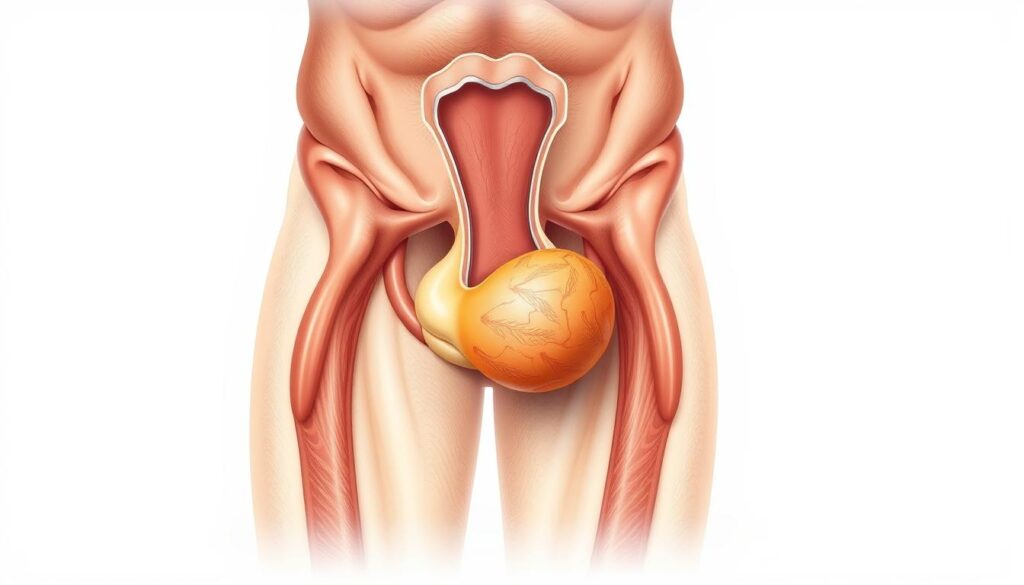
Epididymitis can cause testicular pain and a swollen scrotum. This condition inflames the epididymis, causing discomfort. It requires careful medical attention12.
Bacterial or viral infections often cause epididymitis. Sexually transmitted infections like chlamydia and gonorrhea can lead to acute cases. These usually resolve within six weeks1.
E. coli bacteria may also trigger this condition, especially in older people2. Persistent testicular pain could signal various health issues. Look out for discharge or burning sensations during urination.
If you notice these symptoms, seek medical help right away2. Early diagnosis can prevent potential complications.
Key Takeaways
- Epididymitis can affect males of all ages
- Bacterial infections are primary causes
- Symptoms include testicular pain and swelling
- Treatment typically involves antibiotics
- Early diagnosis prevents potential complications
Understanding Epididymitis and Its Impact on Male Health
Epididymitis is a serious condition affecting male reproductive health. It can impact your overall well-being. This inflammation requires attention to prevent complications related to urinary tract infections and fertility.
The epididymis plays a crucial role in sperm development and transportation. Men between 19 and 35 years are most commonly affected by this condition3.
The Epididymis: A Critical Male Reproductive Structure
The epididymis is a tightly coiled tube at the back of each testicle. Its primary functions include:
- Storing mature sperm
- Supporting sperm transportation
- Protecting sperm from potential damage
Types of Epididymitis: Acute vs. Chronic
Knowing the differences between acute and chronic epididymitis is key for proper management:
- Acute Epididymitis: Lasts less than six weeks, typically caused by bacterial infections4
- Chronic Epididymitis: Persists longer than six weeks and may recur even after treatment3
Risk Factors and Common Causes
Several factors can increase your risk of developing epididymitis. These include:
- Sexually transmitted diseases like chlamydia and gonorrhea4
- Recent urological surgeries3
- Urinary tract infections
- Use of medical catheters3
“Prevention is always better than cure, especially when it comes to reproductive health.”
Bacterial infections are the most common cause of epididymitis5. Knowing these risk factors can help protect your reproductive health. Take steps to prevent complications like male infertility.
Common Symptoms and Warning Signs of Testicular Pain
Recognizing epididymitis symptoms is vital for quick treatment. Men should watch for specific signs that might indicate a serious condition6.
