The human reproductive system is a complex network of organs. It plays crucial roles in human biology and goes beyond simple functions. Understanding these intimate parts can help you appreciate your body’s incredible design.
The reproductive system is more than just organs. It’s a sophisticated mechanism for human continuation and sexual experiences. Each component serves a unique purpose in our biological design1.
Understanding these structures helps demystify sexual health and personal anatomy. Multiple organs work together seamlessly in the reproductive system. Your body’s design includes sensitive areas like the clitoris.
The clitoris contains thousands of nerve endings. It plays a critical role in sexual pleasure21.
Key Takeaways
- The reproductive system is a complex network of interconnected organs
- Each reproductive structure serves unique biological functions
- Sexual anatomy varies significantly between individuals
- Reproductive health involves understanding your body’s intricate design
- Nerve endings play crucial roles in sexual sensation and pleasure
Understanding the Anatomy of the Penis
The male reproductive system is a complex network of structures crucial for reproductive health. Your penis is a sophisticated biological system with intricate functions. It’s more than just an external organ.
Knowing your body’s anatomy helps maintain better reproductive health. It also aids in addressing potential concerns early. Let’s explore the fascinating world of penile structures and functions.
External Structures of the Penis
The penis contains soft tissue, muscles, and complex blood vessel networks. Its main functions are sexual intercourse and urination. Penises vary in length, girth, and appearance, but share common features.
- Shaft: The main body of the penis
- Glans: The tip of the penis
- Urethra: Internal channel for urine and semen
The average flaccid penis size is about 3.5 inches. When erect, it’s slightly over 5 inches3.
Internal Structures and Functions
Inside, your penis has critical components supporting reproductive system functions. The urethra channels both urine and semen during ejaculation4.
| Structure | Function |
|---|---|
| Testes | Produce sperm and testosterone4 |
| Prostate Gland | Secretes alkaline fluid for semen4 |
| Seminal Vesicles | Contribute up to 80% of ejaculatory fluid3 |
Common Concerns Regarding Penile Health
Maintaining reproductive health requires awareness of potential conditions. Some common concerns include:
- Erectile dysfunction
- Sexually transmitted infections
- Structural abnormalities
Regular check-ups and understanding your body are key to maintaining optimal reproductive health.
Stay informed and proactive to ensure the well-being of your male reproductive system5. Knowledge is power when it comes to your health.
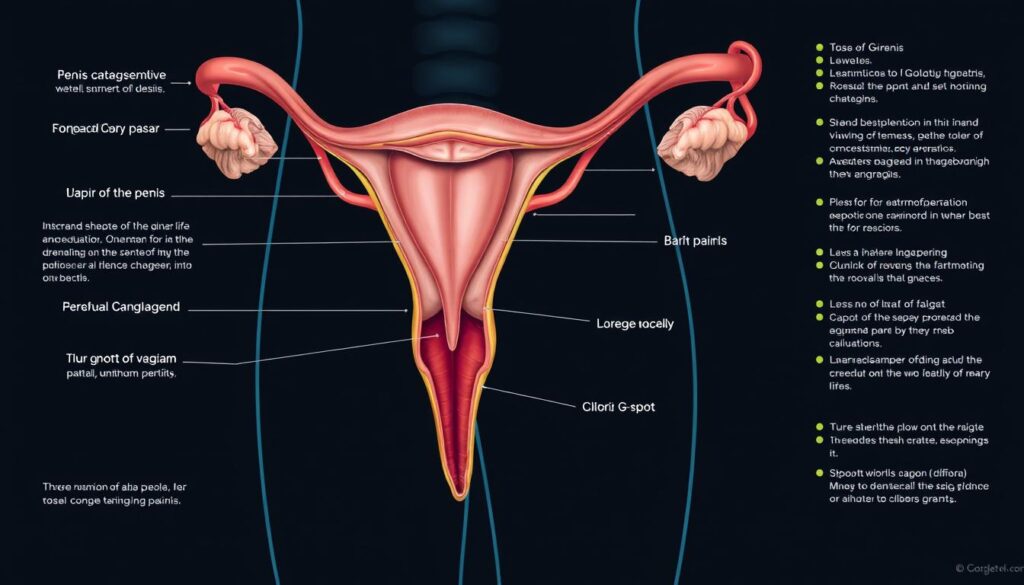
Exploring the Anatomy of the Vagina
The female reproductive system is vital for health. The vagina is key in this complex biological network. It serves many essential functions throughout a woman’s life.
