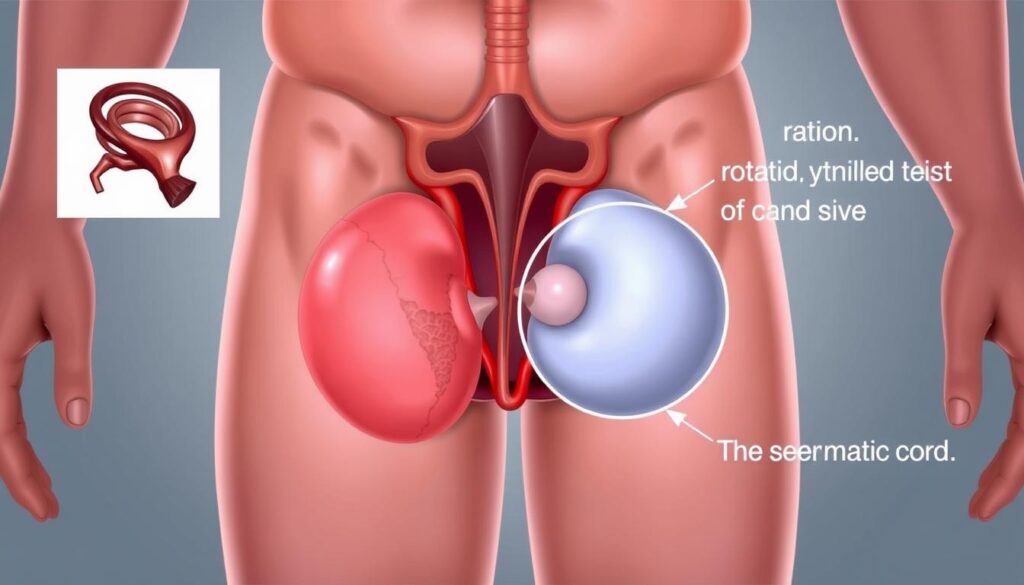
Testicular torsion is a serious urologic emergency. It can strike without warning, putting your health at risk. Young males aged 12-18 are most likely to experience this twisted testicle condition1.
Quick action is vital to save your testicle and avoid complications. This happens when the spermatic cord twists, cutting off blood supply. Sudden pain may wake you up at night1.
Many males have a genetic trait that raises their risk. This can affect both testicles, making fast response crucial1. It can occur after exercise, minor injuries, or even during sleep1.
Key Takeaways
- Testicular torsion is most common in males aged 12-182
- Immediate medical attention is critical to prevent testicle damage
- Sudden scrotal pain can be a warning sign
- Family history may increase risk of occurrence1
- The condition can potentially impact future fertility3
What is Testicular Torsion?
Testicular torsion is a critical medical emergency affecting male reproductive health. It requires immediate attention and understanding. This condition can severely impact genital well-being.
Testicular torsion happens when a testicle rotates, twisting the spermatic cord. This cuts off blood flow to the scrotum4. It’s a sudden and painful condition that can affect males of all ages.
Adolescents are most commonly affected by this medical situation. Quick action is crucial to prevent long-term damage.
Understanding the Condition
Several factors can lead to testicular torsion:
- Inherited anatomical traits allowing free testicle rotation
- Rapid physical growth during puberty
- Vigorous physical activities
- Minor genital trauma
- Unexpected temperature changes
Anatomical Insights
The scrotum houses two testicles connected by spermatic cords. When these cords twist, blood flow gets restricted. This causes sudden pain and potential long-term damage5.
Critical Statistics
Key facts about testicular torsion include:
- Occurs in approximately one in 4,000 males4
- Most common in 12- to 18-year-old males5
- Can be saved 90% of the time when treated within 4-6 hours5
“Early recognition and swift medical intervention are crucial for preserving testicular health.”
Knowing the signs of testicular ischemia is vital. Understanding potential genital trauma risks helps you respond quickly to this serious condition4.
Recognizing Symptoms of Testicular Torsion
Knowing testicular torsion signs is vital to prevent serious issues. This urologic emergency needs quick action. Being aware of specific symptoms can help identify a twisted testicle.
Severe Pain in One Testicle
Scrotal pain is often the main sign of testicular torsion. You might feel sudden, intense discomfort that’s sharp and unbearable6.
About 65% of teens report sudden, severe pain in the scrotum, testicle, or groin area6.
Swelling and Tenderness
The affected testicle may swell and become very tender. You might see big changes in your scrotum’s size and look.
These symptoms can develop fast. They require immediate medical check-up.
