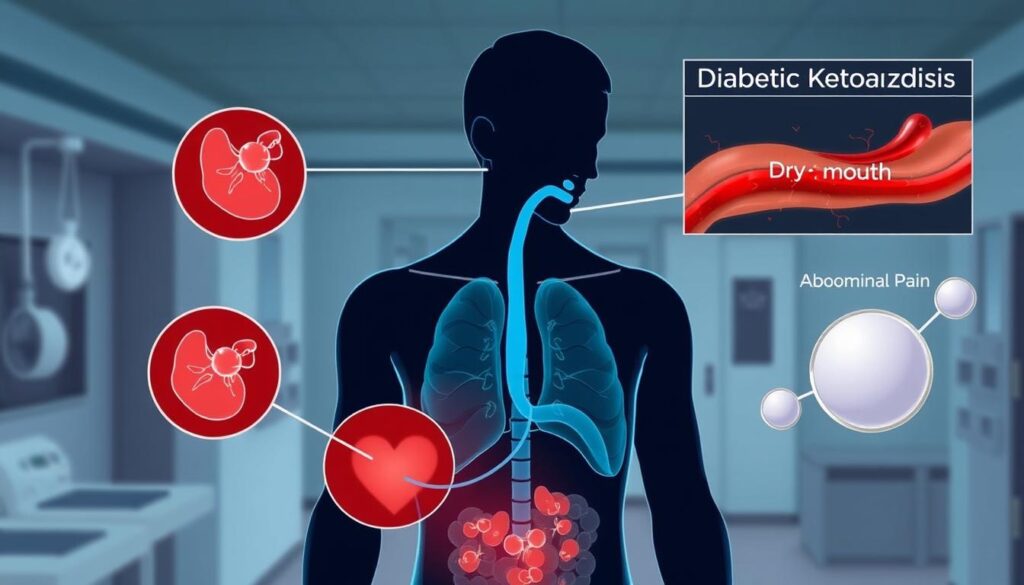
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a severe health issue that can occur suddenly. It happens when your body can’t manage blood sugar properly. This leads to a dangerous buildup of ketones in your blood1.
DKA can develop quickly, sometimes within 24 hours1. It’s most common in type 1 diabetes but can affect type 2 diabetics who need insulin2. If left untreated, DKA can cause loss of consciousness or even death1.
Your risk goes up if you often miss insulin doses. Certain health conditions can also increase your chances of DKA1. Sometimes, DKA is the first sign that someone has diabetes, especially in type 2 cases1.
Key Takeaways
- DKA can develop quickly and is potentially life-threatening
- Early detection is crucial for preventing severe complications
- Both type 1 and type 2 diabetics can experience DKA
- Consistent insulin management is essential
- Monitoring blood sugar and ketone levels can help prevent DKA
Understanding Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a serious complication of type 1 diabetes. It happens when there’s not enough insulin in the body. This leads to dangerous changes in how your body works.
Without insulin, your body can’t use sugar for energy. Instead, it burns fat. This creates ketones, which make your blood acidic. If left untreated, it can be life-threatening.
What is Diabetic Ketoacidosis?
DKA occurs when your body lacks insulin. It breaks down fat for energy, causing ketones to build up. This makes your blood acidic, which can harm your health3.
The condition develops when your body can’t use glucose properly. This leads to very high blood sugar levels.
Causes of DKA
Multiple factors can trigger diabetic ketoacidosis, including:
- Missed insulin doses
- Severe infections
- Physical or emotional stress
- Hormonal imbalances
- Certain medications
The quick production of ketones makes your blood acidic. This can disrupt how your body normally works3.
Who is at Risk for DKA?
People with type 1 diabetes are most likely to get DKA. Risk factors include:
- Inconsistent insulin management
- Recent diagnosis of diabetes
- Uncontrolled blood sugar levels
- Concurrent health complications
Early recognition and prompt medical intervention are crucial for managing diabetic ketoacidosis effectively.
When you don’t have enough insulin, your body reacts in different ways. You might breathe differently or have changes in your body salts3. Knowing these signs can help you get help quickly.
Recognizing the Warning Signs of DKA
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious condition that can develop quickly. It threatens your health if left unchecked. Knowing the warning signs helps you take swift action and protect yourself.
Early Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore
Catching DKA early is vital for your health. Look out for these initial warning signs:
- Excessive thirst and frequent urination
- Unexplained fatigue and weakness
- High blood sugar levels above 240 mg/dL4
- Presence of ketones in your urine4
Severe Symptoms to Watch For
As DKA worsens, you might experience more intense symptoms. These require immediate attention:
- Fruity breath odor – a distinctive sign of ketone buildup
- Severe nausea and persistent abdominal pain
- Shortness of breath and rapid, deep breathing4
- Confusion or altered mental state
When to Seek Medical Attention
Call your doctor if you notice these critical signs:
- Blood sugar levels stay above 300 mg/dL5
- Ketones are found in your urine or blood4
- Multiple DKA symptoms occur at once
- Persistent dehydration with no relief
“Early recognition of DKA symptoms can be life-saving. Always trust your body and seek professional medical advice when something feels wrong.”
Untreated DKA can lead to severe health risks. These include loss of consciousness and life-threatening complications5. Stay alert to these warning signs.
Your proactive approach to monitoring symptoms is crucial. It can make a big difference in managing your diabetes effectively.
Managing DKA and Prevention Strategies
Managing diabetic ketoacidosis requires a thorough diabetes care plan. Your strategy should focus on avoiding complications and keeping blood sugar steady. Blood sugar monitoring is vital for spotting early warnings and preventing emergencies6.
Effective Treatment Options
DKA needs quick medical help. Treatment usually involves insulin therapy in a hospital. Doctors give IV fluids and fix electrolyte balance6.
Diabetics must work with their doctors on custom treatment plans7. This helps manage the condition better.
Tips for Preventing DKA
Check blood sugar often, especially when sick or stressed. Always carry medical ID and teach family about your condition.
Follow your meal plan carefully. If you miss insulin, call your doctor right away6.
Lifestyle Changes That Benefit Your Health
Eat a balanced diet and stay active. Manage stress and drink plenty of water.
Regular insulin use and blood sugar checks are crucial. They help prevent serious health issues7.
FAQ
What is Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)?
What are the main causes of Diabetic Ketoacidosis?
What are the early warning signs of DKA?
How quickly can DKA develop?
When should I seek medical attention for DKA?
How is Diabetic Ketoacidosis treated?
Can DKA be prevented?
Who is most at risk for developing DKA?
Source Links
- Diabetic ketoacidosis: Know the warning signs-Diabetic ketoacidosis – Symptoms & causes – Mayo Clinic – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetic-ketoacidosis/symptoms-causes/syc-20371551
- Diabetic ketoacidosis – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/diabetic-ketoacidosis/
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA): Practice Essentials, Background, Pathophysiology – https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/118361-overview
- About Diabetic Ketoacidosis – https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/about/diabetic-ketoacidosis.html
- Diabetic ketoacidosis: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia – https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000320.htm
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA): Care Instructions – https://myhealth.alberta.ca/Health/aftercareinformation/pages/conditions.aspx?hwid=tw12221
- Adult Diabetic Ketoacidosis – StatPearls – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560723/