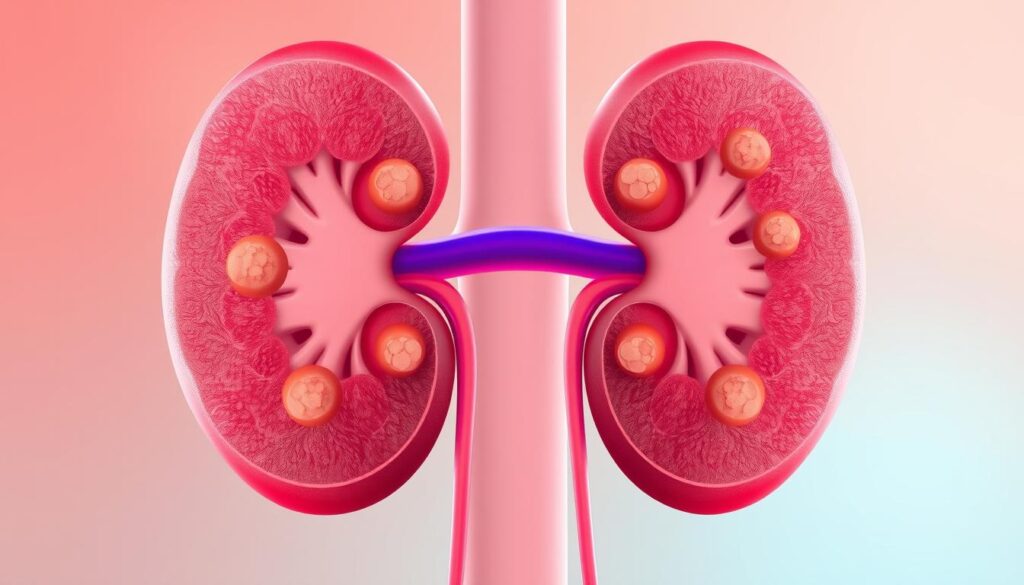
Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) is an inherited condition affecting thousands in the U.S. This genetic disorder impacts the kidneys, causing fluid-filled cysts to form1.
About 600,000 Americans live with PKD. Over time, these cysts can grow and potentially harm kidney function12.
PKD is more common than you might think. Autosomal Dominant PKD accounts for over 90% of cases. It usually appears between ages 30 and 502.
Your genes play a big role in PKD. If your parents have it, you might too1.
Key Takeaways
- PKD is a genetic kidney disorder affecting around 600,000 Americans
- Symptoms can appear between ages 30 and 50
- Genetic inheritance significantly impacts disease transmission
- Multiple types of PKD exist with varying characteristics
- Early detection and management are crucial for patient outcomes
What is Polycystic Kidney Disease?
Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) is a genetic disorder affecting kidney health and function. Kidneys filter waste, control blood pressure, and make essential hormones. Learning about PKD can help you handle its challenges better.
PKD causes fluid-filled cysts to grow in the kidneys. These cysts can harm kidney function over time3. Without treatment, they may lead to serious problems.
Types of Polycystic Kidney Disease
There are two main types of PKD: Autosomal Dominant (ADPKD) and Autosomal Recessive (ARPKD). Each type has unique features.
- Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD):
- Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD):
- Rarer form of the disease
- Requires both parents to carry the faulty gene3
- Can be diagnosed in the womb or shortly after birth
“Knowledge is the first step in managing any genetic condition.” – Kidney Health Experts
About 25% of ADPKD cases happen without a known family history3. In the UK, PKD affects between 30,000 and 70,000 people3.
Potential Complications
PKD can cause health issues beyond kidney problems. These may include hypertension, urinary tract infections, and kidney stones3. Knowing these risks helps you take steps to protect your health.
Symptoms of Polycystic Kidney Disease
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) often develops slowly without noticeable signs. Knowing early warnings is key for timely treatment and kidney health management.
Common PKD Symptoms to Recognize
PKD symptoms usually show up in adulthood. Recognizing these signs can help you take proactive steps toward your health. Here are key symptoms to watch:
- High blood pressure often appears early in PKD progression5
- Kidney pain in the back or sides6
- Blood in urine (hematuria)
- Abdominal swelling or enlarged abdomen
- Frequent headaches
- Development of kidney stones
Understanding Symptom Progression
Most PKD patients don’t notice symptoms until ages 30 to 605. Over 60 percent of patients report abdominal and flank pain6.
A study of 171 patients showed symptom frequency as:
| Symptom | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Low back pain | Most common |
| Abdominal pain | Very frequent |
| Headaches | Moderate occurrence |
When to Consult a Doctor
See a doctor if you have ongoing kidney pain or blood in urine. Also, get checked if PKD runs in your family.
Early detection allows for better management and possible interventions.
“Knowledge is the first step in managing your kidney health” – Nephrology Expert
Keep track of your symptoms and get regular check-ups. This helps monitor PKD progression and prevent possible complications.
Causes and Risk Factors
Genetic factors play a crucial role in polycystic kidney disease (PKD). This inherited kidney condition affects about 500,000 people in the United States7.
