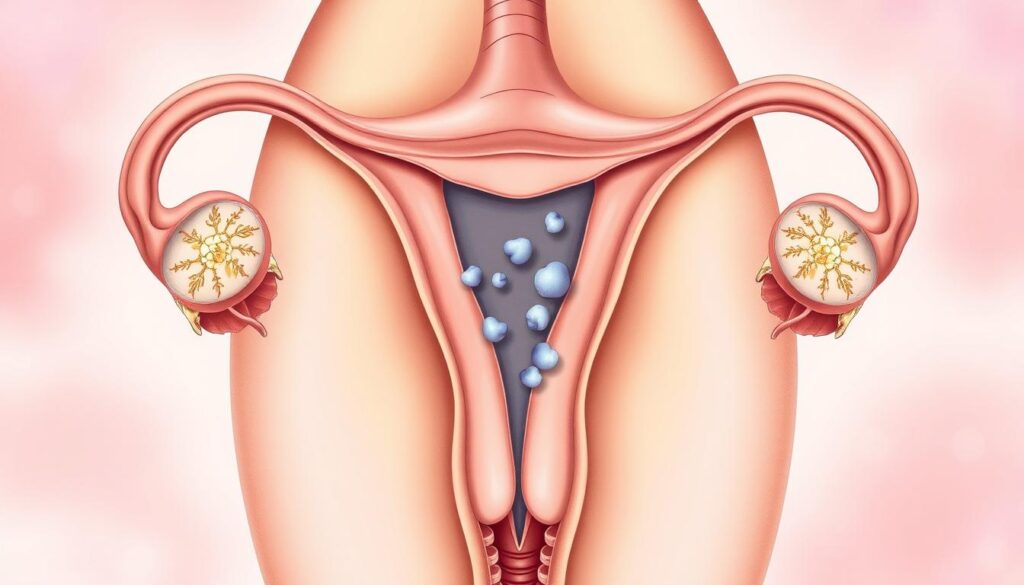
Uterine polyps are growths in your uterus’s inner lining. They can vary in size and potential risks1. Most are harmless, but knowing about them is vital for your health2.
Your risk of these growths goes up as you age. It peaks in your fifties and may drop after menopause1. Being overweight can raise estrogen levels, making polyps more likely1.
Uterine polyps are more common than you might think. Studies show 10% to 24% of women may get them2. The good news? Most aren’t cancerous2.
Key Takeaways
- Uterine polyps are typically benign endometrial growths
- Risk increases with age and hormonal changes
- Most polyps are noncancerous
- Regular gynecological check-ups aid in early detection
- Treatment options vary based on size and symptoms
What Are Uterine Polyps and Their Common Symptoms
Uterine polyps are abnormal growths in your uterus’s inner lining. These soft protrusions can affect your reproductive health. They range from tiny millimeter-sized growths to larger formations like a golf ball3.
Understanding Growth Patterns and Sizes
Polyps form when uterine lining cells overgrow, creating irregular structures. They can vary greatly in size and appearance.
- From a few millimeters to several centimeters
- Most common in women aged 40-50 years4
- Can occur in approximately 24-51% of women with abnormal uterine bleeding4
Recognizing Key Symptoms
Early identification of uterine polyps can help manage potential complications. Be aware of these key symptoms:
- Postmenopausal bleeding
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Heavy menstrual flow
- Unexpected bleeding between periods
- Potential challenges with infertility3
“Understanding your body’s signals is the first step toward proactive health management.”
Risk Factors and Hormonal Influences
| Risk Factor | Impact on Uterine Polyps |
|---|---|
| Obesity | Increases risk significantly4 |
| Hormone Therapy | Can stimulate polyp growth |
| Tamoxifen Use | Higher likelihood of developing polyps4 |
Uterine polyps are sensitive to estrogen. Hormonal changes can directly influence their development and growth.
About 3-10% of women with infertility may have uterine polyps as an underlying cause4. This highlights the importance of early detection and treatment.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options for Uterine Polyps
Uterine polyps affect 10-24% of women undergoing medical procedures5. These growths can vary in size and health impact. Professional evaluation is key for proper care.
Understanding your diagnostic and treatment options is vital. Doctors use various methods to examine uterine polyps.
- Transvaginal ultrasound
- Hysterosonography
- Hysteroscopy
- Endometrial biopsy
A hysteroscopy allows doctors to see and remove polyps with minimal invasion. Most polyps are benign. However, some may contain precancerous changes6.
Treatment options vary based on individual factors. Your doctor will help choose the best approach for you.
- Watchful waiting for small, asymptomatic polyps
- Hormone therapy to manage symptoms
- Polypectomy for larger or problematic polyps
Understanding your specific case is key to determining the most appropriate treatment approach.
Hormone therapy can ease symptoms, but effects might not last6. Surgical removal through hysteroscopy is common and effective. Doctors often send removed polyps for lab tests6.
| Treatment Option | Recommended For |
|---|---|
| Watchful Waiting | Small, asymptomatic polyps |
| Hormone Therapy | Symptomatic cases with mild symptoms |
| Polypectomy | Larger polyps or potential cancer risk |
Polyps rarely come back after treatment. Yet, ongoing check-ups help ensure your reproductive health6. Your doctor can guide you through this process.
Conclusion
Uterine polyps are key to your reproductive health. These growths can affect your well-being, though most are non-cancerous. They may cause abnormal bleeding and occur in women of various ages78.
Irregular periods or fertility issues? See a doctor. Endometrial polyps can hinder fertility by disrupting the uterine lining. Your doctor can use ultrasound or hysteroscopy to check for these growths9.
Treatment options vary based on your needs. They range from observation to surgery like hysteroscopic polypectomy. Managing uterine polyps is easy with professional help9.
Many polyps show no symptoms. But early detection can prevent future health problems. Regular check-ups are crucial for your reproductive well-being8.
FAQ
What exactly are uterine polyps?
What symptoms might indicate I have uterine polyps?
Who is most at risk for developing uterine polyps?
How are uterine polyps diagnosed?
What treatment options are available for uterine polyps?
Can uterine polyps affect my fertility?
Are uterine polyps cancerous?
Source Links
- Uterine Polyps – https://www.columbiadoctors.org/treatments-conditions/uterine-polyps
- Uterine Polyps: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment – https://www.cancercenter.com/cancer-types/uterine-cancer/risk-factors/uterine-polyps
- Uterine polyps-Uterine polyps – Symptoms & causes – Mayo Clinic – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/uterine-polyps/symptoms-causes/syc-20378709
- Uterine Polyps – Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment – http://www.medparkhospital.com/en-US/disease-and-treatment/uterine-polyps
- Uterine Polyp Symptoms and Treatment – https://www.brighamandwomens.org/obgyn/resources/uterine-polyps
- Uterine polyps-Uterine polyps – Diagnosis & treatment – Mayo Clinic – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/uterine-polyps/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20378713
- Endometrial polyps – UpToDate – https://www.uptodate.com/contents/endometrial-polyps
- Endometrial polyps: Pathogenesis, sequelae and treatment – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6501471/
- Endometrial Polyps (Uterine Polyps): Symptoms & Treatment | Indira IVF – https://www.indiraivf.com/blog/endometrial-uterine-polyps-causes-symptoms-treatment