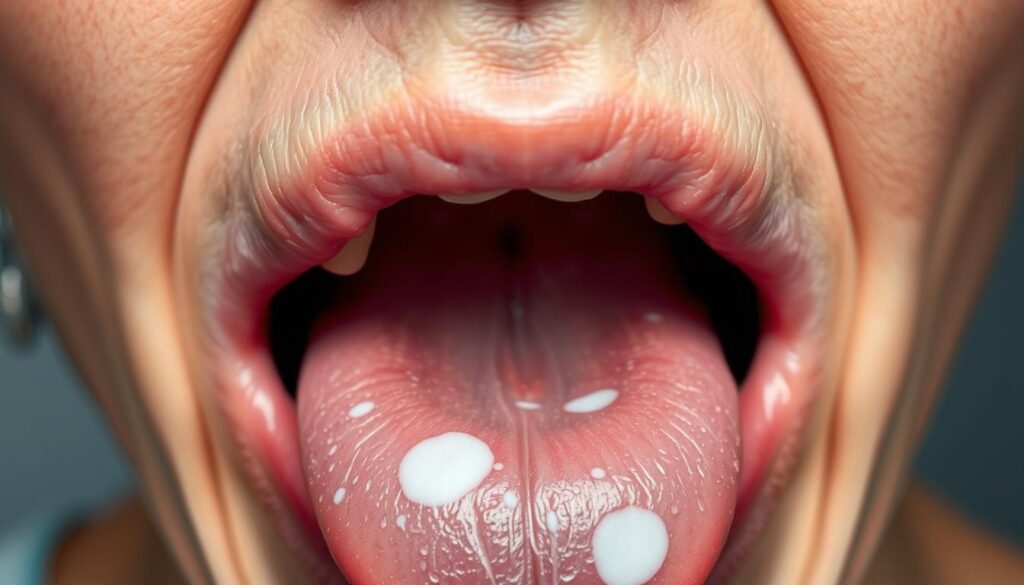
Leukoplakia is a complex oral condition that needs your attention. It appears as white or gray patches inside your mouth. These patches can develop on your gums, cheeks, or tongue, signaling potential health issues1.
Leukoplakia mainly affects older adults. The patches are often slightly raised with a hard surface1. This precancerous condition is crucial to understand for good oral health.
Smokers are six times more likely to develop these white patches2. Tobacco use, especially pipe smoking, is a major cause of leukoplakia1. About 5% of oral leukoplakia cases might turn into oral cancer2.
Some people face higher risks. Those with weak immune systems, like HIV/AIDS patients, can get oral hairy leukoplakia1. This type is linked to the Epstein-Barr virus and needs careful medical watch3.
Key Takeaways
- Leukoplakia presents as white or gray patches in the mouth
- Smoking significantly increases the risk of developing leukoplakia
- Some leukoplakia patches may be precursors to oral cancer
- Older adults are more susceptible to this condition
- Professional medical evaluation is crucial for proper diagnosis
What is Leukoplakia and Why Should You Care?
Leukoplakia is a serious oral condition that needs your attention. White patches in your mouth might seem harmless. However, they could signal health risks that need careful monitoring.
Understanding the Basics
Leukoplakia appears as thick, white patches on the oral mucosa. These patches can’t be easily removed or classified as another condition4. In Germany, about 2.3% of men and 0.9% of women have this condition4.
Most cases occur in middle-aged individuals4.
Common Symptoms to Recognize
- White or gray patches that persist in your mouth5
- Patches on the tongue, gums, or mouth floor5
- Rough or smooth surface textures
- Irregular shapes and edges
Potential Risks and Concerns
Leukoplakia carries a significant oral cancer risk. Up to 30% of untreated cases may become squamous cell carcinoma4. The change happens within epithelial cells, making early detection vital.
| Leukoplakia Type | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Homogeneous | Uniform white patches |
| Verrucous | Warty or textured appearance |
| Erosive | Potentially more aggressive |
Certain populations face higher risks. People with weak immune systems, like HIV patients, may develop hairy leukoplakia. The Epstein-Barr virus triggers this type45.
