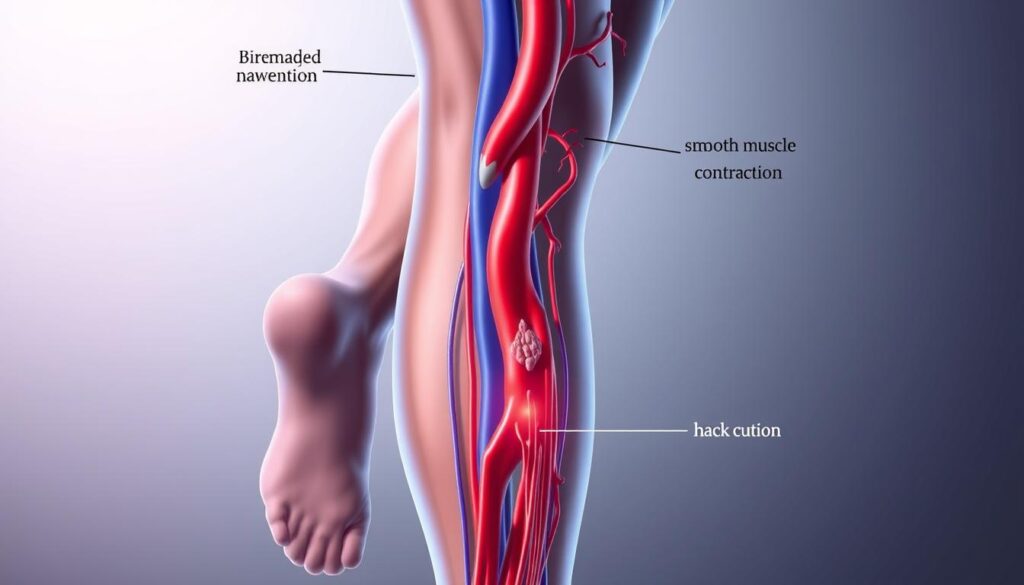
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is a serious health issue affecting millions of Americans. It silently impacts blood circulation throughout your body. Atherosclerosis, a complex process, can narrow your blood vessels and restrict blood flow1.
An estimated 10 to 14 million people in the U.S. have PAD. Understanding this condition is vital for maintaining your cardiovascular health1.
Your PAD risk increases with age, lifestyle choices, and underlying medical conditions. Black individuals have a higher chance of developing PAD2. People 75 and older are especially vulnerable to this circulatory challenge2.
Claudication, a key PAD symptom, can cause leg pain during physical activities. About 40 to 50 percent of patients experience intermittent claudication1. This signals potential arterial narrowing.
If left untreated, PAD can lead to severe complications. These include gangrene and possible amputation2.
Key Takeaways
- PAD affects 10-14 million Americans
- Atherosclerosis is the primary cause of arterial blockage
- Risk increases with age and specific racial backgrounds
- Early detection can prevent serious complications
- Lifestyle modifications can help manage PAD
Understanding Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
Peripheral artery disease is a serious health issue affecting blood circulation. It impacts millions of Americans, creating significant challenges for those diagnosed3.
PAD occurs when arteries narrow or block, limiting blood flow to limbs. Atherosclerosis, the buildup of plaque in arterial walls, is the main cause4.
What is Peripheral Artery Disease?
PAD is a vascular condition mainly affecting people over 50. The ankle-brachial index helps diagnose blood flow issues and detect potential limb ischemia5.
- Affects blood circulation in extremities
- Caused by plaque buildup in arteries
- Increases risk of cardiovascular events
Symptoms to Watch For
Intermittent claudication is the most common PAD symptom. You might feel leg pain or cramping during physical activities5.
This could signal underlying circulation problems.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Leg Pain | Cramping during walking or exercise |
| Numbness | Reduced sensation in legs or feet |
| Skin Changes | Slower hair growth, shiny skin texture |
Early detection and management are crucial for preventing serious complications associated with peripheral artery disease.