Testicular pain can show up in different ways. Key symptoms include:
- Unilateral testicular pain and tenderness
- A swollen scrotum that feels warm to the touch
- Palpable swelling of the epididymis
- Pain during urination
Men aged 19-35 are more likely to get epididymitis from STIs. Bacterial infections often cause this issue, leading to groin discomfort67.
Other warning signs to look out for include:
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Lower abdominal or pelvic pain
- Occasional blood in the semen
- Potential fever
“Any persistent scrotal pain or swelling requires immediate medical attention to prevent potential long-term complications.”
A urinary tract infection can also cause these symptoms, especially in older men. Chronic epididymitis develops slowly and may last over six weeks67.
Warning: Some symptoms of epididymitis can mimic more serious conditions like testicular torsion, which requires emergency surgical intervention. Sudden, severe testicular pain needs immediate medical help7.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options for Epididymitis
Grasping the proper diagnostic approach and treatment for epididymitis is vital for your well-being. Doctors use various methods to accurately diagnose and manage this condition.
Medical Examination Procedures
Your doctor will perform a thorough evaluation to diagnose epididymitis. This includes a physical exam of the scrotum and urinalysis to check for infections.
They’ll also screen for sexually transmitted infections. A scrotal ultrasound may be done to rule serious conditions.
Antibiotic Treatment Protocols
Antibiotics are the main treatment for epididymitis8. The type prescribed depends on the underlying cause.
- For sexually transmitted infections: Ceftriaxone plus doxycycline
- For non-sexually transmitted cases: Levofloxacin or alternative antibiotics
Prompt and appropriate antibiotic treatment can prevent potential complications and ensure faster recovery.
Home Care and Pain Management
You can manage epididymitis at home to ease discomfort. Rest and elevate the scrotum. Use nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for pain relief.
Apply cold compresses to the affected area. Wear supportive underwear to reduce movement and pain.
When to Seek Emergency Care
Call your doctor right away if you have severe testicular pain or a high fever. Seek help if there’s no improvement after 72 hours of treatment8.
Also, watch for signs of spreading infection. Quick action can prevent serious complications.
Most epididymitis cases have a high success rate. Symptoms usually clear up within three months8. Follow your doctor’s advice and finish all antibiotics for best results.
Conclusion
Epididymitis can greatly affect your reproductive health and life quality. Symptoms range from mild discomfort to severe testicular pain. Early detection and proper treatment are vital for managing this issue.
Your proactive approach is crucial when dealing with epididymitis. Young, sexually active males should know the risks and prevention methods. Safe sex, good hygiene, and quick medical help can lower your chances of getting this condition.
If you have ongoing scrotal discomfort, see a doctor right away. They can provide an accurate medical evaluation of epididymitis. This step is key to your health.
Treatment often includes antibiotics for infections and pain management strategies9. Chronic epididymitis may affect fertility, so addressing symptoms early is important10. Stay informed and take action to protect your reproductive health.
FAQ
What exactly is epididymitis?
What are the main symptoms of epididymitis?
How is epididymitis diagnosed?
What treatment options are available?
How long does epididymitis last?
Can epididymitis affect fertility?
When should I seek emergency medical care?
How can I prevent epididymitis?
Source Links
- Epididymitis – STI Treatment Guidelines – https://www.cdc.gov/std/treatment-guidelines/epididymitis.htm
- Epididymitis – https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/epididymitis
- Epididymitis | Aurora Health Care – https://www.aurorahealthcare.org/services/urology/epididymitis
- Epididymitis – Symptoms and causes – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/epididymitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20363853
- What Is Epididymitis? – https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17697-epididymitis
- Epididymitis – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/epididymitis/
- Epididymitis | Advocate Health Care – https://www.advocatehealth.com/health-services/urology/epididymitis
- Everything You Need to Know About Epididymitis – https://www.healthline.com/health/epididymitis
- Epididymitis : Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment – https://www.artfertilityclinics.com/in/en/art-blog/epididymitis-causes-symptoms-treatment
- Epididymitis: Types, Causes, Symptoms & Treatment | Indira IVF – https://www.indiraivf.com/blog/epididymitis-types-causes-symptoms-treatment