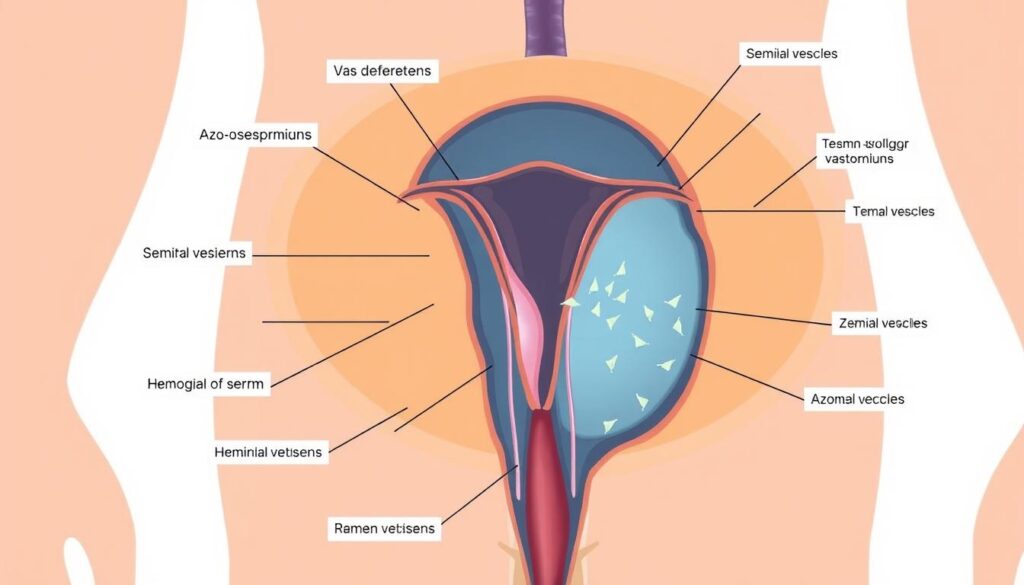
Azoospermia is a condition where semen contains no sperm. It affects 1% of men and 10% of infertile men12. This can be a tough challenge for couples trying to start a family.
The causes of azoospermia are varied. Pre-testicular issues include poor nutrition, certain medications, and hormonal imbalances1. Pituitary disorders or low testosterone levels can also lead to this condition1.
Testicular problems can contribute to azoospermia too. Genetic conditions like Klinefelter’s syndrome can impair sperm production1. Undescended testicles and Sertoli-cell-only syndrome are other potential causes1.
External factors may also play a role. These include infections, chemical exposures, and cancer treatments1. Each case is unique and requires careful evaluation.
Hope exists through modern medical techniques. Advanced reproductive technologies can help many couples1. Testicular sperm extraction (TESE) and intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) are promising options.
Key Takeaways
- Azoospermia affects 1% of men in the general population
- Multiple factors can cause absence of sperm in semen
- Genetic and environmental factors play significant roles
- Advanced medical techniques can help some couples conceive
- Professional medical evaluation is crucial for understanding the condition
Understanding Erectile Dysfunction and Its Impact
Erectile dysfunction (ED) impacts millions of men worldwide. It challenges both physical and emotional well-being. ED affects personal confidence and relationship dynamics.
ED is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection for satisfactory sex. At least 30 million American men struggle with this condition regularly3. The prevalence increases with age, making it a significant health concern.
Definition and Key Characteristics
ED isn’t a single condition. It’s a complex mix of physical and psychological factors. Causes range from heart issues to mental health challenges.
Prevalence and Risk Factors
- 18.4% of men in the U.S. have experienced erectile dysfunction4
- Smoking increases ED risk by 51%3
- Diabetes significantly impacts erectile function
- Mental health conditions like depression heighten ED risk by 40%3
Physical vs. Psychological Causes
| Physical Causes | Psychological Causes |
|---|---|
| Cardiovascular diseases | Depression |
| Diabetes | Anxiety |
| Hormonal imbalances | Relationship stress |
ED treatments include medications like Viagra and Cialis. Lifestyle changes and addressing underlying health issues can help4. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and mental health support can improve symptoms.