“Understanding your body’s signals can help you take proactive steps toward better cardiovascular health.”
Key Risk Factors for PAD
Knowing PAD risk factors helps protect your vascular health. Some risks are controllable, while others depend on age and genetics.
Age and Gender Considerations
PAD risk increases with age. About 6.5 million Americans over 40 have this condition6.
People over 65 are more vulnerable. Both men and women face higher risks as they age6.
Lifestyle Choices and Habits
Lifestyle greatly affects PAD development. Smoking is the biggest risk factor. 80% of PAD patients are current or former smokers.
Tobacco use can boost PAD risk by 400%7. Smokers may show atherosclerosis symptoms ten years earlier than non-smokers7.
- Physical inactivity
- Poor diet
- Obesity
- Chronic stress
Medical Conditions that Contribute
Some medical conditions raise your risk of critical limb ischemia and possible revascularization:
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Kidney disease
African Americans have a higher PAD risk than other racial groups6. Family history of heart disease can also increase your chances7.
Understanding these factors helps manage vascular health and prevent PAD progression. Regular check-ups and lifestyle changes are vital for good circulation.
Steps to Minimize Your Risk of PAD
Protecting yourself from peripheral artery disease (PAD) requires a proactive health approach. Reducing arterial plaque buildup can lower your risk of this serious condition. Over 6.5 million Americans aged 40 and older are affected by PAD8.
Healthy Eating and Nutrition
Your diet plays a critical role in managing PAD risk. The Mediterranean diet can prevent PAD and stabilize blood sugar levels8.
Include omega-3 fatty acids and plant-based proteins like chickpeas and edamame in your meals. Add soluble fibers from apples and oatmeal to support your cardiovascular health8.
These dietary choices can help reduce cholesterol levels and minimize claudication symptoms.
Importance of Regular Exercise
Physical activity is a powerful tool in managing PAD. Regular exercise can prevent disease progression and reduce symptoms89.
Your healthcare provider might recommend supervised exercise programs to improve circulation. These programs could potentially reduce the need for invasive procedures like angioplasty9.
Monitoring Your Health with Professionals
Regular check-ups are essential for early detection and management of PAD. Your doctor can recommend medications to prevent blood clots and improve blood flow8.
Discuss potential treatments with your healthcare provider. These may include cholesterol-lowering medications, antiplatelet drugs, or surgical interventions in severe cases9.
FAQ
What is Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)?
What are the main symptoms of PAD?
Who is most at risk for developing PAD?
How is PAD diagnosed?
Can PAD be prevented?
What are potential complications of untreated PAD?
What treatments are available for PAD?
How often should I get checked for PAD?
Source Links
- Diagnosing and Treating Peripheral Arterial Disease – https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/diagnosing-and-treating-peripheral-arterial-disease
- What is Peripheral Artery Disease? – https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/peripheral-artery-disease/about-peripheral-artery-disease-pad
- Understanding Peripheral Vascular Disease | Baird Vascular Institute – https://www.vcuhealth.org/services/baird-vascular-institute/for-patients/understanding-peripheral-vascular-disease
- Understanding Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) | New York, NY – https://www.drbenvenisty.com/blog/understanding-peripheral-artery-disease-pad/
- Understanding Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): What You Need to Know – https://www.tmh.org/blogs/understanding-peripheral-artery-disease-pad-what-you-need-know
- About Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) – https://www.cdc.gov/heart-disease/about/peripheral-arterial-disease.html
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): Symptoms & Treatment – https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17357-peripheral-artery-disease-pad
- Peripheral artery disease self-care: Tips for managing PAD | HCA Houston Healthcare – https://www.hcahoustonhealthcare.com/healthy-living/blog/peripheral-artery-disease-self-care-tips-for-managing-pad
- Prevention and Treatment of PAD – https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/peripheral-artery-disease/prevention-and-treatment-of-pad