“Early recognition and professional evaluation are your best defenses against potential oral health complications.”
Regular dental check-ups help detect and manage leukoplakia effectively5. Good oral hygiene is also key in maintaining your mouth’s health.
Causes of Leukoplakia: What You Need to Know
Leukoplakia has complex origins, but several key factors contribute to its development. Understanding these causes can help you protect your oral health. Let’s explore the main reasons behind this condition.
Tobacco Use and Its Impact
Tobacco use is the leading cause of leukoplakia. Smoking greatly increases the risk of developing white patches in the mouth. Smokers are six times more likely to experience leukoplakia than non-smokers.
Oral health experts recommend quitting tobacco to lower your chances of getting this condition. Kicking the habit can significantly improve your oral health.
Alcohol Consumption and Oral Health
Long-term alcohol use plays a big role in leukoplakia development. The risk increases substantially when combined with tobacco use. Reducing alcohol intake can help prevent leukoplakia.
Additional Contributing Factors
- Injury to the inside of the cheek
- Rough teeth or poorly fitting dentures
- Inflammatory conditions
Hairy leukoplakia, a specific type, is often linked to the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). This variant is common in people with weakened immune systems. Those with HIV or organ transplants are at higher risk.
| Risk Factor | Impact on Leukoplakia |
|---|---|
| Tobacco Use | Highest Risk Factor |
| Alcohol Consumption | Significant Risk |
| Weakened Immune System | Increases Susceptibility |
Oral leukoplakia affects 1-2% of the population. Most cases appear in patients over 40 years old6. Knowing these risk factors can help you make smart choices about your oral health.
Prevention is always better than cure when it comes to oral health.
Treatment Options for Leukoplakia
Leukoplakia is a precancerous oral condition that needs careful management. Understanding your treatment options is vital. Your care may involve several approaches to address these white mouth patches7.
Treatment choices depend on how severe your condition is. Doctors might suggest surgical removal using lasers, cold tools, or surgical knives7. Some research has looked into vitamin A, retinoids, and other treatments8.
Most studies on these treatments show low-quality results. The overall evidence remains limited8.
For hairy leukoplakia, doctors may prescribe antiviral medicines7. Regular check-ups are crucial because the condition can come back7.
Systemic vitamin A might help reduce cancer risk. It’s shown a notable reduction rate compared to placebo8.
See a doctor if you notice lasting oral lesions. Your treatment plan will likely include lifestyle changes and possible medical treatments. Ongoing monitoring is key to managing this dysplasia well7.
FAQ
What exactly is leukoplakia?
Am I at risk of developing leukoplakia?
How serious is leukoplakia?
What are the typical symptoms of leukoplakia?
How is leukoplakia treated?
Can leukoplakia be prevented?
Is hairy leukoplakia different from regular leukoplakia?
Source Links
- Leukoplakia – UF Health – https://ufhealth.org/conditions-and-treatments/leukoplakia
- Leukoplakia: Symptoms, causes, and prevention – https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/317689
- Oral Health and Leukoplakia – https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/dental-health-leukoplakia
- Oral leukoplakia: why it can be dangerous – https://curaprox.us/blog/post/oral-leukoplakia-why-it-can-be-dangerous?srsltid=AfmBOorgTsFufi1h-w4foGy9nI3-iRu-5FcAnutQ7M8NSvDe5Uiuijz4
- Leukoplakia – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/leukoplakia/
- PDF – https://www.brighamandwomens.org/assets/BWH/surgery/oral-medicine-and-dentistry/pdfs/oral-leukoplakia-bwh.pdf
- Leukoplakia – Diagnosis and treatment – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/leukoplakia/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20354411
- Interventions for treating oral leukoplakia to prevent oral cancer – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6457856/