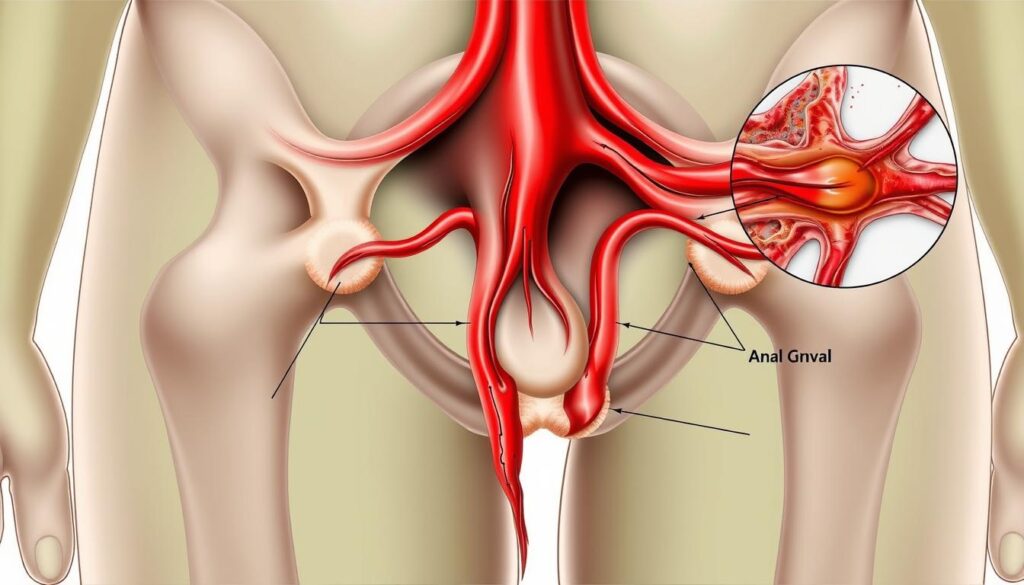
Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the lower rectum and anus. They affect millions worldwide, causing discomfort and concern1. Learning about hemorrhoids can help you manage them better2.
The risk of hemorrhoids increases as you get older. By age 50, about half of all people will have experienced this condition2. Your rectum and anus tissues weaken over time, making hemorrhoids more likely1.
Several factors can lead to hemorrhoids. These include being overweight, having chronic constipation, and pregnancy13. Even sitting for long periods can raise your risk.
Hemorrhoids are similar to varicose veins and can be internal or external1. They may cause rectal bleeding and discomfort. However, most cases aren’t serious and can be managed with proper care.
Key Takeaways
- Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the lower rectum and anus
- Risk increases with age, especially after 45
- Lifestyle factors significantly impact hemorrhoid development
- Most hemorrhoid cases are treatable and not dangerous
- Proper diet and exercise can help prevent hemorrhoids
What Are Hemorrhoids and Their Symptoms?
Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the anal and rectal area. They cause discomfort and affect many people. Understanding hemorrhoids can help you manage and prevent this painful condition4.
About 5% of Americans have hemorrhoid symptoms. Half of adults over 50 develop these uncomfortable protrusions4. These swollen blood vessels can cause significant distress.
Prolapsed hemorrhoids and anal itching are common issues. They can make daily activities uncomfortable.
Understanding Hemorrhoid Types
There are two primary types of hemorrhoids that can affect your health:
- Internal hemorrhoids (occurring inside the rectum)
- External hemorrhoids (forming under the skin around the anus)
Common Symptoms to Recognize
Identifying hemorrhoid symptoms early can help you seek proper treatment. Watch for these signs:
- Rectal bleeding during bowel movements
- Persistent anal itching
- Pain or discomfort in the anal region
- Swelling around the anus
- Visible lumps near the anal opening
Complications and Risk Factors
| Risk Factor | Impact on Hemorrhoids |
|---|---|
| Chronic constipation | Increases strain during bowel movements |
| Prolonged sitting | Reduces blood circulation |
| Low-fiber diet | Contributes to difficult bowel movements |
External hemorrhoids can sometimes develop into thrombosed hemorrhoids. These are particularly painful and require medical attention5. Knowing these differences helps you decide when to see a doctor.
“Early recognition and proper management can significantly reduce hemorrhoid discomfort and prevent potential complications.”
Causes of Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids occur when blood vessels in your lower rectum swell. Increased pressure in this area leads to inflammation. Understanding the causes can help prevent and manage this condition.
Common Risk Factors
Several factors raise your chances of getting hemorrhoids. About 1 in 20 people in the U.S. face this issue6.
- Pregnancy, which increases rectal pressure6
- Obesity and excess body weight
- Advanced age, particularly over 506
- Genetic predisposition6
Lifestyle Choices Contributing to Hemorrhoids
Your daily habits can increase hemorrhoid risk. Straining during bowel movements and sitting for long periods are common causes7.
