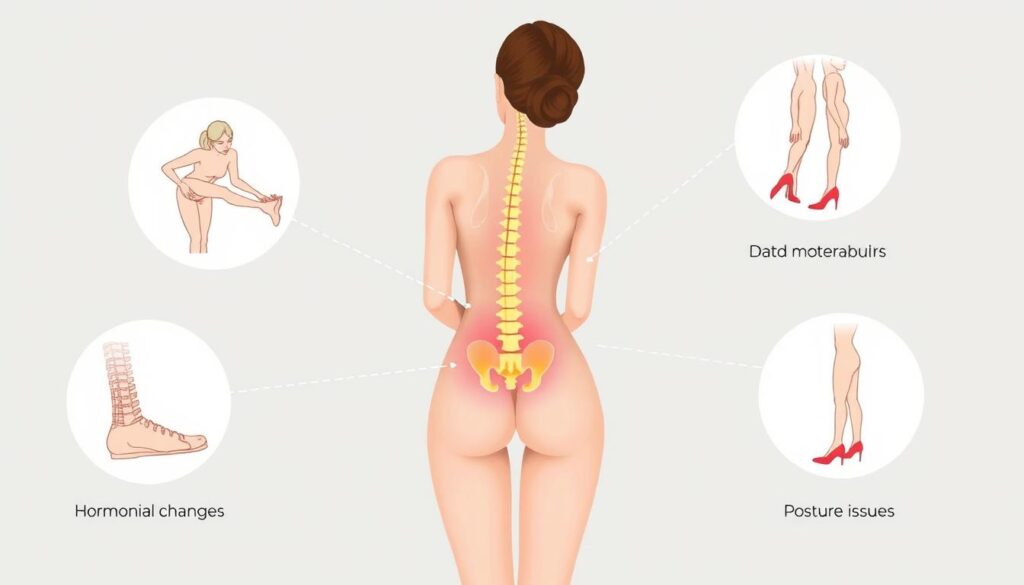
Many women face lower back pain throughout their lives. Knowing the causes helps manage and prevent discomfort. Women have unique pain triggers due to their body structure1.
Female lower back pain can stem from muscle strain, hormonal changes, and reproductive health issues. The wider female pelvis affects spine alignment and stress distribution1. This creates unique pressures that can trigger discomfort.
Muscle strain, injuries, and degenerative conditions influence back health. Women may experience pain from menstrual cramps, endometriosis, and pregnancy-related changes1. Understanding these causes helps develop targeted pain management strategies.
Key Takeaways
- Lower back pain in women has multiple unique triggers
- Anatomical differences contribute to back pain risk
- Reproductive health conditions can cause significant discomfort
- Hormonal changes impact back pain experiences
- Proper understanding helps develop effective management strategies
Understanding Female-Specific Back Pain Triggers
Women face unique lower back pain challenges. Hormonal changes, reproductive health, and physical shifts can affect back comfort and stability2. Knowing these triggers helps manage and prevent chronic discomfort.
Hormonal and Menstrual Cycle Impacts
PMS and menstrual pain often cause lower back discomfort. Worldwide, 50-90% of women experience dysmenorrhea, which includes intense lower back pain3.
Hormonal changes affect muscle tension and pain sensitivity during menstrual cycles2. This can increase discomfort before and during periods.
- Menstrual cramps frequently trigger lower back pain
- Hormonal shifts can increase muscle sensitivity
- Pain typically intensifies before and during menstruation
Pregnancy-Related Back Pain
Pregnancy brings major physical changes affecting the back. Over two-thirds of pregnant women experience lower back pain4.
The body’s center of gravity shifts, weight increases, and hormones change. These factors contribute to pregnancy-related back discomfort2.
| Pregnancy Back Pain Causes | Impact |
|---|---|
| Weight Gain | Increased spinal pressure |
| Hormonal Changes | Ligament relaxation |
| Posture Shifts | Altered spine alignment |
Reproductive Health Conditions
Several reproductive conditions can cause lower back pain. Endometriosis affects about 190 million women globally3.
Pelvic inflammatory disease and uterine fibroids can also lead to chronic back discomfort4. These conditions require proper medical attention.
“Understanding your body’s signals is the first step in managing reproductive health-related back pain.”
Being aware and proactive can greatly reduce the impact of female-specific back pain causes2. Seek medical advice for persistent discomfort.
Lower Back Pain Causes in Females
Women face unique factors behind lower back pain. Understanding these can help manage and prevent discomfort. Causes range from muscle strain to complex conditions5.