The Vaginal Canal and Its Structural Significance
Your vaginal canal is a remarkable muscular tube. It can stretch up to 200% due to its incredible elasticity6. The average width is 2.5 to 3.0 inches, with a length of 3 to 4 inches6.
This flexible structure enables critical reproductive functions. These include menstrual flow, sexual intercourse, and childbirth.
Components of the Vulva
The external female genitalia, known as the vulva, has several important structures:
- Labia (outer and inner lips)
- Clitoris with thousands of nerve endings7
- Vaginal opening
- Bartholin’s glands that provide lubrication7
Transformations Throughout a Woman’s Life
Your reproductive system anatomy changes during different life stages. Hormonal shifts influence these transformations. They occur during:
- Puberty
- Menstrual cycles
- Pregnancy
- Menopause
Each stage brings unique physiological adaptations. These highlight the complexity of female reproductive health.
The body’s ability to adapt and transform is a testament to the remarkable design of the female reproductive system.
| Reproductive Organ | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Ovaries | Produce eggs and hormones, approximately grape-sized6 |
| Fallopian Tubes | 10-12 centimeters long, transport eggs6 |
| Uterus | Pear-shaped organ between bladder and rectum6 |
The Clitoris and G-Spot: Key Areas of Pleasure
Female sexual anatomy is complex and fascinating. The clitoris and G-spot are crucial erogenous zones8. They offer unique sensations and potential for intense experiences.
Anatomy of the Clitoris
The clitoris is more than meets the eye. It extends internally with a network of erectile tissue and nerves8. The glans has about 8,000 nerve endings, making it incredibly sensitive.
Located at the top of the vulva, the clitoris is surprisingly large. Research shows it’s about 3 1/2 to 4 1/4 inches long8.
Understanding the G-Spot
The G-spot is still debated in scientific circles. Some research suggests it’s related to the internal clitoris structure9. It’s located 2-3 inches inside the vagina and can trigger intense sexual responses9.
About 18-25% of women report G-spot orgasms. However, 70-80% need clitoral stimulation to climax10.
How They Contribute to Sexual Arousal
Understanding these sensitive areas is key to reproductive health. Many women enjoy combining G-spot and clitoral stimulation. Studies show this can lead to more intense orgasms10.
Explore your body and learn about potential reproductive issues. This can help you develop a healthier relationship with your sexuality through comprehensive sexual health education.
FAQ
What is the primary function of the human reproductive system?
How does the male reproductive system work?
What are the key components of the female reproductive system?
What is the clitoris, and why is it important?
What is the G-spot, and how does it relate to sexual pleasure?
What are some common health concerns in the reproductive system?
How do hormones influence the reproductive system?
How does the reproductive system change throughout a person’s life?
Source Links
- Everything you should know about the clitoris – https://helloclue.com/articles/cycle-a-z/what-is-the-clitoris
- Clitoris: Anatomy, Location, Purpose & Conditions – https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/22823-clitoris
- Male Reproductive System – https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/9117-male-reproductive-system
- Overview of the Male Anatomy – https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/overview-of-the-male-anatomy
- Penis anatomy: Functions and common conditions – https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/penis-anatomy
- The Female Anatomy 101: An Intimate Look At Our Bodies – https://axiawh.com/resources/the-female-anatomy-101/
- Female Sexual Anatomy | Vulva, Vagina and Breasts – https://www.plannedparenthood.org/learn/health-and-wellness/sexual-and-reproductive-anatomy/what-are-parts-female-sexual-anatomy
- Anatomy, Function, Care and Conditions of the Clitoris – https://www.webmd.com/women/anatomy-function-care-conditions-clitoris
- The G-Spot: How to Find It (Diagram) & How To Stimulate It – https://www.naturalcycles.com/cyclematters/g-spot
- G Spot and Clitoris – https://www.vaginismus-center.com/en/g-spot-and-clitoris