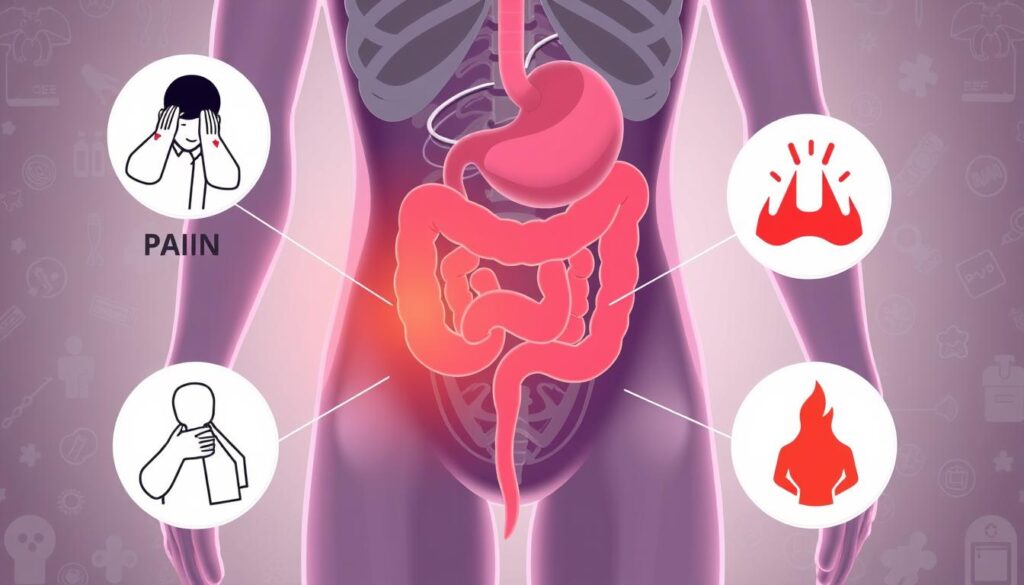
Appendicitis is a serious medical issue that can greatly impact your health. It occurs when your appendix becomes inflamed, causing painful and potentially dangerous symptoms. Immediate medical care is crucial.
Appendicitis mostly affects people aged 10 to 30. Men have a slightly higher risk of developing this condition.
Recognizing appendicitis symptoms can help you get prompt medical help. Common signs include sudden stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite. A low-grade fever may also occur.
Up to 40% of patients might develop a fever. This shows the body’s immune response to the infection1.
Untreated appendicitis can lead to severe problems. A burst appendix can spread infection throughout your belly. This may cause life-threatening peritonitis2.
In such cases, doctors might need to drain an abscess. They may also surgically remove the appendix2.
Key Takeaways
- Appendicitis primarily affects people aged 10-30
- Symptoms include abdominal pain, nausea, and fever
- Prompt medical attention is crucial to prevent complications
- Men have a slightly higher risk of developing appendicitis
- Surgical intervention is often necessary
What is Appendicitis and Why Does it Happen?
Appendicitis is a serious medical condition affecting people of all ages. It involves the small, finger-shaped appendix connected to your large intestine. Early detection and treatment are crucial for managing this potentially dangerous issue.
Understanding the Appendix’s Role
The appendix is a tiny pouch in the lower right side of your abdomen. Its exact function remains a bit of a mystery. However, researchers think it might support your immune system and store helpful gut bacteria.
Common Causes of Appendix Inflammation
Appendix inflammation often happens when the organ becomes blocked. This blockage can lead to serious complications. Several factors can trigger this condition:
- Hardened stool (fecaliths) blocking the appendix opening
- Enlarged lymphoid tissues
- Intestinal infections
- Parasitic invasions
Risk Factors for Developing Appendicitis
Your chance of getting appendicitis depends on various personal traits. Some key risk factors include:
| Risk Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Age | Most common between 10-30 years old3 |
| Gender | Slightly higher risk for males3 |
| Family History | Increased potential for developing condition3 |
“Understanding your body’s signals can be the key to preventing serious health complications.”
Pay attention to symptoms like abdominal tenderness, constipation, and diarrhea. These signs shouldn’t be ignored. If you have ongoing discomfort, talk to a doctor right away4.
Appendicitis needs immediate medical care5. Knowing the early signs could save your life. Don’t hesitate to seek help if you suspect something’s wrong.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Appendicitis
Appendicitis can hit fast, catching many off guard. Knowing its symptoms could save lives. Quick action is key for timely medical help.
