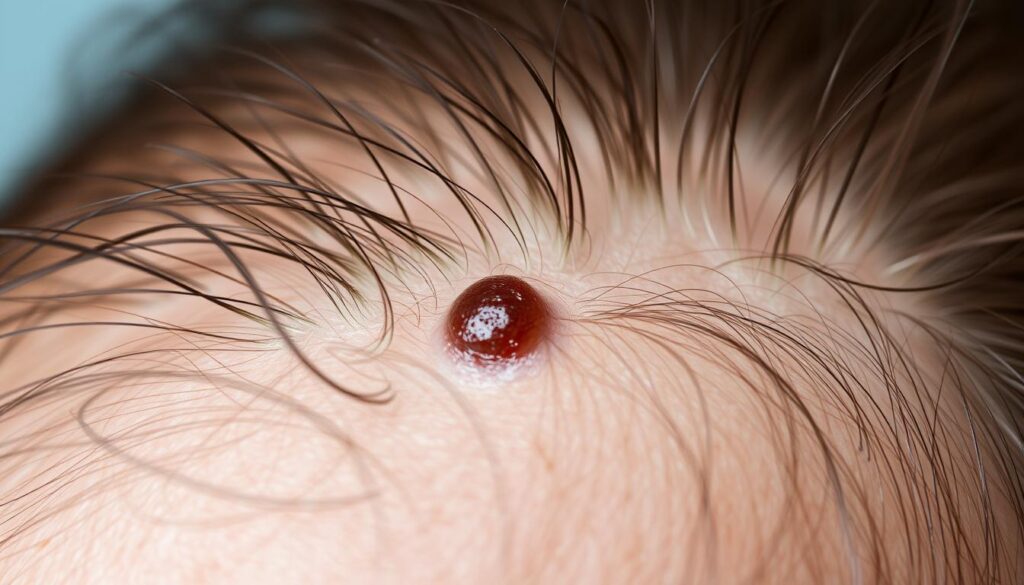
Melanoma is the most dangerous form of skin cancer. It develops from melanocytes, cells that produce pigment in your skin, eyes, and hair1. Knowing how melanomas relate to hair follicles can help you spot warning signs early2.
Scientists have made exciting discoveries about melanoma origins in hair follicles. They found that melanocyte stem cells in hair follicles can change and cause cancer13. This new insight challenges what we thought we knew about skin cancer.
Melanoma causes most skin cancer deaths. Yet, it makes up only a small part of skin cancer cases2. Spotting melanoma early can greatly improve treatment results.
Key Takeaways
- Melanomas can develop from stem cells in hair follicles
- Melanocytes produce pigment and can transform into cancerous cells
- Early detection is crucial for successful treatment
- Hair follicle structure plays a significant role in melanoma development
- Understanding cellular changes helps improve diagnostic approaches
What Are Melanomas?
Melanomas are dangerous skin cancers that need your attention. They grow from melanocytes, cells that make skin pigment4. These complex tumors can be very serious.
Early detection of melanoma is vital. Most start in the skin as cutaneous melanoma4. Though less common, they can spread fast.
Types of Melanomas
Melanomas come in different forms. Each type has its own traits:
- Superficial Spreading Melanoma: Accounts for approximately 70% of skin melanomas4
- Nodular Melanoma: Represents around 20% of cases4
- Lentigo Maligna Melanoma: Typically occurs in older individuals and grows slowly4
- Acral Lentiginous Melanoma: More common in individuals with darker skin tones4
Symptoms to Watch For
Melanoma can start as a change in a mole. It can also appear as a new growth5. Look for moles with:
- Irregular borders
- Varied color patterns
- Diameter larger than 1/4 inch
- Changes in size or shape
Risk factors include family history and severe sunburns. Extensive UV exposure and many moles also increase risk5.
“Early detection is your best defense against melanoma progression.”
Know the melanoma stages and warning signs. This can improve treatment outcomes. Always see a doctor for skin check-ups5.
The Role of Hair Follicles in Skin Health
Hair follicles are vital for skin health and protection. These tiny structures do more than just produce hair. They’re biological powerhouses that defend your body in many ways6.
Hair follicles serve multiple critical purposes in skin health. They protect against environmental damage and regulate temperature. They also provide sensory information and support immune responses7.