Understanding ED is the first step towards effective management and improved quality of life.
Talking to healthcare professionals can help manage ED. They can create a personalized plan to restore your sexual health.
Common Physical and Psychological Causes of ED
Erectile dysfunction (ED) has many root causes. These range from physical health issues to mental challenges. Finding the cause is key to effective treatment5.
Vascular and Cardiovascular Challenges
Heart health greatly affects ED solutions. Heart disease, clogged arteries, and high blood pressure can hurt sexual function5. Diabetes is especially tough, making ED two to three times more likely5.
Hormonal Imbalances
Testosterone levels and hormone changes can affect sexual performance. Lifestyle changes for ED often target these hormone issues. Fixing them can help restore healthy erections.
Neurological Conditions
Brain and nerve disorders like multiple sclerosis can cause ED. These conditions disrupt nerve signals needed for sexual response. This makes it hard to get and keep an erection.
Lifestyle Factors and Habits
Daily habits can greatly influence ED. Key factors include:
- Smoking
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Lack of physical activity
- Being overweight5
“Your sexual health is deeply connected to your overall physical and mental well-being.”
Mental factors also play a big role in ED. Anxiety, depression, and stress can hurt sexual performance6.
A medical expert can help create ED solutions just for you6. They’ll address both physical and mental causes.
Diagnosing and Treating Erectile Dysfunction
Diagnosing erectile dysfunction (ED) starts with a thorough medical history and physical exam. Your doctor will look for potential underlying causes. Blood tests can reveal conditions like diabetes or hormonal imbalances that might cause ED7.
Specialized tests help pinpoint ED’s root cause. Doppler ultrasound checks blood flow in the penis. Nocturnal erection tests evaluate nighttime erectile function7.
ED treatment options are varied and effective. About 70% of men respond well to oral medications like Viagra and Cialis8. Self-injection therapy with Alprostadil has an 85% success rate for those who don’t respond to pills8.
Vacuum erection devices and penile implants offer additional solutions. Proper device usage helps 75% of men achieve successful erections8.
Your lifestyle greatly impacts ED management. Regular exercise and a healthy diet can improve erections as effectively as medications9. Quitting smoking and reducing alcohol intake can boost your sexual health.
Managing stress is also key to enhancing overall well-being. A slimmer waistline can contribute to better erectile function. These lifestyle changes can make a significant difference in managing ED.
FAQ
What exactly is erectile dysfunction (ED)?
How common is erectile dysfunction?
What are the main causes of erectile dysfunction?
Can lifestyle changes help with erectile dysfunction?
What treatment options are available for erectile dysfunction?
Is erectile dysfunction a sign of a more serious health problem?
Can psychological factors really cause erectile dysfunction?
At what age should I be concerned about erectile dysfunction?
Source Links
- Azoospermia – https://www.med.unc.edu/urology/patientcare/adult-non-cancer/male-fertility/azoospermia/
- Azoospermia – https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/azoospermia
- The Basics of Erectile Dysfunction – https://www.webmd.com/erectile-dysfunction/understanding-erectile-dysfunction-basics
- Understanding Erectile Dysfunction – https://healthcare.utah.edu/the-scope/health-library/all/2024/03/understanding-erectile-dysfunction
- Symptoms & Causes of Erectile Dysfunction – NIDDK – https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/urologic-diseases/erectile-dysfunction/symptoms-causes
- Is Erectile Dysfunction Psychological? – https://www.healthline.com/health/erectile-dysfunction/psychological
- Diagnosis of Erectile Dysfunction – NIDDK – https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/urologic-diseases/erectile-dysfunction/diagnosis
- Erectile Dysfunction (ED): Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment – https://www.urologyhealth.org/urology-a-z/e/erectile-dysfunction-(ed)
- Erectile dysfunction – Diagnosis and treatment – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/erectile-dysfunction/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20355782