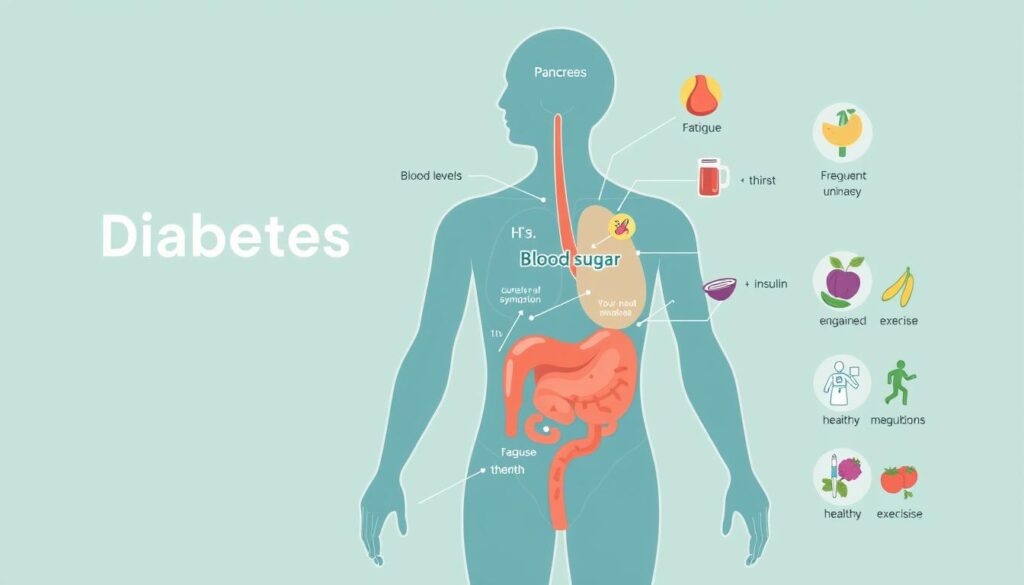
Diabetes affects how your body handles blood glucose. This chronic condition can impact people of all ages. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form1.
Your body’s insulin and glucose management determines your diabetes risk2. Type 1 and type 2 diabetes have different characteristics. Type 1 often starts in childhood or teenage years2.
Type 2 diabetes can develop at any age. It’s more common in people over 40. However, cases in children are rising2.
Knowing your risk factors is vital. Family history, genetics, and environment play key roles2. Some ethnic groups have higher type 2 diabetes risk2.
Being overweight or obese increases prediabetes and type 2 diabetes risk2. Diabetes can lead to serious health issues. These include heart disease, nerve damage, and kidney problems2.
Over 1 in 3 Americans have prediabetes. Sadly, more than 80% don’t know they have it1.
Key Takeaways
- Diabetes impacts blood glucose processing and can affect anyone
- Type 2 diabetes is the most prevalent form of the disease
- Family history and lifestyle significantly influence diabetes risk
- Regular health monitoring is crucial for early detection
- Healthy lifestyle choices can help manage and prevent diabetes
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes affects how your body handles blood sugar. It’s a chronic condition that impacts millions of Americans. Managing insulin and blood glucose levels is key.
Diabetes is a major health issue in the United States. About 37.3 million people have this condition. That’s 11.3% of the population3.
Understanding diabetes is vital for your health. It can help you take better care of yourself.
Understanding Diabetes Types
Diabetes comes in different forms. Each type has its own traits:
- Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition where the pancreas stops producing insulin
- Type 2 Diabetes: The most common form, where your body becomes resistant to insulin4
- Gestational Diabetes: Occurs during pregnancy
- Prediabetes: A warning stage before full diabetes development
How Diabetes Impacts Your Body
Diabetes can disrupt your blood sugar balance. This can lead to two main issues:
- Hyperglycemia: Abnormally high blood sugar levels
- Hypoglycemia: Dangerously low blood sugar levels
“Diabetes doesn’t define you, but managing it carefully can help you live a full, healthy life.”
Unmanaged diabetes can cause serious problems. It may increase risks to your heart, kidneys, feet, and eyes3.
Type 2 diabetes makes up 90-95% of all cases4. Knowing your personal risk is crucial.
| Diabetes Type | Prevalence | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Type 1 | 5-10% of cases | Autoimmune, insulin-dependent |
| Type 2 | 90-95% of cases | Insulin resistance, lifestyle-related |
| Gestational | Pregnancy-specific | Temporary hormonal impact |
Understanding diabetes is the first step to better health. Knowing your risk can help you make smart choices.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Diabetes
Diabetes shows up through various symptoms that might seem subtle at first. Catching these signs early can lead to proper medical care. Your body sends important signals you shouldn’t ignore.