A low-fiber diet can also lead to problems. Jobs requiring extended sitting may cause blood to pool in rectal vessels6.
“Prevention is always better than cure when it comes to hemorrhoids.”
Genetics and Hemorrhoids
Your genes play a big role in hemorrhoid risk. If your family has a history, you’re more likely to get them6.
Weakening of supporting tissues in the anal area can cause hemorrhoids. This is common in older people and pregnant women7.
Knowing these causes helps you take steps to lower your risk. You can maintain better rectal health with this knowledge.
Treatment Options for Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids can be managed through various treatment methods. These range from simple home remedies to medical procedures. Let’s explore the options to ease your discomfort and promote healing8.
At-Home Remedies for Relief
Mild hemorrhoid symptoms can often be relieved with home treatments. These include sitz baths, ice packs, and witch hazel compresses. Increasing fiber in your diet can also help.
- Sitz baths with warm water
- Applying ice packs to reduce swelling
- Using witch hazel compresses
- Increasing dietary fiber intake
Over-the-Counter Treatments
Doctors often suggest using over-the-counter products for a week. These can help with mild pain, swelling, and itching from external hemorrhoids8. Common treatments include:
- Topical creams containing hydrocortisone
- Hemorrhoid-specific ointments
- Medicated suppositories
Medical Interventions
For stubborn hemorrhoids, medical treatments are available. Rubber band ligation is the top choice for grades I to III hemorrhoids9. It’s known for its effectiveness.
Other medical options include:
- Sclerotherapy
- Infrared photocoagulation
- Electrocoagulation
Surgical Options for Severe Cases
Surgery like hemorrhoidectomy may be needed when other treatments fail8. These outpatient procedures are usually for large or recurrent hemorrhoids. They also help with persistent bleeding.
- Large hemorrhoids
- Recurrent hemorrhoid issues
- Persistent bleeding
When to Seek Medical Attention
See a doctor if you have ongoing symptoms or heavy bleeding. Severe pain or hemorrhoids that don’t improve with home care also need medical attention.
- Persistent symptoms
- Heavy bleeding
- Severe pain
- Hemorrhoids that do not improve with home treatments
Remember, early intervention can prevent more serious complications and provide faster relief.
For more details on hemorrhoid treatments, check out the Mayo Clinic’s hemorrhoid treatment guide.
Preventative Measures for Hemorrhoids
Preventing hemorrhoids involves improving your health and lifestyle. Smart changes in diet and habits can lower your risk. Understanding how daily routines affect your digestive system is key1011.
Smart Dietary Strategies
Your diet is crucial in preventing hemorrhoids. Add fiber supplements and eat more fruits and vegetables. This helps keep your bowel movements smooth.
Women should aim for 25 grams of fiber daily, while men need 38 grams10. Try adding whole grains and legumes to your meals.
Include fiber-rich foods in your diet to support digestive health11.
Hydration and Exercise Essentials
Staying hydrated is vital in preventing hemorrhoids. Drink eight glasses of water daily to keep stools soft and avoid constipation10.
Regular exercise improves circulation and reduces pressure in the rectal area1011. Choose activities that boost overall fitness and support your digestive system.
Reducing Strain During Bowel Movements
Don’t sit on the toilet for too long. This can increase anal pressure and cause hemorrhoids10.
Use the bathroom promptly when you feel the urge. A footstool can improve your posture and reduce straining11.
These simple tips can help prevent uncomfortable hemorrhoid symptoms.
FAQ
What exactly are hemorrhoids?
What are the most common symptoms of hemorrhoids?
What causes hemorrhoids to develop?
Are hemorrhoids dangerous?
What are the treatment options for hemorrhoids?
How can I prevent hemorrhoids?
Can pregnancy cause hemorrhoids?
What’s the difference between internal and external hemorrhoids?
Source Links
- Hemorrhoids – Symptoms and causes – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hemorrhoids/symptoms-causes/syc-20360268
- Hemorrhoids – https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/hemorrhoids
- Hemorrhoids: Symptoms, causes, and treatments – https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/73938
- Hemorrhoids: Symptoms & Causes | NewYork-Presbyterian – https://www.nyp.org/digestive/hemorrhoids
- Hemorrhoids – https://www.healthline.com/health/hemorrhoids
- Hemorrhoids – https://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/understanding-hemorrhoids-basics
- Hemorrhoids | Piles | MedlinePlus – https://medlineplus.gov/hemorrhoids.html
- Treatment of Hemorrhoids – NIDDK – https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/hemorrhoids/treatment
- Hemorrhoids: Diagnosis and Treatment Options – https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2018/0201/p172.html
- Hemorrhoid Prevention – Orange County Hemorrhoid Clinic – https://orangecountyhemorrhoidclinic.com/hemorrhoids/hemorrhoid-prevention/
- Preventing Hemorrhoids | Georgia Hemorrhoid Institute – https://www.georgiahae.com/what-causes-hemorrhoids/prevention/