Muscle strain is a main source of lower back pain. Sudden movements or poor posture can trigger painful muscle injuries. Women are prone to specific back pain conditions6.
- Herniated discs pressing on nerves
- Sciatica causing radiating pain
- Disc degeneration with age
- Sacroiliac joint dysfunction
Age plays a role in back pain risk. Most cases start after 30 years old5. Genetics can make some people more likely to have chronic pain5.
| Condition | Female Prevalence |
|---|---|
| Chronic Lower Back Pain | More Common in Women |
| Piriformis Syndrome | Higher in Women |
| Coccydynia | 5x More Likely in Women |
Female hormones play a crucial role in muscle and bone degeneration, directly impacting pain sensitivity6.
Lifestyle choices can worsen back pain risks. These include prolonged sitting, smoking, and lack of exercise5. Knowing these causes helps you take steps to manage back discomfort.
Common Risk Factors and Prevention Strategies
Back pain can greatly affect your daily life. Understanding its causes and prevention methods is crucial. Women face unique challenges in maintaining back health.
Lifestyle and Physical Activity Considerations
Your daily habits impact back pain prevention. Age, lack of exercise, and sitting too much can cause issues.
Walking, swimming, and cycling can strengthen back muscles. These low-impact activities improve overall fitness.
- Engage in gentle stretching exercises
- Practice core-strengthening workouts
- Avoid prolonged periods of inactivity
Posture and Ergonomic Solutions
Good posture is key to preventing back pain. Focus on alignment when sitting or standing. Use ergonomic solutions to reduce muscle strain.
Choose chairs with good lumbar support. Take regular breaks to avoid prolonged sitting.
| Posture Tips | Recommended Actions |
|---|---|
| Standing | Use a low footstool to reduce lower back strain |
| Sitting | Use a pillow for additional lower back support |
Weight Management and Exercise Benefits
Maintaining a healthy weight is vital for back health. Extra weight puts stress on back muscles and joints.
Regular exercise helps manage weight and strengthens core muscles. This provides back pain relief and prevents future issues.
Your back health is a journey of consistent care and mindful movement.
By using these strategies, you can lower your risk of chronic back pain. You’ll also improve your overall physical well-being7.
Conclusion
Lower back pain in women needs a well-rounded approach. You have many ways to ease discomfort. Most back pain cases get better within six to twelve weeks with proper care8.
Start with gentle exercises, heat therapy, and over-the-counter pain relievers. See a doctor if pain persists, worsens, or comes with fever or leg numbness. Some lower back pain management may need expert help9.
Improve your back health with lifestyle changes. Keep a healthy weight, practice good posture, and do targeted exercises. Women face unique back pain issues due to hormones and body differences8.
Personalized care can help manage and reduce lower back pain10. Your back pain journey is unique. Listen to your body and get expert help when needed.
Be patient with your healing process. With the right approach, you can boost your life quality. You can also lessen back pain’s effect on your daily activities.
FAQ
What are the most common causes of lower back pain in women?
How does pregnancy affect lower back pain?
Can menstrual cycles cause lower back pain?
What reproductive conditions might cause lower back pain?
How can I prevent lower back pain?
When should I see a doctor about my lower back pain?
How do hormones impact lower back pain?
Are there specific exercises that can help relieve lower back pain?
Source Links
- Lower back pain causes in females and their treatment – https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/lower-back-pain-causes-in-females
- What Causes Lower Back Pain in Females – Top 5 Causes – https://illinoispain.com/blog/what-are-common-causes-of-lower-back-pain-in-women/
- Understanding Female Back Pain: Causes and Symptoms Chart – https://premiaspine.com/chart-of-female-back-pain/
- What Causes Lower Back Pain In Females? – HSSH – https://hssh.health/blog/what-causes-lower-back-pain-in-females/
- Lower Back Pain Causes | Aurora Health Care – https://www.aurorahealthcare.org/services/aurora-spine-services/lower-back-pain/causes
- Back Pain in Females: Pain Conditions and Causes of Back Pain – SAPNA Pain Management Blog – https://www.sapnamed.com/blog/back-pain-in-females-pain-conditions-and-causes/
- Managing Lower Back Pain in Women: Causes and Treatments – https://wildhawkphysicaltherapy.com/lower-back-pain-in-women-causes-treatments-and-prevention/
- Gender-Related Issues in the Management of Low-Back Pain: A Current Concepts Review – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10660510/
- Symptoms and Causes of Back Pain – https://www.ada.org/resources/practice/wellness/symptoms-and-causes-of-back-pain
- Low back pain in women before and after menopause – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4612559/