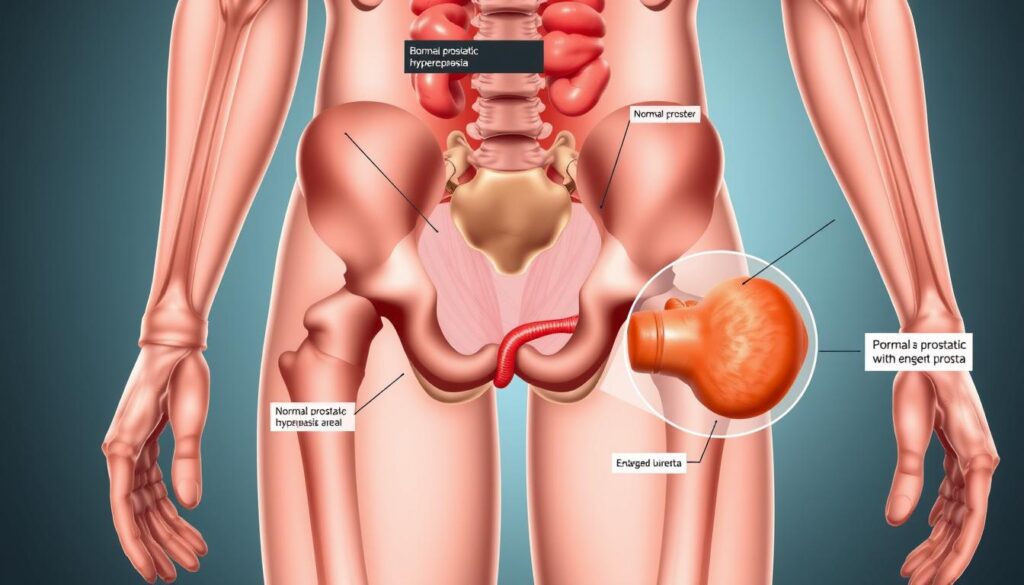
Prostate enlargement can disrupt your daily life with bothersome urinary symptoms. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is common in aging men. It affects the prostate gland and impacts urinary function1.
BPH rarely causes issues before 40. However, lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) become more likely after this age1. Your prostate health is influenced by genetics, lifestyle, and overall well-being.
Family history is a key factor in prostate issues1. Conditions like diabetes can increase your BPH risk1. Maintaining a healthy weight and exercising regularly can help reduce these risks1.
BPH is a non-cancerous prostate enlargement that can cause uncomfortable urinary symptoms. While there’s no cure, various treatments can effectively manage and ease these symptoms.
Key Takeaways
- BPH is a common condition affecting men as they age
- Symptoms rarely appear before age 40
- Family history and lifestyle impact prostate health
- Obesity can increase BPH risk
- Multiple treatment options are available
Understanding Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is a common condition affecting older men. It causes the prostate gland to enlarge, leading to urinary issues. Knowing about BPH can help you manage your health better.
What is BPH?
BPH is a non-cancerous growth of the prostate gland. As the prostate grows, it can squeeze or block the urethra. This can make urination difficult.
BPH is a natural part of aging in men. It doesn’t mean you have cancer.
How Common is BPH?
BPH becomes more common as men age. Experts estimate that BPH affects:
- 5-6% of men ages 40-64
- 29-33% of men ages 65 and older2
Risk Factors for Developing BPH
Several factors can increase your chances of getting BPH:
- Age (40 and older)
- Family history
- Chronic health conditions
| Risk Factor | Impact on BPH |
|---|---|
| Heart disease | Increases risk |
| Type 2 diabetes | Elevates probability |
| Obesity | Contributes to development |
| Physical inactivity | Can worsen symptoms |
Knowing these risk factors can help you protect your prostate health. Talk to your doctor about treatments like alpha-blockers or 5-alpha reductase inhibitors2. These can help manage BPH symptoms.
“Knowledge is the first step in managing your prostate health effectively.”
Recognizing the Symptoms of BPH
Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) can signal Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH). Recognizing these signs early helps identify potential prostate issues. Many men face urinary symptoms that may require medical attention.
BPH impacts many men as they age. By 55, one in four men experience symptoms. This number rises sharply in later years.
At 80, nearly 90% of men report some BPH-related urinary symptoms3. These symptoms can significantly affect daily life and comfort.
Urinary Frequency and Urgency
A common BPH symptom is an increased need to urinate. You might feel a sudden urge to use the bathroom. Frequent trips throughout the day become normal.