Genetic Foundations of PKD
PKD genetics show two main inheritance patterns. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) impacts 1 in 500 to 1,000 Americans7.
ADPKD has specific genetic traits. Most cases come from inherited gene mutations. A small portion stems from new spontaneous changes7.
- 90% of cases result from inherited gene mutations from an affected parent7
- 10% stem from new spontaneous gene mutations7
- Primary gene mutations occur in PKD1 (85-90% of cases) and PKD2 (10-15% of cases)8
Inheritance Patterns
Gene mutations have different inheritance patterns:
- Autosomal Dominant PKD: Only one parent needs to carry the mutated gene
- Autosomal Recessive PKD: Both parents must carry the gene mutation
“Genetics plays a pivotal role in determining your risk of developing polycystic kidney disease”
Environmental Influences
While genetics are key, environmental factors can speed up disease progression. Some risk factors may worsen kidney damage.
- Age over 30
- Male gender
- Excessive analgesic drug use
Knowing your genetic background helps make smart healthcare choices. It’s vital for managing this inherited kidney disease.
Diagnosis of Polycystic Kidney Disease
PKD diagnosis involves multiple techniques. Your doctor will use various methods to identify and assess the condition. These approaches help ensure an accurate diagnosis.
Advanced Imaging Techniques
Kidney imaging is vital for PKD diagnosis. Common methods include:
- Ultrasound scans to detect kidney cysts
- CT scans for detailed kidney structure analysis
- MRI scans to evaluate cyst size and kidney changes9
Genetic Testing Insights
Genetic tests offer definitive info about PKD. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) can be confirmed through special screenings9.
Tests might return negative results in about 10% of cases. This can happen even though they’re more sensitive than imaging9.
Early detection is key to managing polycystic kidney disease effectively.
Family History Assessment
Your family’s medical history is crucial in PKD diagnosis. Doctors will examine your genetic background closely. ADPKD is often found in adults over 30 when symptoms become clearer9.
| Diagnostic Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Ultrasound | Detect kidney cysts |
| Genetic Testing | Confirm PKD genetic mutations |
| Family History Review | Assess genetic risk factors |
Diagnostic tools are powerful, but they’re not enough alone. Talking to a kidney specialist is the best way to confirm PKD. They can provide the most reliable diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Polycystic Kidney Disease
PKD management focuses on slowing disease progression and improving life quality. Patients have several strategies to manage their condition effectively. There’s no complete cure, but treatment can help.
PKD treatment involves multiple approaches for kidney disease management. It also aims to maintain overall health. Your healthcare team will create a personalized plan for your needs.
Lifestyle Modifications
Key lifestyle changes can significantly impact PKD progression:
- Maintain a balanced, kidney-friendly diet
- Engage in regular physical activity
- Quit smoking
- Limit alcohol consumption
- Manage stress effectively
Medications and Therapies
Blood pressure control is crucial in PKD management10. Doctors prescribe specific medications to address various aspects of the disease.
| Medication Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| ACE Inhibitors | Blood pressure regulation |
| ARBs | Kidney function protection |
| Tolvaptan | Slowing cyst growth10 |
Gene therapy shows promising potential for future PKD management11. Researchers explore new ways to prevent cyst formation and slow disease progression.
Early intervention and consistent medical care are key to managing polycystic kidney disease effectively.
Severe cases might require dialysis or kidney transplantation. Regular check-ups with your nephrologist help monitor your condition. They also allow for adjustments to your treatment plan.
Managing Polycystic Kidney Disease
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) management requires a holistic approach. Your daily choices can greatly affect how you handle this condition. Focus on your overall health and well-being to navigate PKD effectively.
Creating a Kidney-Friendly Diet Plan
A kidney-friendly diet is crucial for PKD management. Your nutrition strategy should include low-sodium foods and plenty of fresh produce. Whole grains and lean protein sources are also important.
- Low-sodium food choices
- Plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables
- Whole grains
- Lean protein sources
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease affects over 13 million people worldwide. Dietary management is critical for ADPKD patients. They should focus on eating foods that support kidney health.
Importance of Hydration
Proper hydration is key for PKD management. Drinking enough water may slow kidney cyst growth. Aim to drink water throughout the day. Consult your doctor about the right amount for your condition.
“Your diet and hydration are powerful tools in managing polycystic kidney disease.”
Regular Medical Check-ups
Routine medical monitoring is vital for effective PKD management. Your healthcare team will track kidney function and blood pressure levels. They’ll also look for potential complications and assess treatment effectiveness.
- Kidney function
- Blood pressure levels12
- Potential complications
- Treatment effectiveness
About 80% of ADPKD patients have high blood pressure. Regular check-ups are crucial for early intervention and proper care.
Key Management Strategies
Successful PKD management involves several key strategies. These include maintaining a healthy weight and controlling blood pressure. Following a kidney-friendly diet and staying hydrated are also important.
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Control blood pressure
- Follow a kidney-friendly diet
- Stay hydrated
- Engage in regular medical consultations
By using these strategies, you can actively manage your PKD. This approach can help improve your quality of life and overall health.
