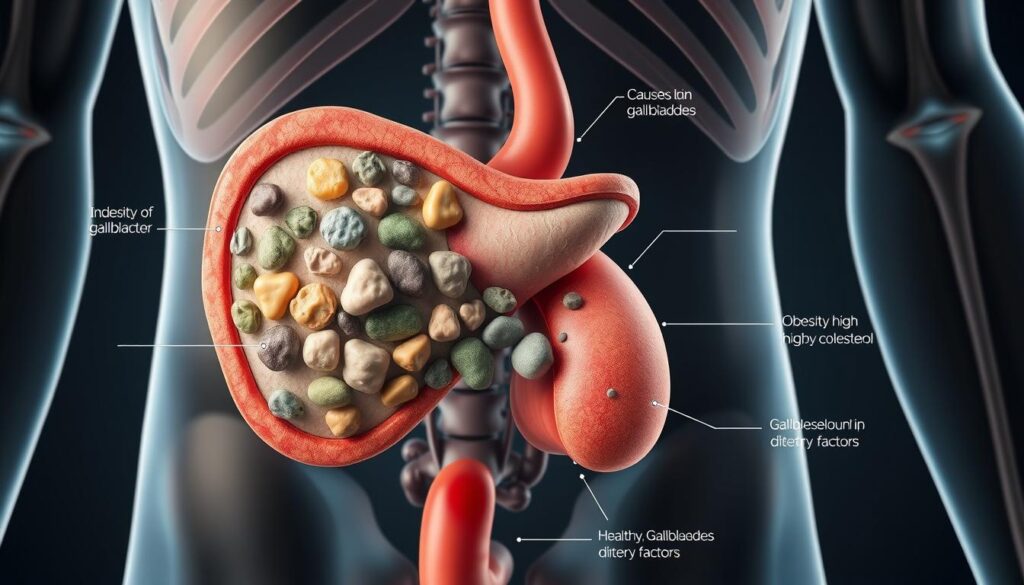
Gallstones are hard deposits in your gallbladder that can cause health issues. They range from tiny specks to golf ball-sized formations1. Knowing about gallstones is important because they can lead to serious problems if ignored.
Women face a higher risk of gallstones than men2. Your chances of getting them increase after 40. Lifestyle and genes also play a role12.
Cholesterol gallstones are the most common type. Being overweight, inactive, and eating poorly can raise your risk of these stones12.
Key Takeaways
- Gallstones can vary dramatically in size
- Women have higher risk of developing gallstones
- Age and lifestyle significantly impact gallstone formation
- Cholesterol gallstones are most common
- Some gallstones may require medical intervention
What Are Gallstones and How Do They Form?
Gallstones are tiny, solid deposits that form in your gallbladder. They can cause health issues for many people. These small formations can greatly affect your digestive system and overall health3.
Gallstones have unique traits. They vary in size, from tiny sand-like specks to large golf ball-sized masses4.
Types of Gallstones
Your gallbladder can develop two main types of stones:
- Cholesterol stones: These make up about 75% of gallstones. They’re yellowish-green and form when bile has too much cholesterol3.
- Pigment stones: Smaller and darker, these form when bile has high levels of bilirubin.
Key Factors Contributing to Gallstone Formation
Several factors influence gallstone development:
- Genetic predisposition3
- Imbalances in bile composition
- Impaired gallbladder function
- Demographic characteristics
Your risk increases with certain conditions:
- Obesity
- Rapid weight loss
- Diabetes
- High triglyceride levels
Interestingly, cholesterol stones are not directly related to blood cholesterol levels, contrary to popular belief4.
Knowing how your gallbladder works can help you manage potential risks. Not all gallstones cause symptoms. Learning about their formation can guide your prevention strategies5.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Gallstones
Gallstones can be sneaky. Many people have them without knowing it. But when symptoms show up, they need attention.
Knowing the warning signs helps protect your health. It also helps you get medical help quickly.
Common Symptoms to Watch For
Gallstones often show specific signs. You might feel:
- Sudden, intense biliary colic in the upper right abdomen
- Abdominal pain that can radiate to your back or right shoulder
- Persistent nausea and vomiting
- Pain lasting from several minutes to hours
About 20 million Americans have gallstones. Doctors diagnose about 1 million new cases each year6.
