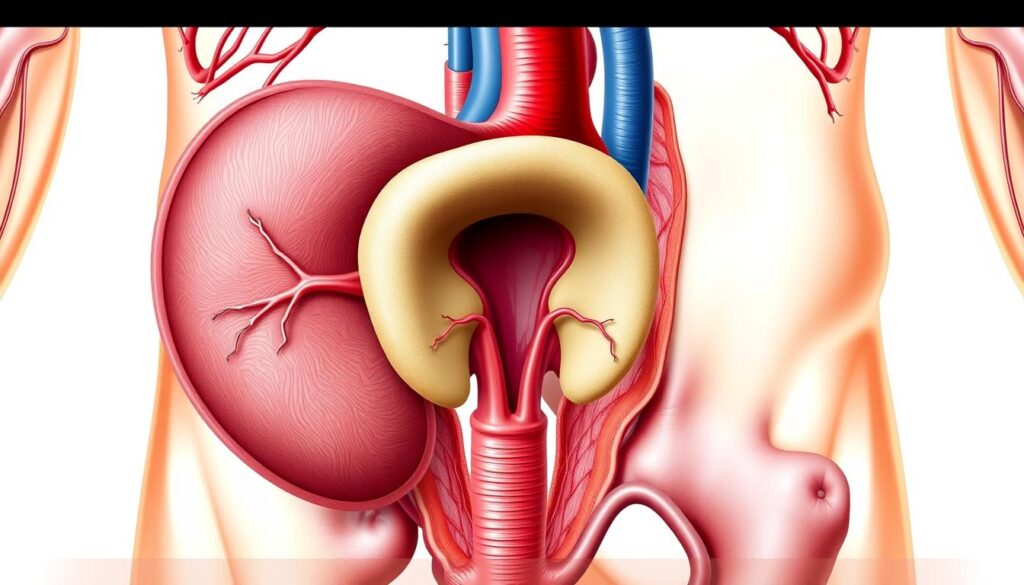
The prostate is vital for male wellness. This small gland plays a key role in reproduction1. It’s about the size of a ping-pong ball, located deep in the groin.
Your prostate changes as you age. It starts walnut-sized in your 20s. By 60, it might be as big as a lemon2. These changes can affect your health.
Prostate health is more than just size. It makes healthy semen for sperm transport and fertilization1. The gland produces important nutrients like PSA enzymes, zinc, citrate, and fructose1.
Key Takeaways
- The prostate is a small gland crucial for male reproductive health
- Prostate size changes naturally with age
- Regular check-ups are essential for monitoring prostate health
- Understanding prostate function helps prevent potential issues
- Lifestyle choices can positively impact prostate wellness
Understanding the Prostate Gland: Location and Function
The prostate is a crucial male reproductive organ. It’s small but mighty, playing a significant role in men’s health. Let’s explore its location, anatomy, and function.
Where Is Your Prostate Located?
Your prostate sits deep inside the groin. It’s between the base of the penis and the rectum. The gland surrounds the urethra, a passage for urine and semen3.
It’s about the size of a walnut. However, its size can change as you age3.
Prostate Zones and Anatomy
The prostate has several distinct zones. Each zone has unique characteristics:
- Peripheral Zone (PZ): Comprises 70% of the prostate and is the most common site for cancer development45
- Central Zone (CZ): Makes up about 20-25% of the gland and is relatively resistant to disease45
- Transition Zone (TZ): Represents approximately 5% of the prostate in young men but can grow significantly with age4
The Essential Role in Male Reproduction
Your prostate is vital for male reproductive health. It produces prostatic fluid, which makes up 20-30% of semen volume4. This fluid helps sperm travel and survive, boosting fertility.
The prostate contains an enzyme called 5-alpha-reductase. It converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a more potent hormone4. DHT is responsible for male characteristics.
“The prostate might be small, but its impact on male reproductive health is immense.”
An adult prostate typically weighs about 11 grams. However, it can range from 7 to 16 grams5. Hormones like testosterone influence its size and function throughout life.
Knowing your prostate’s anatomy and function is important. It helps you take steps to maintain your reproductive health.
Common Prostate Problems and Warning Signs
Prostate health matters for men of all ages. Your prostate can develop conditions affecting urinary and reproductive function. Prostate symptoms can signal potential underlying issues.
Prostate cancer affects one in seven men. The risk increases significantly after age 506. About 50 percent of men ages 51-60 experience BPH.
This rises to 80 percent for men over 707. Prostatitis is the most common issue for men under 508.
| Condition | Key Characteristics | Age Group |
|---|---|---|
| BPH | Non-cancerous prostate enlargement | 50+ years |
| Prostatitis | Inflammation or infection | All ages |
| Prostate Cancer | Abnormal cell growth | 50+ years |
Warning signs of prostate problems include:
- Frequent urination
- Difficulty starting urination
- Weak urine stream
- Blood in urine or semen
- Pelvic or lower back pain
“Early detection is key to managing prostate health effectively”
Early screening through digital rectal exams and PSA tests can help detect potential issues. Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are crucial for maintaining prostate health6.
Conclusion
Proactive care is key to your prostate health journey. Understanding risks and taking preventive steps can help manage potential health challenges. Prostate cancer affects about 1 in 8 males during their lifetime9.
Regular screening and awareness are vital for men’s well-being. PSA tests offer complex insights into potential health risks. However, research shows that benefits don’t always outweigh potential harms10.
Discuss personalized screening strategies with your doctor. Consider your individual risk factors and medical recommendations. Optimal prostate health involves more than just medical tests.
Regular exercise and a balanced diet can greatly impact your prostate care. Prostate problems become more common after age 50. Prostatitis affects about 10-15% of males in the United States9.
Stay informed and listen to your body. Prioritize your health through consistent check-ups and healthy lifestyle choices. Knowledge is your most powerful tool in managing prostate health.
Stay educated and proactive. Work closely with your healthcare provider. This approach will help you navigate challenges and maintain overall well-being.
FAQ
What exactly is the prostate gland?
What are the most common prostate health issues?
What symptoms should I watch out for?
Who is at highest risk for prostate problems?
How can I maintain good prostate health?
What diagnostic tests are used for prostate issues?
What treatment options are available for prostate conditions?
At what age should I start prostate screenings?
Source Links
- Prostate Gland – https://www.pcf.org/about-prostate-cancer/what-is-prostate-cancer/prostate-gland/
- Understanding Prostate Changes – https://www.cancer.gov/types/prostate/understanding-prostate-changes
- What is prostate cancer? – https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/prostate-cancer/about
- What is prostate, Anatomy, Functions and Diseases – https://dreminozbek.com/en/what-is-prostate-anatomy-functions-and-diseases/
- Prostate – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prostate
- Prostate cancer – Symptoms and causes – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/prostate-cancer/symptoms-causes/syc-20353087
- 6 Signs of Prostate Problems and What They Could Mean – https://www.hackensackmeridianhealth.org/en/healthu/2023/05/25/6-signs-of-prostate-problems-and-what-they-could-mean
- Prostate Problems – NIDDK – https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/urologic-diseases/prostate-problems
- Prostate: Functions, diseases, structure, and tests – https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/319859
- Conclusion – Prostate cancer screening with a PSA test – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK558469/