain relievers like acetaminophen
- Antipsychotic medications
Infection-Related Factors
Infections can also lead to SJS. Some linked infections are:
- Pneumonia
- HIV
- Cold sores
- Glandular fever
SJS can occur while taking medicine or up to two weeks after stopping. It affects more females than males, with a 2:1 ratio5.
Risk Factors and Prevalence
| Population Group | SJS Incidence |
|---|---|
| General Population | 2-7 cases per million annually5 |
| HIV Patients | 0.95-1 per 1000 individuals5 |
“Understanding potential triggers is crucial for prevention and early intervention.”
Genetic factors play a big role in SJS risk. Some gene variations can increase SJS risk with certain medicines5.
These include HLA-B*15:02 and HLA-B*58:01. Knowing your genetic makeup can help prevent SJS.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS) requires swift medical attention. This life-threatening condition needs a thorough diagnostic approach for patient safety6.
Diagnostic Process
Healthcare providers use a comprehensive approach to diagnose SJS. This includes:
- Detailed medical history review
- Comprehensive physical examination
- Skin biopsy to confirm diagnosis
- Blood tests to assess overall health
Treatment Strategies
SJS requires immediate hospitalization. Treatment often needs intensive care management. Key approaches include:
- Discontinue potential trigger medications
- Provide robust supportive care
- Manage pain and prevent infections
Critical Intervention Steps
Early action can greatly affect patient outcomes. Treatment usually involves:
- Fluid replacement
- Wound care management
- Specialized eye treatments
- Potential use of medications like corticosteroids
Quick recognition and treatment are vital in managing this complex medical condition7.
SJS mortality rates range from 4.8-9%. This highlights the need for fast medical care6.
Patients may need 2-4 weeks in the hospital. Long-term issues can include scarring and organ problems7.
Remember, your quick response and professional medical care can make a critical difference in managing Stevens-Johnson Syndrome.
Living with Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS) recovery is a challenging journey. It can impact various aspects of your health. Skin regrowth may take two to three weeks, with overall recovery spanning several weeks to months.
Collaborate closely with your healthcare team when managing this medication reaction. Always wear a medical information bracelet and keep a detailed health history. Possible complications include skin changes, eye problems, and breathing issues8.
Many patients experience anxiety and stress due to SJS. The psychological impact can be significant9.
Prevention is crucial for those who’ve had SJS. Avoid the original triggering medication and similar drugs forever. The FDA suggests genetic testing, especially for Asian and South Asian people.
Learn more about SJS prevention at this helpful resource. Support groups and specialized doctors can provide valuable guidance for managing this condition9.
SJS is rare, affecting about 1-2 people per million each year10. Each patient’s experience is unique. Comprehensive medical support can help you navigate life with Stevens-Johnson Syndrome8.
FAQ
What is Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS)?
What are the main symptoms of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome?
What causes Stevens-Johnson Syndrome?
Who is at highest risk for developing SJS?
How is Stevens-Johnson Syndrome diagnosed?
What is the treatment for Stevens-Johnson Syndrome?
What are the potential long-term effects of SJS?
How can I prevent Stevens-Johnson Syndrome?
Source Links
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome-Stevens-Johnson syndrome – Symptoms & causes – Mayo Clinic – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/stevens-johnson-syndrome/symptoms-causes/syc-20355936
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/stevens-johnson-syndrome/
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis: MedlinePlus Genetics – https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/stevens-johnson-syndrome-toxic-epidermal-necrolysis/
- Stevens-Johnson Syndrome – https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/stevens-johnson-syndrome
- A Compilation of Drug Etiologies of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10718167/
- Stevens–Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: A Review of Diagnosis and Management – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8472007/
- Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS) – https://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/stevens-johnson-syndrome
- Stevens-Johnson Syndrome: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment – https://www.healthline.com/health/stevens-johnson-syndrome
- The psychological impact of Stevens–Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis on patients’ lives: a Critically Appraised Topic – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7687230/
- Stevens–Johnson syndrome – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stevens–Johnson_syndrome