- Protecting against environmental damage
- Regulating temperature
- Providing sensory information
- Supporting immune responses
Structure of Hair Follicles
Hair follicles are complex organs within skin layers. They contain follicular melanocytes, which produce pigment for hair growth. These stem cells can divide and transform into cells needed for skin regeneration7.
Functions Beyond Hair Growth
Hair follicles do more than grow hair. They shield against UV light and minor scratches6. The nerves around hair follicles give important information about your surroundings6.
| Follicle Function | Biological Contribution |
|---|---|
| Pigment Production | Melanin generation |
| Sensory Perception | Environmental interaction |
| Protective Mechanism | UV and physical damage defense |
Skin is the second-largest organ in the body, with hair follicles being integral to its complex functionality6.
Your hair follicles change with environmental conditions. Studies show they can affect melanoma growth. Sun exposure greatly impacts how these follicles behave8.
How Melanomas Develop
Melanomas form through complex biological processes involving genetic mutations and environmental factors. Understanding this helps you spot potential risks and protect your skin. Recognizing these mechanisms is crucial for early detection and prevention.
Factors Contributing to Melanoma Formation
Several key factors influence melanoma development. Your risk increases based on genetic predisposition, UV radiation exposure, and skin type.
The number of moles and your personal and family medical history also play significant roles. Being aware of these factors can help you take preventive measures.
- Genetic predisposition
- UV radiation exposure5
- Skin type and number of moles
- Personal and family medical history
Genetic Mutations and Melanomas
Genetic mutations transform healthy melanocytes into cancerous cells. These changes disrupt normal cell growth and division5. DNA alterations trigger uncontrolled cell growth, leading to various melanoma stages.
The Importance of UV Radiation
UV radiation is a primary trigger for melanoma development. People near the equator or at higher elevations face increased risks. This is due to more intense sun exposure5.
| Melanoma Type | Prevalence | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Superficial Spreading | 70% | Most common type |
| Nodular | 20% | Aggressive growth pattern |
| Acral Lentiginous | 5% | Occurs on palms and soles |
Early detection and understanding melanoma’s development can significantly improve treatment outcomes.
Melanoma rates have surged in recent years, especially among young adults9. Your vigilance and proactive approach to skin health are vital. Regular skin checks and sun protection can make a big difference.
Connection Between Hair Follicles and Melanomas
Hair follicles and melanoma development are closely linked. Recent findings highlight how follicular melanocytes contribute to melanoma origins. This research area is crucial for understanding skin cancer development.
Hair Follicles as a Potential Melanoma Source
Hair follicles may be a source of melanomas. NYU School of Medicine researchers found that skin cancers might start in follicle pigment-making stem cells10.
These stem cells can change before responding to hair growth signals. They can move from follicles into the skin’s outer layers. Genetic mutations in these cells might trigger melanoma growth10.
- Immature stem cells in hair follicles can acquire oncogenic changes before responding to normal hair growth signals10
- Melanocyte stem cells can migrate from hair follicles into the skin’s outer layers10
- Genetic mutations in these cells can potentially trigger melanoma development10
Research Insights into Melanoma Development
A Nature Communications study showed oncogenic pigment-making stem cells can move from follicles and form melanomas10. Researchers used a special mouse model to track stem cell movement accurately.
The complexity of melanoma origins suggests that these cancer cells can emerge from multiple stem cell sources within hair follicles and skin layers.
Impact on Treatment Approaches
This new understanding of melanoma development opens doors for new treatments. Researchers found that changed melanocyte stem cells need specific proteins to grow and move10.
| Research Focus | Key Findings |
|---|---|
| Stem Cell Migration | Confirmed movement of oncogenic cells from hair follicles |
| Genetic Mutations | Identified specific genetic changes triggering melanoma |
| Signaling Proteins | WNT and endothelin crucial for cell proliferation |
Knowing these complex processes helps show why early detection is vital. Regular, thorough skin checks are key for catching melanomas early.
Early Detection of Melanomas
Early detection of melanoma can save lives. Skin cancer screening is vital for identifying dangerous skin changes. Melanoma detection techniques have greatly improved recently11.
Knowing melanoma signs is your best defense. Digital dermoscopy examines skin lesions with amazing precision11.
