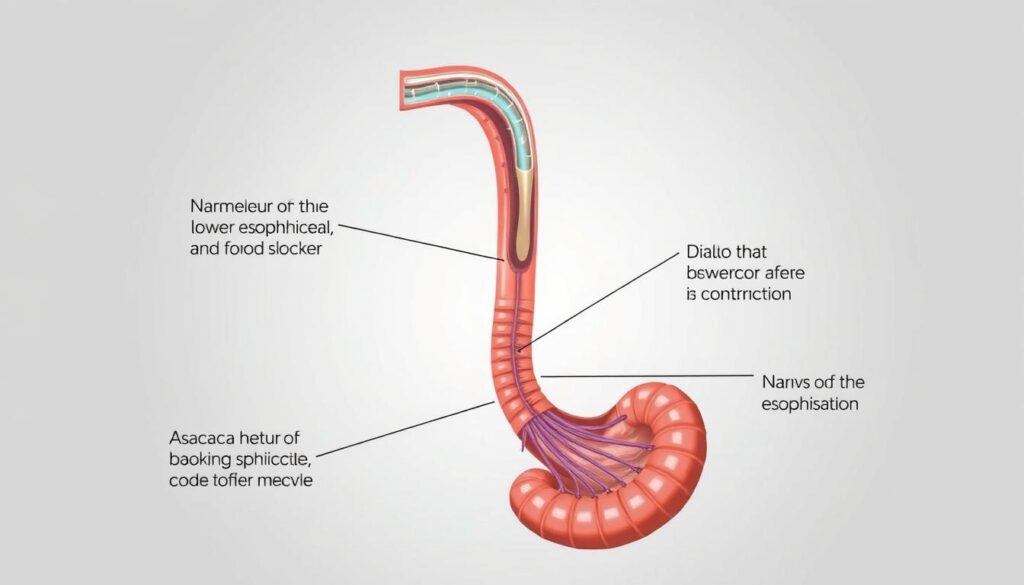
Achalasia is a rare disorder that affects your esophagus and digestive health. It makes it hard to move food through your esophagus. This condition causes uncomfortable symptoms that can be distressing1.
Achalasia is not common. It affects about 8 to 12 people out of 100,000. Adults between 30 and 60 years old are more likely to have it1.
If you have trouble swallowing often, you might have achalasia. This problem affects the lower part of your esophagus. Men get achalasia twice as often as women do1.
People with achalasia are more likely to get autoimmune disorders. Understanding this condition is important for better health care1.
Key Takeaways
- Achalasia is a rare swallowing disorder affecting 8-12 people per 100,000
- The condition primarily impacts adults aged 30-60
- Men are more likely to develop achalasia
- Symptoms include difficulty swallowing and potential weight loss
- Multiple treatment options are available to manage symptoms
What is Achalasia: Understanding the Rare Swallowing Disorder
Achalasia is a rare digestive disorder affecting the ability to swallow food. It impacts about 1 in 100,000 people, mainly those aged 25 to 60.
Understanding the Disorder’s Characteristics
Achalasia involves a malfunction in your esophageal muscles. The lower esophageal sphincter (LES) doesn’t relax properly. This prevents food from entering your stomach smoothly2.
Types of Achalasia
Achalasia presents in three distinct types:
- Type 1 (Classic Achalasia): Minimal muscle contraction
- Type 2: Characterized by esophageal compression
- Type 3 (Spastic Achalasia): Abnormal contractions near the stomach
Common Risk Factors
Several risk factors can contribute to developing achalasia:
- Age between 25-60 years
- Allergic disorders
- Adrenal insufficiency
- Presence of Allgrove syndrome
Impact on Digestive System
Achalasia severely disrupts your digestive process. Food builds up in the esophagus, potentially causing it to widen and twist.
This can lead to serious issues like regurgitation and chest pain. It also increases the risk of pneumonia3.
Managing achalasia requires specialized medical intervention and careful monitoring.
Treatment Considerations
Several options exist for managing achalasia. These include esophageal dilation, Heller myotomy, pneumatic dilation, and POEM.
Each method aims to reduce lower esophageal sphincter pressure. They also work to improve swallowing function3.
| Treatment Method | Invasiveness | Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|
| Pneumatic Dilation | Minimally Invasive | Short |
| POEM | Minimally Invasive | Quick |
| Heller Myotomy | Surgical | Moderate |
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial for managing achalasia effectively.
