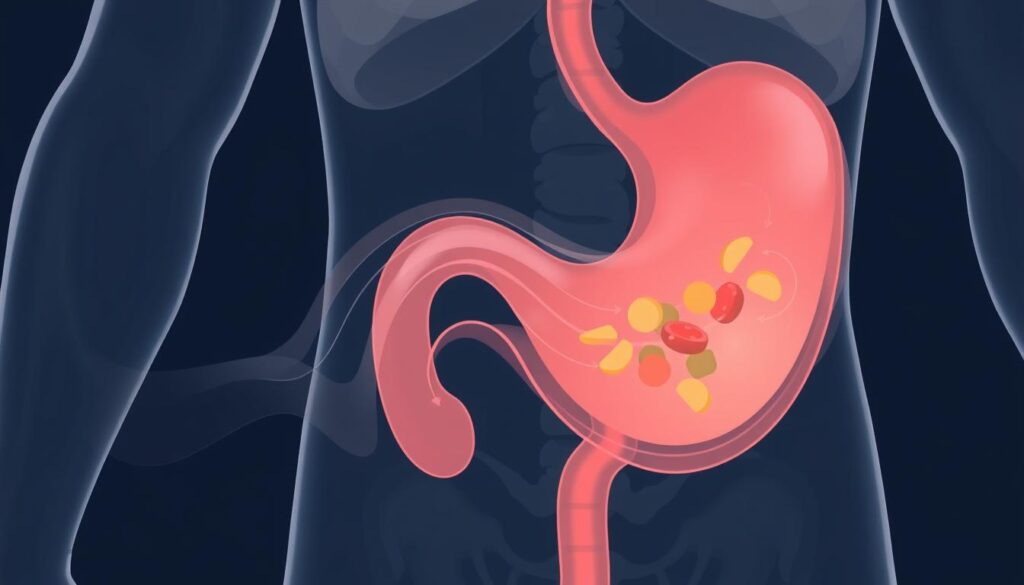
Gastroparesis is a tricky digestion problem that slows down your stomach’s emptying process. It makes your stomach muscles struggle to move food through your system. This stomach slowdown can really mess with your daily life and health1.
Think of your stomach as a strong pump that usually processes meals fast. But with gastroparesis, this pump gets lazy. Food stays in your stomach longer than it should1.
This can cause you to feel full quickly, bloated, and even lose weight without trying. Diabetes is often behind gastroparesis. High blood sugar can hurt the nerves that control stomach muscles1.
People with other health issues might also get this tough digestive problem2.
Key Takeaways
- Gastroparesis disrupts normal stomach emptying processes
- Symptoms include bloating, nausea, and unexpected weight loss
- Diabetes is a significant contributor to this condition
- Nerve damage can cause delayed gastric emptying
- Multiple medical conditions can trigger gastroparesis
Understanding Gastroparesis and Its Impact on Digestion
Gastroparesis is a tricky digestion disorder that messes with your stomach’s normal work. It changes how your body handles food, affecting your daily life and health3.
What Happens in Your Stomach During Gastroparesis
In gastroparesis, stomach muscles have trouble moving food through your system. Food can stay in your stomach too long, causing discomfort4.
This condition turns normal digestion into a tough task. Your usual food processing becomes a real challenge.
- Delayed stomach emptying
- Impaired muscle contractions
- Persistent food retention
The Role of the Vagus Nerve in Gastric Motility
Your vagus nerve controls stomach muscle movements. If damaged, it can mess up normal gastric stasis, causing gastroparesis4.
This nerve damage stops smooth muscle contractions. Without these, food can’t move properly through your system.
“Gastroparesis turns your digestive system into a complex maze of challenges” – Gastroenterology Insights
How Gastroparesis Affects Your Daily Life
Gastroparesis can really shake up your life. Patients often face persistent symptoms that mess with eating and overall health3.
- Nausea affects 95% of patients
- Abdominal pain occurs in over 80% of cases
- Severe bloating impacts approximately 40% of individuals
Knowing these issues helps you deal with this tricky digestive problem. It’s key to managing gastroparesis and its effects4.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Delayed Gastric Emptying
Gastroparesis can disrupt your daily life with complex symptoms. Recognizing these signs helps you seek proper medical care5. Early detection is key to managing this condition effectively.