Visual exams are crucial for early identification. No blood test exists for melanoma11.
Importance of Regular Skin Checks
Regular skin checks help catch issues early. Focus on these key areas:
- Face and neck
- Arms and hands
- Legs and feet
- Back and chest
- Hair-bearing areas
Dermoscopy: A Powerful Detection Tool
Dermoscopy is an advanced skin cancer screening method. It allows doctors to examine skin lesions in great detail11.
| Detection Method | Accuracy | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Visual Exam | 70-80% | Basic screening |
| Digital Dermoscopy | 94.40% | High precision detection |
Signs of Melanoma in Hair Areas
Melanoma can occur in unexpected places, including hair-bearing areas. Look out for these warning signs:
- Changes in pigmentation
- Unusual moles or growths
- Asymmetrical skin patches
- Border irregularities
Early detection is your most powerful weapon against melanoma.
Caucasians have a higher risk of malignant melanoma. Regular screenings are crucial for this group11.
Your proactive approach can make a big difference. Catch potential skin cancer early through regular checks.
Treatment Options for Melanomas
Understanding melanoma treatment options can empower you to make informed health decisions. Each patient’s journey is unique, requiring a personalized approach to treatment12.
Surgical Procedures
Surgery is a primary strategy for addressing melanomas. Doctors may recommend different approaches based on the cancer’s stage.
- Wide excision to remove the tumor
- Sentinel lymph node biopsy for staging13
- Lymph node dissection for advanced cases13
Immunotherapy and Targeted Treatments
Modern melanoma treatment has advanced with immunotherapy and targeted therapies. Personalized medicine now offers more precise and effective options.
- Checkpoint inhibitor drugs like pembrolizumab
- Targeted therapy for BRAF gene mutations13
- Combination treatments tailored to genetic profiles13
Personalized Treatment Strategies
Your melanoma treatment plan depends on several key factors. These include cancer stage, genetic mutations, and overall health.
| Treatment Factor | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Cancer Stage | Determines surgical and medical interventions13 |
| Genetic Mutations | Guides targeted therapy selection13 |
| Patient Health | Influences treatment tolerance and options |
Remember, early detection and personalized treatment are your strongest allies in fighting melanoma.
Ongoing research expands our understanding of melanoma treatment. This offers hope for more effective and targeted therapies in the future13.
Preventive Measures Against Melanomas
Skin cancer prevention requires a comprehensive approach to health and sun safety. Understanding key prevention steps can significantly reduce your risk. Protect yourself by adopting crucial safety measures14.
Sun Safety Tips
Smart sun protection is vital for skin cancer prevention. UV radiation causes nearly 70% of melanomas. Shield your skin with these key strategies14:
- Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher
- Wear protective clothing and wide-brimmed hats
- Avoid direct sunlight during peak hours (10 am – 4 pm)
- Seek shade whenever possible
Skin Care Practices
Healthy skin maintenance goes beyond sun protection. Regular skin examinations are essential for skin cancer prevention. Understanding your personal risk factors is crucial too.
| Risk Factor | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|
| UV Exposure | Use sunscreen, limit sun exposure |
| Skin Type | Extra protection for fair-skinned individuals |
| Family History | More frequent dermatology check-ups |
Importance of Regular Dermatologist Visits
Routine dermatology check-ups can detect potential issues early. Early detection greatly improves survival rates. Over 99% of early-detected melanomas result in successful treatment15.
“Prevention is always better than cure when it comes to skin health.”
Protecting your skin is a lifelong commitment. Implement these preventive measures to reduce skin cancer risk. Maintain healthy skin for years to come16.
Living with Melanoma
A melanoma diagnosis can be tough. But knowing how to handle it can boost your chances of survival. Every patient’s journey is different. Building a strong support system is key.
Coping with Diagnosis
Finding out you have melanoma can stir up many emotions. It’s okay to feel scared or anxious. Professional help can teach you how to cope better17.
Support groups are great for sharing experiences. They can also give you emotional strength.