Nausea and Vomiting
Testicular torsion often causes intense physical responses, including:
- Sudden nausea
- Repeated vomiting
- Abdominal discomfort
Changes in Testicular Position
Watch the position of your testicles. One testicle might look higher or at an odd angle7.
This unusual positioning can be a key sign of possible testicular torsion.
“Early recognition of symptoms can prevent permanent damage to the testicle” – Urological Experts
This condition most often affects teenagers7. It occurs in 3.8 per 100,000 males under 18 years old yearly8.
About 35-40% of patients wait too long for help. This delay can cause permanent testicle damage6.
| Age Group | Torsion Likelihood |
|---|---|
| 11-19 years | 65% of cases |
| Neonates | Rare, but possible |
If you have these symptoms, get medical help right away. Surgery within 6 hours can stop permanent damage7.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Testicular pain can signal a serious condition. It should never be ignored. Recognizing potential urologic emergencies is crucial for preserving health and preventing complications.
Understanding the Urgency of Testicular Pain
Severe testicle pain requires swift action. Quick medical care is vital for conditions like testicular torsion7. Untreated, it can cause permanent damage.
Young males are at higher risk. About 65% of cases happen between ages 12 and 189.
Critical Signs Requiring Emergency Care
- Sudden, severe testicle pain
- Swelling or unusual positioning of the testicle
- Nausea and vomiting accompanying testicular pain
- Fever or chills
Navigating Medical Communication
Be ready to give detailed info to your doctor. A Doppler ultrasound might be needed to check blood flow7.
Quick treatment is key. The best window is within 4-6 hours to avoid lasting damage9.
*Prompt medical intervention can save your testicle and prevent long-term health complications.*
Testicular torsion affects 1 in 4,000 males under 25. Know the warning signs and act fast9.
Prevention and Care Tips
Protecting your male reproductive health needs proactive strategies and awareness. In pediatric urology, prevention is crucial for managing testicular condition risks. If you have a family history, consult a healthcare professional to identify potential vulnerabilities10.
Preventive measures are key to minimizing risks. Wear protective gear during contact sports and be aware of your body. This helps detect early signs of problems.
Surgical intervention might be recommended for those with inherited traits increasing testicular torsion likelihood11. Regular check-ups are vital, especially for teenage boys at most risk11.
Lifestyle Changes to Minimize Risk
Your lifestyle can greatly impact male reproductive health. Avoid activities that might harm your testicles. Seek medical help for unusual pain or swelling immediately.
Quick treatment within 6 hours can save over 90% of testicle function11. Waiting more than 12 hours increases the risk of testicle removal10.
Resources for Further Information
Stay informed by consulting reliable medical resources. The medical community offers extensive information on testicular health. Modern medicine ensures a normal life even if you lose a testicle.
Prosthetic options and comprehensive care can help manage potential complications in pediatric urology. Regular check-ups and prompt action are key to maintaining reproductive health.
FAQ
What is testicular torsion?
Who is most at risk for testicular torsion?
What are the main symptoms of testicular torsion?
How serious is testicular torsion?
What causes testicular torsion?
How is testicular torsion treated?
Can you prevent testicular torsion?
What happens if testicular torsion is left untreated?
Can I still have children after losing a testicle?
When should I go to the emergency room?
Source Links
- Testicular torsion: Get emergency treatment for severe testicle pain-Testicular torsion – Symptoms & causes – Mayo Clinic – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/testicular-torsion/symptoms-causes/syc-20378270
- Testicular Torsion – https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15382-testicular-torsion
- Testicular Torsion: Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment – https://www.urologyhealth.org/urologic-conditions/testicular-torsion
- Testicular Torsion | Causes, Symptoms & Treatment – https://www.cincinnatichildrens.org/health/t/testicular-torsion
- Testicular Torsion (for Teens) – https://kidshealth.org/en/teens/torsion.html
- Testicular torsion: Signs, causes and what to do – Children’s Health – https://www.childrens.com/health-wellness/testicular-torsion-signs-causes-what-to-do
- Testicular torsion – https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/testicular-torsion
- Testicular Torsion: Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Management – https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2013/1215/p835.html
- Testicular Torsion: Definition, Symptoms, and Treatment – https://www.healthline.com/health/testicular-torsion
- Testicular torsion: Get emergency treatment for severe testicle pain-Testicular torsion – Diagnosis & treatment – Mayo Clinic – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/testicular-torsion/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20378274
- Testicle Pain & Testicular Torsion – https://www.healthychildren.org/English/health-issues/conditions/genitourinary-tract/Pages/Testicular-Torsion.aspx