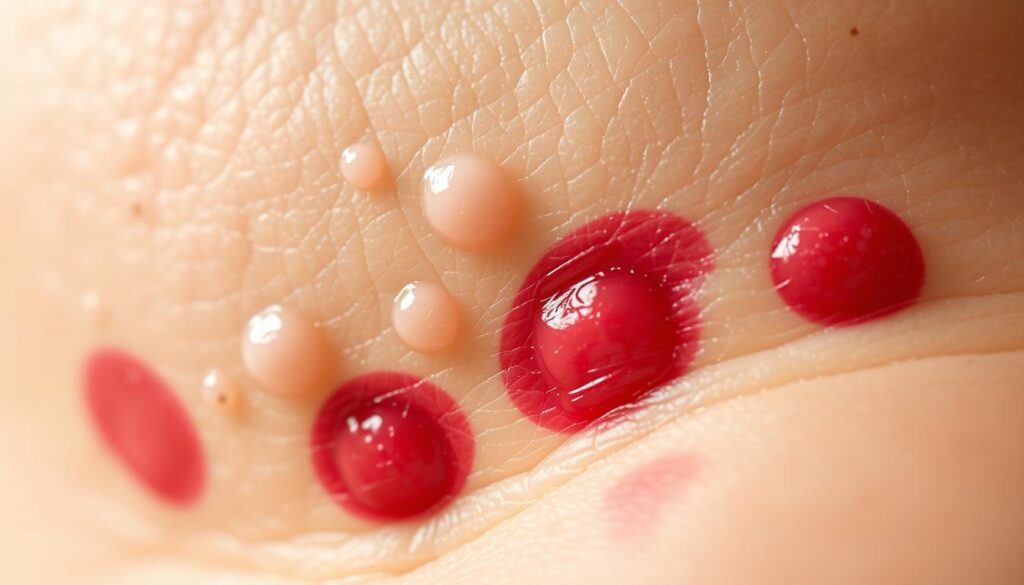
Bullous pemphigoid is a rare skin disorder that affects older adults. It’s an autoimmune condition that creates large, fluid-filled blisters on the skin. This condition can significantly impact a person’s health and daily life12.
The immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells in this disorder. This attack leads to an intense inflammatory response, causing discomfort. Healthcare providers help patients understand and manage this unique condition2.
People over 60 are most likely to develop bullous pemphigoid. The condition can last for several years before it fully resolves12.
Certain medications can increase the risk of developing this condition. These include diuretics, antibiotics, and NSAIDs. Cancer treatments and radiation therapies may also raise the risk1.
Key Takeaways
- Bullous pemphigoid is an autoimmune skin disorder affecting older adults
- The condition causes large, fluid-filled blisters on the skin
- Treatment requires careful medical management
- Risk increases with certain medications and medical treatments
- Most cases resolve within a few years
What is Bullous Pemphigoid?
Bullous pemphigoid is a complex skin disease that affects the body’s defense system. It happens when your immune system attacks your skin’s base layer. This creates unique problems for those with the condition3.
Understanding Autoimmune Skin Disorders
In autoimmune skin disorders, your body makes antibodies that harm healthy skin. These conditions cause distinct skin reactions that can be uncomfortable and noticeable.
Common Signs and Symptoms
- Large, tense blisters across skin folds
- Intense itching preceding blister formation
- Skin inflammation and redness
- Potential changes in skin coloration
Risk Factors and Age-Related Concerns
Bullous pemphigoid mainly affects people over 50. It’s most common in those over 80 years old3.
The condition has some unique features:
| Age Group | Risk Level | Prevalence |
|---|---|---|
| 50-60 years | Low | Rare occurrences |
| Over 80 years | High | Most common |
The disease affects men and women equally3. Certain brain conditions like dementia and Parkinson’s disease increase risk.
Some medical treatments can also be linked to this condition3.
Understanding your body’s unique immune responses is key to managing autoimmune skin disorders.
Common Triggers and Contributing Factors
Bullous pemphigoid is a complex autoimmune skin disorder affecting mostly older adults. Various factors can spark its development4. Recognizing these triggers helps understand the condition’s underlying mechanisms5.
Several environmental and medical factors can increase your risk of bullous pemphigoid. These include specific medications, medical treatments, and skin injuries.
