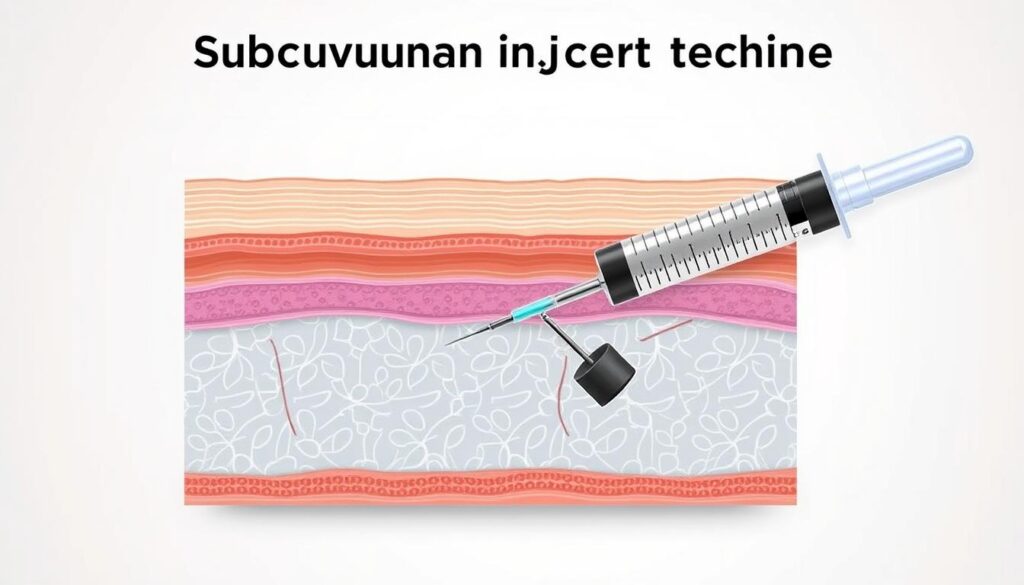
Subcutaneous injections deliver medications into the fatty layer under your skin. These SubQ injections offer a targeted approach for various treatments. They can make your injection experience safer and more comfortable12.
Insulin, blood thinners, and fertility drugs can be given through subcutaneous injections. These medications are absorbed slowly, releasing gradually over time. Some can last up to 24 hours21.
Choosing the right injection site is vital for success. Good spots include your upper arms, outer thighs, and belly area. These places offer easy access to fatty tissue21.
Key Takeaways
- Subcutaneous injections deliver medication into the fatty layer under the skin
- Medications are absorbed slowly, providing gradual treatment
- Common injection sites include arms, legs, and abdomen
- Different medications require specific injection techniques
- Proper site rotation helps prevent tissue damage
Essential Preparation Steps for Subcutaneous Injection
Careful planning is key for a safe subcutaneous injection. Proper prep ensures effective treatment and reduces discomfort. It also minimizes potential complications during the procedure.
Gathering Your Supplies
Collect all necessary materials before starting your injection. Essential supplies include:
- Medication
- Sterile needles and syringes3
- Alcohol pads for cleaning
- Gauze or bandages
- Puncture-resistant disposal container4
Pre-injection Preparation
Start by washing your hands for at least 20 seconds3. Choose a clean, dry area with good lighting.
Take refrigerated medication out 30 minutes before use. This allows it to reach room temperature4.
Careful preparation is the foundation of a safe injection process.
Understanding Proper Storage
Proper medication storage is crucial for effectiveness. Most medicines have specific storage needs:
| Medication Type | Storage Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Room Temperature Medications | Store at 68-77°F (20-25°C) |
| Refrigerated Medications | Store between 36-46°F (2-8°C) |
Always check the medication’s expiration date and appearance. Discoloration or unusual texture may mean it’s no longer safe4.
Pro Tip: Rotate your injection sites to prevent skin irritation. This also helps maintain medication effectiveness3.
Subcutaneous Injection Sites and Techniques
Picking the right spot for a subcutaneous injection is key for effective medication delivery5. Common sites include the belly, outer arm, thigh, and buttocks5. Each spot offers unique benefits for different types of medicine5.
The proper technique for these injections involves several steps. First, pick a site with enough fatty tissue6. Then, clean the area well before injecting.
Next, pinch the skin to make a 2-inch fold. Lastly, put the needle in at a 45 to 90-degree angle7.
- Choose an injection site with adequate fatty tissue6
- Clean the area thoroughly before injection
- Pinch the skin to create a 2-inch fold
- Insert the needle at a 45 to 90-degree angle7
Different meds need specific injection methods. Insulin, hormones, and certain vaccines often use subcutaneous injections5. Short needles (5/8 inches) with 25 or 27 gauge thickness work best5.
Pro tip: Always rotate injection sites to prevent tissue damage and potential complications.
Inject the medicine slowly when doing a subcutaneous shot. Hold the needle in place for a few seconds after7. This helps ensure proper absorption.
After injecting, use a gauze pad to apply gentle pressure. Watch the site for any signs of bad reactions7.
Safety is crucial when giving subcutaneous injections. Be ready to spot and handle allergic reactions. Always follow proper medical steps6.
Conclusion
Mastering SubQ injections empowers you to manage your healthcare routine. With practice, you’ll gain confidence in safe and effective administration. Understanding factors like needle selection and technique is crucial for a better experience8.
Your comfort during injections depends on several key elements. Smaller needles can reduce pain significantly8. Skin thickness varies across body areas, affecting needle length choice8.
Careful site selection and rotation maintain tissue health and optimize absorption9. Precision and care are vital when performing SubQ injections. Factors like volume, speed, and solution composition impact comfort and effectiveness8.
Consult your healthcare provider for a personalized injection strategy. Each injection is a chance to improve your technique. Stay patient, maintain hygiene, and follow professional guidance.
Your dedication to mastering SubQ injections will greatly benefit your health management. Remember, practice makes perfect in this essential healthcare skill.
FAQ
What is a subcutaneous injection?
What supplies do I need for a subcutaneous injection?
What are the best sites for subcutaneous injections?
How do I properly inject medication subcutaneously?
How should I store my medication?
How often should I rotate injection sites?
What should I do if I’m nervous about giving myself an injection?
Are there any risks associated with subcutaneous injections?
Source Links
- Giving a subcutaneous injection – https://www.med.umich.edu/1libr/NursingUnits/Giving_Subcutaneous_Injection.pdf
- Subcutaneous (SQ) injections: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia – https://medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000430.htm
- How To Give a Subcutaneous (SubQ or SQ) Injection – https://www.oncolink.org/cancer-treatment/cancer-medications/medication-safety/how-to-give-a-subcutaneous-subq-or-sq-injection
- How to Give Yourself a Subcutaneous Injection Using a Prefilled Syringe – https://www.mskcc.org/cancer-care/patient-education/how-give-yourself-subcutaneous-injection-using-prefilled-syringe
- Subcutaneous Injection: Definition and Patient Education – https://www.healthline.com/health/subcutaneous-injection
- Vaccine Administration Route and Site – https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/admin/administer-vaccines.html
- Administering Subcutaneous Injections | College of Nursing – https://nursing.ecu.edu/cils/administering-subcutaneous-injections/
- Subcutaneous Injection of Drugs: Literature Review of Factors Influencing Pain Sensation at the Injection Site – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6822791/
- Effective method for drug injection into subcutaneous tissue – Scientific Reports – https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-017-10110-w