Only 20% of people with gallstones get symptoms within twenty years6.
Critical Warning Signs
“Not all gallstone symptoms are created equal. Some require immediate medical attention.”
Get emergency medical care if you have:
- Severe abdominal pain that doesn’t go away
- Yellowing of skin or eyes (jaundice)
- High fever with chills
- Persistent nausea and vomiting
Eating can trigger gallstone pain. It causes gallbladder contractions7.
Women are at higher risk. They’re three times more likely to get gallstones than men7.
When to Get Checked
Don’t ignore repeated symptoms. See a doctor if you have frequent stomach pain.
Finding gallstones early can prevent problems. These include acute inflammation or bacterial infections7.
Exploring Treatment Options for Gallstones
Gallstones can be treated in several ways. Your symptoms, health, and medical history determine the best option for you.
Gallstone management includes lifestyle changes, medical treatments, and surgery. Each approach targets different aspects of the condition.
Dietary and Lifestyle Modifications
Simple changes can help manage gallstones. These include eating a balanced diet and exercising regularly.
- Maintain a balanced diet low in saturated fats
- Achieve and maintain a healthy body weight
- Exercise regularly
- Stay hydrated
Medical Treatments and Medications
Bile acid medications can help dissolve smaller gallstones. One example is ursodeoxycholic acid8. These treatments may take up to 2 years and aren’t always effective8.
Surgical Procedures for Gallstone Removal
Surgery becomes necessary when other treatments don’t work. Here are some options:
- Laparoscopic cholecystectomy: This minimally invasive surgery takes 60-90 minutes. Recovery usually lasts about 10 days8.
- ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography): This procedure removes stones from bile ducts in about 30 minutes8.
- Lithotripsy: This technique uses shock waves to break up gallstones.
“The most appropriate treatment depends on individual patient factors and should be discussed thoroughly with a healthcare professional.”
Your doctor will help choose the best treatment for your gallstones9. They’ll consider your unique situation to create a plan.
Preventing Gallstones: Tips for a Healthier Lifestyle
Gallstones affect up to 15% of Americans during their lifetime10. To protect yourself, focus on weight management, smart eating, and regular exercise.
Eat more fiber to ward off gallstones. Aim for five daily servings of fruits and veggies. Include whole grains and lean proteins in your meals10.
Cut down on saturated fats. Instead, choose foods rich in omega-3s like salmon and walnuts10. A balanced diet can significantly lower your risk of gallstones.
Exercise regularly to maintain a healthy weight. This can greatly reduce your chances of developing gallstones11. Aim for 150 minutes of moderate activity each week.
Losing just 10% of your body weight over six months can make a big difference10. It substantially lowers your risk of gallstone formation.
Get regular check-ups, especially if you’re at higher risk. This includes people over 40, women, and those with a family history11. Talk to your doctor about prevention strategies.
Stay informed and take action. By being proactive, you can minimize your gallstone risk and boost your overall health.
FAQ
What exactly are gallstones?
Who is most at risk of developing gallstones?
What symptoms should I watch out for?
How are gallstones typically treated?
Can I prevent gallstones?
Are gallstones dangerous?
Source Links
- Gallstones-Gallstones – Symptoms & causes – Mayo Clinic – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gallstones/symptoms-causes/syc-20354214
- Gallstones – https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/gallstones
- Definition & Facts for Gallstones – NIDDK – https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/gallstones/definition-facts
- Gallstones – https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/diseases-conditions/gallstones
- Gallstones – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/gallstones/
- Symptoms of Gallstones | Rhode Island Hospital Patient Guide – https://www.brownhealth.org/centers-services/general-and-gastrointestinal-surgery/about-gallstones/symptoms-gallstones
- What You Need To Know About Gallstones – https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/7313-gallstones
- Gallstones – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/gallstones/treatment/
- Gallstones-Gallstones – Diagnosis & treatment – Mayo Clinic – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gallstones/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20354220
- Anti-gallstones Diet: What Foods to Eat and What to Avoid – https://health.umms.org/2022/09/30/anti-gallstones-diet/
- Understanding and Preventing Gallstones | Gastro MD – https://gastro-md.com/2023/11/22/understanding-and-preventing-gallstones-a-comprehensive-guide/