- Medications that impact hemidesmosomal proteins4
- Medical treatments like radiation therapy
- Skin trauma or burns
- Underlying chronic conditions
Certain medications may trigger the condition. Here’s a breakdown of potential trigger impacts:
| Medication Category | Potential Trigger Impact |
|---|---|
| Antibiotics | Can initiate immune response |
| Beta-blockers | May alter immune system functioning |
| NSAIDs | Potential inflammatory trigger |
| Diuretics | Can modify immune protein interactions |
In bullous pemphigoid, your immune system attacks specific proteins, causing tense blisters. This process often leads to severe itching and skin inflammation4.
The complexity of bullous pemphigoid lies in its diverse triggering mechanisms and individual variability.
Not everyone exposed to these triggers will develop bullous pemphigoid. Genetic factors and individual immune responses play crucial roles5.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options of Bullous Pemphigoid
Bullous pemphigoid is a complex skin condition that requires careful diagnosis and treatment. Understanding the best ways to manage this challenging disease is crucial for effective care.
Your healthcare journey starts with finding the right approach. Identifying effective strategies is key to managing this skin condition successfully.
Medical Examination and Testing Methods
Diagnosing bullous pemphigoid involves a thorough medical exam. This usually includes specialized skin tests. Doctors often perform:
- Physical skin examination
- Skin biopsy
- Blood tests to detect specific antibodies
- Immunofluorescence mapping
Treatment Approaches
Your treatment plan aims to manage symptoms and control the autoimmune response. Topical treatments are crucial in addressing bullous pemphigoid6:
| Treatment Category | Specific Medications | Primary Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Corticosteroids | Clobetasol propionate | Reduce inflammation |
| Immunosuppressants | Azathioprine, Rituximab | Suppress immune response |
| Antibiotics | Dapsone, Doxycycline | Control blisters |
Managing Side Effects
Treatments are vital, but they can cause potential complications. Oral steroids may lead to side effects like:
- Weakened bones
- Increased diabetes risk
- Stomach ulcers
- Eye problems
Patients need ongoing monitoring to manage these potential risks7. Most people follow a treatment plan for six months to five years before achieving long-term remission7.
Managing bullous pemphigoid requires patience, careful medical supervision, and a personalized approach to treatment.
Wear loose-fitting cotton clothes to manage symptoms. Be mindful of your diet, especially if blisters appear in sensitive areas67.
Conclusion
Bullous pemphigoid is a complex autoimmune skin disorder. It requires patience and thorough medical care. Your healthcare team will guide you through managing this blistering condition8.
This condition significantly affects the elderly, especially those over 70. Medical advancements offer hope for better treatment. Ongoing clinical trials explore new ways to target specific inflammatory pathways8.
Your treatment may need careful monitoring and adjustments. Doctors are developing new therapies to reduce side effects. Regular specialist visits can help manage symptoms and improve life quality9.
Stay informed about your health. Work closely with your healthcare providers. Understand your treatment options and keep a positive outlook. These steps can help you manage this skin condition successfully89.
FAQ
What is Bullous Pemphigoid?
Who is most at risk for developing Bullous Pemphigoid?
What are the main symptoms of Bullous Pemphigoid?
How is Bullous Pemphigoid diagnosed?
What treatment options are available?
Is Bullous Pemphigoid contagious?
How long does Bullous Pemphigoid typically last?
Are there any potential complications of Bullous Pemphigoid?
Source Links
- Bullous pemphigoid – Symptoms and causes – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/bullous-pemphigoid/symptoms-causes/syc-20350414
- Bullous pemphigoid – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/bullous-pemphigoid/
- Bullous Pemphigoid: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment — DermNet – https://dermnetnz.org/topics/bullous-pemphigoid
- Bullous Pemphigoid: Trigger and Predisposing Factors – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7600534/
- Bullous Pemphigoid: Know the Facts – https://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/what-is-bullous-pemphigoid
- Bullous pemphigoid – Diagnosis and treatment – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/bullous-pemphigoid/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20350419
- Bullous pemphigoid: Diagnosis and treatment – https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/a-z/bullous-pemphigoid-treatment
- A blistering new era for bullous pemphigoid: A scoping review of current therapies, ongoing clinical trials, and future directions – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8435812/
- Bullous pemphigoid – PMC – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6486083/