- Feeling a sudden, urgent need to urinate
- Urinating more frequently throughout the day
- Experiencing difficulty controlling bladder urges
Difficulty Starting or Stopping Urination
BPH can make urination challenging. Obstructive symptoms often cause trouble.
- Trouble initiating urination
- Weak urine stream
- Intermittent urine flow
- Straining to urinate
Nocturia: Waking at Night to Urinate
Nighttime urination, or nocturia, is another key BPH sign. You may wake up multiple times to use the bathroom. This disrupts your sleep and affects your rest.
“Understanding your body’s signals is the first step toward managing BPH effectively.”
By age 80, 20% to 30% of men need treatment for severe BPH symptoms4. If these issues persist or impact your life, consult a doctor.
| BPH Symptom Type | Common Manifestations | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency/Urgency | Frequent urination | Disrupted daily activities |
| Urination Difficulties | Weak stream, straining | Incomplete bladder emptying |
| Nocturia | Nighttime bathroom visits | Sleep disruption |
Causes and Mechanisms Behind BPH
Prostate enlargement involves complex factors and intricate mechanisms. Your prostate gland changes as you age. Multiple biological processes influence its growth and potential enlargement. Prostate health research offers fascinating insights into this condition.
Hormonal Changes with Age
Hormonal shifts play a key role in prostate enlargement. As men age, testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) levels change. These changes can trigger abnormal prostate growth.
Autopsy studies show BPH prevalence increases with age. It reaches 88% in men during their 80s5.
Prostate Growth Factors
Several key factors contribute to prostate gland development:
- Hormonal imbalances
- Cellular growth signals
- Inflammatory responses
- Genetic predispositions
Lifestyle Factors Contributing to BPH
Your lifestyle can greatly impact prostate health. Research links metabolic syndrome, obesity, and lack of exercise to faster prostate enlargement6.
A study of 130,454 men revealed connections between lifestyle choices and BPH prevalence6.
“Understanding BPH requires a holistic approach that considers biological, hormonal, and lifestyle influences.”
| Risk Factor | Impact on BPH |
|---|---|
| Age | High |
| Obesity | Moderate |
| Inflammation | Significant |
| Hormonal Changes | Critical |
Knowing these mechanisms helps you manage prostate health better. You can take steps to potentially slow BPH progression.
Treatment Options for BPH
BPH management offers various treatment paths. Your doctor will suggest an approach based on your symptoms and health. The treatment strategy may include lifestyle changes or medical interventions7.
Medications are key in BPH treatment. Alpha-blockers like Tamsulosin help relax prostate muscles. They can improve urinary flow and symptoms significantly7.
5-alpha reductase inhibitors can slow prostate growth. Note that alpha-blockers may cause side effects like dizziness and sexual issues7.
Minimally invasive therapies are available when medicines don’t work. The Rezum system uses radiofrequency water vapor for treatment8. Waterjet Ablation Therapy is another option for specific prostate sizes8.
Surgical options like TURP remain effective for severe cases. Newer laser techniques, such as holmium laser enucleation, show promising results8.
Your BPH treatment should involve close work with your urologist. Each option has unique benefits and risks. Personalized medical guidance is crucial for effective BPH management7.
FAQ
What is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)?
What are the most common symptoms of BPH?
Who is most at risk for developing BPH?
Can lifestyle changes help manage BPH symptoms?
What medical treatments are available for BPH?
Is BPH the same as prostate cancer?
How can I prevent BPH?
When should I see a doctor about BPH symptoms?
Source Links
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) – Symptoms and causes – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/benign-prostatic-hyperplasia/symptoms-causes/syc-20370087
- Enlarged Prostate (Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia) – NIDDK – https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/urologic-diseases/prostate-problems/enlarged-prostate-benign-prostatic-hyperplasia
- BPH symptoms explained | Enlarged prostate causes – https://www.dfwbphtreatment.com/bph-symptoms-and-treatment/bph-symptoms
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) – https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/benign-prostatic-hyperplasia-bph
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia: Evaluation and medical management in primary care – https://www.ccjm.org/content/84/1/53
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): Practice Essentials, Background, Anatomy – https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/437359-overview
- Medical management of benign prostatic hyperplasia – https://www.ccjm.org/content/91/3/163
- Approach Considerations, Alpha-Blockers, 5-Alpha-Reductase Inhibitors – https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/437359-treatment