Early Signs You Should Not Ignore
Your body sends clear warnings when appendicitis starts. Common early symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain that starts near the navel and shifts to the lower right abdomen6
- Sudden loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Low-grade fever
Severe Symptoms: When to Seek Help
Some symptoms need immediate medical care. Watch for these critical warning signs:
- Intense abdominal pain that worsens with movement
- High fever reaching 104°F (40°C)7
- Severe swelling in the belly
- Inability to pass gas
“Appendicitis is a medical emergency that requires prompt treatment to prevent serious complications.”8
Symptoms in Different Age Groups
Appendicitis looks different across age ranges. In the U.S., 1 in 20 people will experience appendicitis during their lifetime6. Here’s what to expect:
| Age Group | Typical Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Children (5-20 years) | Classic abdominal pain, fever, loss of appetite7 |
| Adults (20-30 years) | Sharp right-sided pain, nausea, vomiting8 |
| Pregnant Women | Atypical symptoms like acid reflux, pelvic pain6 |
Spotting appendicitis early is vital. Quick medical care can make a big difference. Don’t ignore the signs your body gives you.
Diagnosing Appendicitis: What to Expect
Persistent abdominal pain may signal appendicitis. Understanding the diagnosis process can help you navigate your medical journey confidently. Let’s explore the steps to identify appendix inflammation.
Your medical team will conduct a thorough evaluation to diagnose appendicitis. This process involves multiple approaches through careful medical investigation. The goal is to ensure an accurate diagnosis.
Medical History and Physical Examination
Your healthcare provider will perform a detailed physical exam. They’ll assess your abdominal tenderness, focusing on areas that might indicate appendicitis9.
Key examination techniques include:
- Checking for localized pain
- Evaluating muscle stiffness
- Assessing potential signs of constipation or diarrhea
Diagnostic Tests and Imaging Techniques
To confirm appendicitis, your doctor will likely order several diagnostic tests10:
| Test Type | Purpose | Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Blood Tests | Check for infection markers | High white blood cell count |
| Urine Tests | Rule out other conditions | Eliminate urinary tract infections |
| Imaging Tests | Visualize appendix | CT scans, ultrasounds |
Preparing for Your Appointment
Before your consultation, document your symptoms. Be ready to describe:
- When pain started
- Pain location and intensity
- Any accompanying symptoms
- Recent medical history
“Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial in managing appendicitis effectively.”
These diagnostic steps might seem daunting. However, they’re designed to provide the most accurate assessment of your condition10.
Treatment Options for Appendicitis
Appendicitis treatment offers several paths. Surgical removal remains the main approach. Modern techniques provide different strategies for this painful condition medical research explores new treatments11.
Laparoscopic surgery is now preferred for appendectomy. It offers smaller incisions and faster recovery. Surgeons perform it under general anesthesia with minimal complications11.
For mild cases, antibiotics might be an option. However, surgery remains the standard approach12.
Recovery time depends on the surgery type. Laparoscopic surgery needs 3-5 days of reduced activity. Open surgery might require 10-14 days11.
Pain management is crucial for healing. Acetaminophen and ibuprofen often help13. After discharge, monitor your incision and avoid heavy lifting13.
Recent studies show promising results for antibiotic treatment. After three months, 70% of patients avoided surgery12. This highlights the need for personalized medical advice12.
FAQ
What exactly is appendicitis?
Who is most likely to develop appendicitis?
What are the early warning signs of appendicitis?
How is appendicitis diagnosed?
What is the standard treatment for appendicitis?
How long does recovery take after an appendectomy?
What complications can occur if appendicitis is not treated?
Are symptoms different for children and adults?
Can appendicitis be prevented?
Source Links
- Appendicitis: Signs, Symptoms and Treatment – https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/8095-appendicitis
- Appendicitis – Symptoms and causes – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/appendicitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20369543
- Appendicitis: Symptoms & Causes | NewYork-Presbyterian – https://www.nyp.org/digestive/appendicitis
- Acute Appendicitis: Symptoms, Causes and Treatment | Ada – https://ada.com/conditions/acute-appendicitis/
- Appendicitis in Children – https://www.chop.edu/conditions-diseases/appendicitis
- Appendicitis – https://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/digestive-diseases-appendicitis
- Appendicitis In Kids and Teens (for Parents) – https://kidshealth.org/en/parents/appendicitis.html
- Appendicitis – https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/appendicitis
- Appendicitis – Diagnosis and treatment – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/appendicitis/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20369549
- Appendicitis Tests: MedlinePlus Medical Test – https://medlineplus.gov/lab-tests/appendicitis-tests/
- Treatment for Appendicitis – NIDDK – https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/appendicitis/treatment
- Treating appendicitis with antibiotics instead of surgery may be good option for some, but not all, patients – https://news.vumc.org/2020/10/05/treating-appendicitis-with-antibiotics-instead-of-surgery-may-be-good-option-for-some-but-not-all-patients/
- Appendicitis | Signs, Diagnosis & Treatment – https://www.cincinnatichildrens.org/health/a/appendicitis