Support Systems and Resources
- Connect with local cancer support organizations
- Join online melanoma patient communities
- Seek counseling from mental health professionals
- Engage family and friends in your support network
“Your support system is your greatest ally in navigating cancer treatment.” – Oncology Specialist
Long-term Follow-up Care
Regular check-ups are crucial for melanoma patients. Your doctors will create a plan just for you. This plan often includes:
- Regular skin examinations
- Periodic blood tests
- Imaging studies to track cancer progression
- Ongoing communication with your healthcare providers
Follow-up care helps spot any cancer return early. It ensures you get full support during recovery18. Stay active in your health care.
Keep talking with your medical team. Follow their advice on screenings19.
Remember, you are not alone in this journey. With the right support and medical care, many patients successfully manage their melanoma and maintain a high quality of life.
Future Research Directions
Melanoma research is advancing rapidly. Scientists are exploring new ways to understand and treat this complex disease. Cutting-edge studies focus on genetic mutations and innovative detection technologies20.
Gene therapy is at the forefront of potential breakthroughs. Researchers are studying how BRAF and NRAS mutations affect melanoma development20. Their goal is to create personalized treatments that could greatly improve patient outcomes21.
Cancer detection technology is improving early diagnosis. New imaging techniques and molecular screening methods are being developed. These innovations could detect melanomas earlier than ever before.
In 2020, there were 324,635 global melanoma diagnoses21. Advanced detection methods could save thousands of lives. They enable more precise and timely interventions.
The outlook for melanoma treatment is bright. Research continues to uncover complex genetic mechanisms in skin cancer. This growing knowledge will lead to more targeted and effective treatments20.
FAQ
What is a melanoma and how is it different from other types of skin cancer?
Can melanomas actually develop in hair follicles?
What are the primary risk factors for developing melanoma?
How can I detect melanoma early?
What treatment options are available for melanoma?
How can I prevent melanoma?
Is there a connection between hair follicles and melanoma progression?
What are the latest research directions in melanoma studies?
Source Links
- Some melanomas may start in hair follicles – https://www.nih.gov/news-events/nih-research-matters/some-melanomas-may-start-hair-follicles
- Hair follicles can be a site of origin for melanoma – https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/326923
- Some Skin Cancers May Start in Hair Follicles – https://nyulangone.org/news/some-skin-cancers-may-start-hair-follicles
- What Is Melanoma Skin Cancer? | What Is Melanoma? – https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/melanoma-skin-cancer/about/what-is-melanoma.html
- Melanoma – Symptoms and causes – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/melanoma/symptoms-causes/syc-20374884
- Hair follicles and their role in skin health – Document – https://go.gale.com/ps/i.do?id=GALE|A222988979&sid=googleScholar&v=2.1&it=r&linkaccess=abs&issn=17469872&p=AONE&sw=w
- Some skin cancers may start in hair follicles – https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2019/11/191104083313.htm
- Melanoma: is hair the root of the problem? – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3768291/
- What is Melanoma? – https://www.roswellpark.org/cancer/melanoma/what-melanoma
- Some deadly skin cancers may originate in hair follicles – https://www.news-medical.net/news/20191104/Some-deadly-skin-cancers-may-originate-in-hair-follicles.aspx
- Early and accurate detection of melanoma skin cancer using hybrid level set approach – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9760861/
- Melanoma Treatment – https://www.cancer.gov/types/skin/patient/melanoma-treatment-pdq
- Treatment of Melanoma by Stage – https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/melanoma-skin-cancer/treating/by-stage.html
- Advances in Prevention and Surveillance of Cutaneous Malignancies – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7709483/
- Skin cancer: What to look for and how to prevent it – https://www.labcorp.com/skin-cancer-what-look-and-how-prevent-it
- Cutaneous Oncology: Strategies for Melanoma Prevention, Diagnosis, and Therapy – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC11320697/
- Short and Simple Melanoma Skin Cancer Guide| Understanding Melanoma – https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/melanoma-skin-cancer/if-you-have-melanoma.html
- Melanoma Information: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment – Cancer Council Victoria – https://www.cancervic.org.au/cancer-information/types-of-cancer/melanoma/melanoma-overview.html
- Some skin cancers originate in hair follicles, says new study – https://www.news-medical.net/news/20191104/Some-skin-cancers-originate-in-hair-follicles-says-new-study.aspx
- Developmental Pathways Activated in Melanocytes and Melanoma – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4221383/
- Molecular Frontiers in Melanoma: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Therapeutic Advances – https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/25/5/2984