Common Warning Signs of Diabetes
Several key symptoms can point to potential diabetes. Here are the most critical signs to watch:
- Polyuria (frequent urination): Urinating more than 7 times in 24 hours5
- Polydipsia (excessive thirst): Constant need to drink water6
- Polyphagia (increased hunger): Feeling hungry even after eating
- Blurred vision: Difficulty focusing due to blood sugar fluctuations6
- Unexplained weight loss: Rapid decrease in body weight6
Less Common Diabetes Indicators
Some symptoms are less obvious but equally important to recognize:
- Diabetic ketoacidosis: Fruity-smelling breath
- Numbness in hands and feet6
- Slow-healing wounds6
- Frequent infections
“Early detection is key to managing diabetes effectively.” – American Diabetes Association
Different diabetes types show symptoms in unique ways. Type 1 diabetes symptoms appear quickly. Type 2 symptoms develop slowly over time5.
If you notice multiple signs, talk to a doctor. They can run tests to check for diabetes6.
| Diabetes Type | Typical Onset | Key Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Type 1 | Childhood/Young Adulthood | Rapid weight loss, frequent urination |
| Type 2 | Adults over 45 | Gradual symptom development, increased thirst |
| Gestational | Pregnancy (24-28 weeks) | Often asymptomatic |
Remember, recognizing these symptoms early can make a significant difference in managing your health.
Causes and Risk Factors of Diabetes
Diabetes is a complex health challenge involving genes and lifestyle choices. Over 38 million Americans live with this metabolic disorder. Understanding its causes is crucial for better management and prevention7.
Genetic Factors in Diabetes Development
Your family history greatly affects your diabetes risk. Having a close relative with diabetes increases your chances of developing it7.
Type 1 diabetes shows how genetic factors can trigger metabolic problems. Your genes play a big role in how your body handles sugar.
- Inherited genetic susceptibility
- Autoimmune response triggers
- Familial metabolic patterns
Lifestyle Choices Influencing Diabetes
Insulin resistance and obesity are main causes of type 2 diabetes. Your daily habits greatly impact your metabolic health8.
Being overweight and inactive significantly raises your diabetes risk. Making healthy choices can help prevent or manage the condition8.
| Risk Factor | Impact on Diabetes |
|---|---|
| Obesity | High risk of type 2 diabetes |
| Physical Inactivity | Increased metabolic dysfunction |
| Age | Higher risk after 45 years |
You can lower your diabetes risk through lifestyle changes. Exercise regularly and maintain a healthy weight. Keep an eye on your health to catch problems early9.
The Centers for Disease Control recommends 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly. This can help prevent type 2 diabetes9.
“Your health is a reflection of your lifestyle choices” – Health Experts
Some ethnic groups have higher diabetes risks. These include African American, Hispanic, Native American, and Asian populations7.
Knowing these factors helps you make smart health choices. You can better prevent or manage diabetes with this knowledge.
Preventing Diabetes in Your Life
Diabetes prevention starts with knowing your personal risk. About 37 million Americans have diabetes, while 96 million experience prediabetes10. Having prediabetes doesn’t mean you’ll get type 2 diabetes. You can take steps to manage your health10.
Your diet plays a key role in preventing diabetes. Choose foods that support healthy blood sugar levels. Experts suggest lifestyle changes to reduce your risk. Losing 5% of your body weight can help reverse prediabetes1011.
Physical activity is a powerful diabetes prevention tool. Exercise for 30 minutes, five days a week to lower your risk11. Regular glucose checks and check-ups can help track your progress.
About 1 in 3 Americans has prediabetes. With the right approach, you can change your health path11. Take control by being proactive.
Work with doctors to create a personal prevention plan. Your commitment to health can prevent type 2 diabetes. It also helps maintain long-term wellness.
FAQ
What exactly is diabetes?
What are the main symptoms of diabetes?
Who is most at risk for developing type 2 diabetes?
Can diabetes be prevented?
What’s the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
How does diabetes affect my body?
What treatments are available for diabetes?
What should I do if I suspect I have diabetes?
Source Links
- Diabetes: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, Prevention, and More – https://www.healthline.com/health/diabetes
- Diabetes – Symptoms and causes – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetes/symptoms-causes/syc-20371444
- What Is Diabetes? – NIDDK – https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/what-is-diabetes
- Diabetes Basics – https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/about/index.html
- Early Signs and Symptoms of Diabetes – https://www.webmd.com/diabetes/understanding-diabetes-symptoms
- Diabetes symptoms: When diabetes symptoms are a concern – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetes/in-depth/diabetes-symptoms/art-20044248
- Type 2 Diabetes – https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/about/about-type-2-diabetes.html
- Type 2 diabetes – Symptoms and causes – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/type-2-diabetes/symptoms-causes/syc-20351193
- Diabetes – https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes
- On Your Way to Preventing Type 2 Diabetes – https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pdfs/prevent/On-your-way-to-preventing-type-2-diabetes.pdf
- Preventing Type 2 Diabetes – NIDDK – https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/preventing-type-2-diabetes