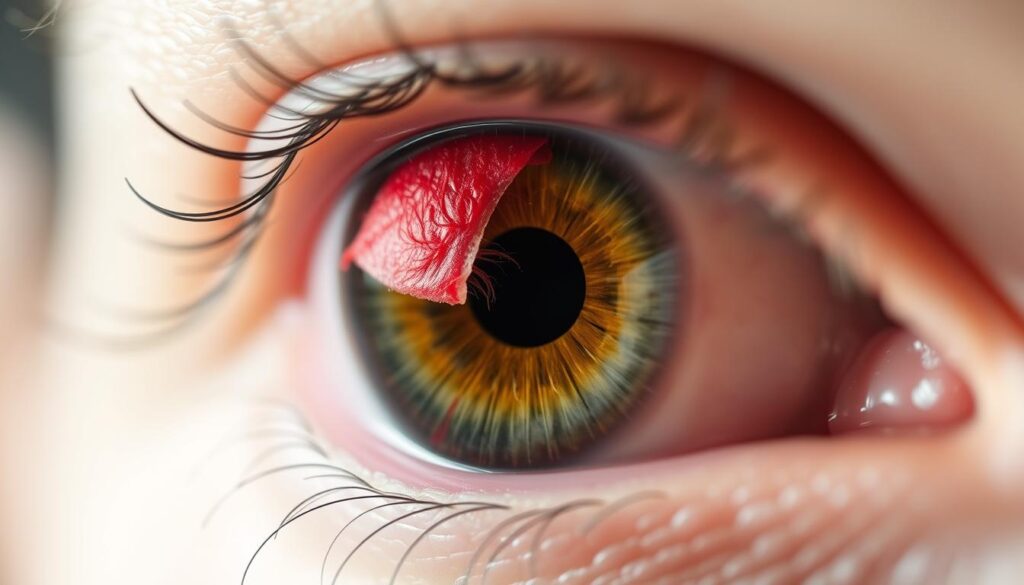
Uveitis is a serious eye inflammation that can harm your vision. It affects the uvea, the middle layer of eye tissue. Without treatment, this autoimmune disorder can lead to vision loss1.
Sudden eye inflammation can cause redness, pain, and blurred vision. Uveitis affects people of all ages, from kids to adults. It’s important to know about this condition2.
Uveitis can affect different parts of your eye. Anterior uveitis is the most common type. It usually occurs in young and middle-aged people21.
Intermediate uveitis affects the vitreous. It can cause blurred vision and floaters2. Knowing the risks and warning signs helps protect your vision.
Early detection prevents long-term problems. Spotting symptoms quickly can save your eyesight. Don’t ignore eye changes or discomfort.
Key Takeaways
- Uveitis is a serious eye inflammation affecting the uvea
- It can impact people of all ages
- Early detection is critical for preventing vision loss
- Multiple types of uveitis exist with different characteristics
- Symptoms include eye redness, pain, and vision changes
What is Uveitis and Its Common Symptoms
Uveitis is a serious eye condition that affects the uvea, the middle layer of your eye. It can harm your vision and eye health. Early detection and treatment are vital for managing this inflammatory disorder3.
Uveitis symptoms can appear quickly or slowly, making it hard to diagnose4. It usually affects one eye, but sometimes both eyes can be involved4.
Types of Uveitis
Eye specialists recognize several types of uveitis based on the area of inflammation:
- Anterior uveitis (iritis): Affects the front of the eye
- Intermediate uveitis: Impacts the retina and blood vessels behind the lens
- Posterior uveitis (choroiditis): Involves the retina or choroid
- Panuveitis: Affects all layers of the uvea3
Key Warning Signs
Knowing uveitis symptoms helps with early treatment. Look out for these warning signs:
- Persistent eye pain
- Intense eye redness
- Increased light sensitivity
- Blurred vision
- Dark floating spots (floaters)
- Decreased overall vision3
“Early detection and treatment of uveitis can prevent potential vision loss and complications,” says ophthalmology experts.
Other conditions can look like uveitis, such as glaucoma, conjunctivitis, and eye injuries4. If you have ongoing eye discomfort or vision changes, see an eye doctor right away4.
National Health Services3Ophthalmology Research Institute
Understanding the Causes and Risk Factors of Uveitis
Uveitis is a complex eye inflammation with various underlying causes. Recognizing risk factors helps in seeking timely medical attention5.
Uveitis origins are diverse and often hard to identify. Many cases link to autoimmune disorders that trigger eye inflammation5.
Key risk factors include:
- Systemic inflammatory conditions
- Infectious diseases
- Genetic predispositions
- Previous eye injury
Specific autoimmune disorders associated with uveitis include:
| Autoimmune Condition | Uveitis Connection |
|---|---|
| Rheumatoid Arthritis | High risk of eye inflammation |
| Crohn’s Disease | Potential trigger for uveitis |
| Multiple Sclerosis | Can cause inflammatory eye responses |
Infectious infections can trigger uveitis development. Cytomegalovirus, syphilis, and toxoplasmosis may lead to eye inflammation5.
Genetic factors can increase your uveitis risk. Some populations experience higher chances of developing this condition6.
Early detection and comprehensive medical evaluation are crucial in managing uveitis and preventing potential vision complications.
An eye injury or surgical procedure might also trigger uveitis. For persistent eye symptoms, consult an eye care professional5.
Conclusion
Uveitis is a serious eye health issue that requires immediate attention. It affects about one in a thousand people and can greatly impact your vision7. Quick detection and treatment are vital to avoid long-term vision problems8.
Managing uveitis needs a thorough approach. Eye doctors are crucial for diagnosing and treating various forms of this condition9. Treatment may involve eye drops, systemic drugs, or targeted therapies8.
Preserving vision starts with knowing your unique case. Different types of uveitis affect patients in various ways. Medical studies show how complex this eye condition can be.
Working with eye care experts helps create a plan just for you9. Your active role is crucial. Regular eye exams and following treatment advice can greatly improve your outlook.
Modern medicine offers hope for managing uveitis effectively. With the right approach, you can tackle this challenging eye condition head-on.
FAQ
What is uveitis?
What are the main types of uveitis?
What are the common symptoms of uveitis?
What causes uveitis?
Who is at risk for developing uveitis?
What complications can uveitis cause if left untreated?
How is uveitis diagnosed and treated?
When should I see a doctor about potential uveitis?
Source Links
- Uveitis – Symptoms, Causes & Treatment | Lions Eye Institute – https://www.lei.org.au/services/eye-health-information/uveitis/
- Uveitis – https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/uveitis
- Uveitis | Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment – https://www.cincinnatichildrens.org/health/u/uveitis
- Uveitis – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/uveitis/
- What is Uveitis? | Conditions & Treatments | UTSW Medical Center – https://utswmed.org/conditions-treatments/uveitis-eye-inflammation/
- Uveitis: Know the Risk Factors, Symptoms & Treatment Options – The Rheumatologist – https://www.the-rheumatologist.org/article/uveitis-know-the-risk-factors-symptoms-treatment-options/
- The Eyes Have It: A Rheumatologist’s View of Uveitis – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6160350/
- Uveitis – Symptoms, diagnosis and treatment – https://bestpractice.bmj.com/topics/en-gb/407
- Uveitis- a rare disease often associated with systemic diseases and infections- a systematic review of 2619 patients – Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases – https://ojrd.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1750-1172-7-57