- Chronic nausea that persists for extended periods
- Frequent vomiting, especially after meals
- Abdominal pain that can range from mild to severe
- Uncomfortable bloating after eating small amounts of food
Your body might struggle with digestion, causing unique experiences. Many patients report early satiety – feeling full quickly after eating little6. This can lead to weight loss and nutrition problems.
“Gastroparesis is like having a digestive system that constantly hits the pause button” – Gastroenterology Specialist
The condition varies widely among individuals. Some people experience occasional symptoms. Others face ongoing digestive issues5.
| Symptom Category | Typical Manifestations |
|---|---|
| Digestive Discomfort | Bloating, abdominal pain, nausea |
| Eating Challenges | Early satiety, reduced appetite |
| Potential Complications | Unintended weight loss, nutritional deficiencies |
Gastroparesis can affect your blood sugar levels. It may also cause constipation due to slow digestion6. Symptoms vary for each person.
A personalized medical evaluation is crucial. This helps determine the best treatment plan for your specific case.
Gastroparesis: Causes and Risk Factors
Knowing what causes gastroparesis can help you handle this tricky digestive problem better. Several key factors play a role in how it develops.
Diabetes-Related Gastroparesis
Diabetes is the top cause of gastroparesis. It affects about one-third of diabetic patients. High blood sugar can harm the vagus nerve, which controls stomach muscles.
Poor diabetes management raises your risk of getting this condition. Taking care of your blood sugar is crucial.
Medical Conditions and Nerve Damage
Other health issues can lead to gastroparesis:
- Viral infections affecting stomach function7
- Neurological disorders like Parkinson’s disease7
- Autoimmune diseases such as scleroderma7
- Hypothyroidism7
Medications and Nerve Interference
Some medicines can worsen or trigger gastroparesis symptoms. These include narcotic pain relievers, antidepressants, and overactive bladder drugs. Surgery near the stomach might damage the vagus nerve too.
Oddly, doctors can’t always find a clear cause. This is called idiopathic gastroparesis. Knowing these triggers helps you work better with your doctor to manage your condition.
Conclusion
Gastroparesis management is key for dealing with this tricky digestive disorder. Most patients with idiopathic gastroparesis are women around 40 years old. The condition affects between 13.8 to 267.7 per 100,000 adults89.
Treating delayed gastric emptying needs a full approach. Only about 5% of patients get better over time. Working with doctors can help control symptoms effectively8.
Most patients have moderate symptoms that greatly affect their life quality. Gastroparesis management takes time and a personal plan. Your treatment may include diet changes, medicines, and lifestyle shifts.
Medical research keeps looking for new ways to help you. These efforts aim to improve understanding and management of your symptoms.
FAQ
What is gastroparesis?
What are the most common symptoms of gastroparesis?
What causes gastroparesis?
Can gastroparesis be cured?
How does diabetes relate to gastroparesis?
What complications can gastroparesis cause?
How is gastroparesis diagnosed?
Can medications help manage gastroparesis?
Source Links
- Gastroparesis – https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/gastroparesis
- Gastroparesis – https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15522-gastroparesis
- Gastroparesis: A turning point in understanding and treatment – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6874806/
- Gastroparesis Symptoms, Treatment, Causes | UCLA Medical School – https://medschool.ucla.edu/news-article/gastroparesis-symptoms-treatment-and-causes
- Gastroparesis | Causes, Symptoms, Treatment & Diet | Guts UK Charity – https://gutscharity.org.uk/advice-and-information/conditions/gastroparesis/
- Gastroparesis – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551528/
- Symptoms & Causes of Gastroparesis – NIDDK – https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/gastroparesis/symptoms-causes
- Progress in gastroparesis- a narrative review of the work of the Gastroparesis Clinical Research Consortium – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9691520/
- Gastroparesis: Etiology, clinical manifestations, and diagnosis – https://www.uptodate.com/contents/gastroparesis-etiology-clinical-manifestations-and-diagnosis