Recognizing the Warning Signs and Symptoms
Achalasia is a rare digestive disorder with distinct symptoms. It can greatly affect your daily life. Recognizing these signs early is key for proper management4.
Dysphagia, or trouble swallowing, is the main symptom of achalasia. You might struggle to move food and drinks down your throat. This can make eating uncomfortable and frustrating5.
- Regurgitation of undigested food
- Chest pain during or after eating
- Recurring heartburn
- Unexplained weight loss
- Coughing, especially at night
Achalasia usually affects people aged 25 to 604. Symptoms often develop slowly, making it hard to spot the problem right away5.
“Early recognition of achalasia symptoms can prevent serious complications and improve treatment outcomes.”
Doctors use esophageal manometry to diagnose achalasia. This test checks muscle movements and finds abnormal esophagus function5.
Untreated achalasia can cause serious health issues. These include malnutrition, pneumonia, and higher risk of esophageal cancer5.
Watch out for ongoing swallowing problems. See a doctor if you have frequent digestive issues. Early diagnosis can help manage this complex condition better.
Treatment Options and Management Strategies
Achalasia treatment offers various approaches to manage symptoms and boost life quality. Working closely with your doctor helps create an effective plan. Understanding your options is key to successful management.
Minimally Invasive Surgical Procedures
Minimally invasive surgeries are gaining popularity for treating achalasia. The POEM (Per-Oral Endoscopic Myotomy) procedure is an innovative approach. It offers similar symptom relief to traditional surgical methods6.
- Laparoscopic Heller myotomy
- Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM)
- Surgical procedures with fundoplication
Non-Surgical Treatment Approaches
Non-surgical treatments offer alternative strategies for patients unsuitable for surgery. Pneumatic dilation effectively stretches the lower esophageal sphincter7.
Esophageal manometry helps determine the best non-surgical approach for your condition7. This test guides doctors in choosing the most suitable treatment option.
Medication and Botox Injections
Botulinum toxin injections can benefit some patients. They’re useful for those with multiple medical conditions or unsuitable for invasive procedures7.
Medications like nitrates and calcium channel blockers provide temporary relief. However, they’re generally less effective for long-term management6.
Every patient’s journey with achalasia is unique, and treatment success depends on individual factors and careful medical evaluation.
Follow-up care and ongoing management are crucial in effectively handling achalasia. Your doctor can help create a personalized approach to manage your condition6.
Conclusion
Achalasia management requires a comprehensive approach to improve life quality. Modern medical advancements offer hope for effective symptom control. Your treatment journey depends on various factors, including condition severity and health characteristics.
Understanding achalasia is crucial for developing a personalized strategy. While lifelong, you’re not alone in this journey. Treatment options have evolved, providing more effective ways to manage symptoms.
Achalasia typically affects people aged 30 to 60. Advanced techniques like high-resolution manometry allow for precise treatment planning. Your medical team will develop a tailored approach addressing your specific needs.
Regular follow-ups and monitoring are essential to track progress. Many patients successfully manage symptoms and maintain a good life quality. Innovative treatments offer hope for those with achalasia.
Stay positive and proactive about your health. With proper medical support, you can navigate this disorder’s challenges. A comprehensive plan helps you continue living a fulfilling life8910.
FAQ
What is Achalasia?
What are the main symptoms of Achalasia?
How is Achalasia diagnosed?
What are the treatment options for Achalasia?
Are there different types of Achalasia?
Can Achalasia be cured?
What causes Achalasia?
What are the potential complications if left untreated?
Source Links
- Achalasia – https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/achalasia
- Patient education: Achalasia (Beyond the Basics) – https://www.uptodate.com/contents/achalasia-beyond-the-basics/print
- What is achalasia? – https://www.roswellpark.org/cancertalk/202406/what-achalasia
- Achalasia – Symptoms and causes – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/achalasia/symptoms-causes/syc-20352850
- Achalasia: Symptoms & Causes | NewYork-Presbyterian – https://www.nyp.org/digestive/esophageal-diseases/achalasia
- ACG Clinical Guidelines: Diagnosis and Management of Achalasia – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9896940/
- Management of achalasia – PMC – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3108680/
- Achalasia – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519515/
- Achalasia – An Update – https://www.jnmjournal.org/journal/view.html?uid=26&vmd=Full
- Pathophysiology of achalasia – https://aoe.amegroups.org/article/view/5440/html