Complications Associated with Polycystic Kidney Disease
Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) can cause serious health issues beyond kidney problems. Knowing these potential complications helps manage your health better. PKD complications need thorough medical care.
PKD patients risk kidney failure, with half facing severe kidney problems by 70. Kidney complications progress slowly but steadily. This can lead to end-stage renal disease1314.
Kidney Failure Risks
Your kidneys may suffer ongoing damage. High blood pressure affects nearly 50% of initial cases. Regular check-ups are vital to track kidney function14.
Other Potential Health Issues
- Cardiovascular problems are common, with increased risk of brain aneurysms15
- Liver cysts affecting approximately 30% of patients under 3013
- Potential pancreatic complications14
Brain aneurysms are a serious concern for ADPKD patients. About 10% develop these life-threatening conditions. Early screening and care can greatly reduce risks15.
“Early detection and comprehensive care are key to managing PKD complications”
Lifestyle changes can help reduce PKD-related heart problems. Regular exercise, healthy eating, and avoiding smoking are beneficial. Your doctor can create a plan to address these health challenges15.
Living with Polycystic Kidney Disease
PKD can be tough, but you can maintain a good life with the right help. Learning to manage your mental health and finding support is key. These steps will boost your overall well-being.
Building a Strong Support System
PKD support groups help patients feel less alone. They offer a place to share and learn from others. Members can get practical advice and find healthcare resources.
- Emotional understanding from people with similar experiences
- Practical advice for managing daily challenges
- Connection with healthcare resources
- Opportunities to share personal experiences
Mental Health Strategies
Good mental health is vital when dealing with a long-term illness. Stress management can greatly improve your well-being16. Ongoing stress may raise blood pressure, a common PKD issue.
“Your mental health is just as important as your physical health in managing PKD.”
Lifestyle Management
Regular exercise can help manage PKD. Walking, swimming, and biking are gentle on the kidneys17. Try to exercise for 30 minutes most days.
This routine will build muscle strength and help control blood pressure16.
| Coping Strategy | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Support Groups | Emotional support and shared experiences |
| Regular Exercise | Improved physical and mental health |
| Stress Management | Reduced blood pressure and emotional strain |
Seeking Professional Help
Don’t be afraid to ask for expert support. PKD patients may feel anxious or depressed16. Counseling, therapy, and support groups can help manage these feelings.
Remember, living with PKD is a journey. With proper support and methods, you can lead an active and fulfilling life.
Research and Advances in Polycystic Kidney Disease
PKD research is evolving rapidly, offering hope to affected patients and families. Scientists are making big strides in understanding this genetic condition. They’re developing new treatment approaches that could change lives.
Current Investigations in PKD Research
Researchers are exploring multiple promising avenues in PKD research. Key areas of focus include:
- Genetic mutation analysis
- Advanced clinical trials
- Potential gene therapy interventions
Groundbreaking Clinical Trials
Current trials are investigating revolutionary treatments for polycystic kidney disease. They target the underlying genetic causes of PKD. Researchers found that PKD1 gene mutations cause about 85% of ADPKD cases18.
These trials aim to develop targeted therapies. The goal is to slow down the progression of the disease19.
| Research Focus | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Gene Therapy | Correcting genetic mutations |
| Molecular Targeting | Interrupting cyst formation |
| Signaling Pathway Studies | Understanding disease mechanisms |
Future Treatment Horizons
The future of PKD treatment looks promising. Emerging research suggests potential breakthrough approaches, including:
- Precision medicine techniques
- Advanced gene therapy strategies
- Targeted molecular interventions
“The key to managing PKD lies in understanding its complex genetic foundations and developing innovative therapeutic approaches.” – PKD Research Consortium
Patients can remain hopeful as research continues. The PKD Foundation has funded over 1,300 research projects. These projects aim to find treatments and potential cures19.
Scientific advancements are ongoing. The outlook for PKD management is becoming more optimistic every day18.
Frequently Asked Questions about Polycystic Kidney Disease
PKD facts can help dispel common kidney disease myths. Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) is a complex genetic condition affecting many worldwide20. Knowing the right information can empower you to manage your health effectively.
Common Myths and Misconceptions
A common myth is that PKD only impacts kidneys. In reality, this genetic disorder can affect multiple organs. PKD affects about 500,000 people in the United States20.
Genetic inheritance plays a crucial role in PKD. Roughly 1 in every 400 to 1,000 people worldwide have Autosomal Dominant PKD20. This challenges the notion that the condition is rare.
Key Takeaways for Patients
Managing PKD requires proactive steps. Regular monitoring and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are essential. Understanding your genetic risks is also crucial.
Blood pressure control is critical. Aim for a goal of less than 120/8020. Engage in 30 minutes of daily physical activity.
Maintain a healthy weight and avoid smoking to support kidney health20. Remember, while PKD is serious, many patients lead fulfilling lives with proper care.
FAQ
What is Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD)?
Is Polycystic Kidney Disease hereditary?
What are the common symptoms of PKD?
How is Polycystic Kidney Disease diagnosed?
Is there a cure for Polycystic Kidney Disease?
Can people with PKD live a normal life?
What complications can arise from Polycystic Kidney Disease?
Are there any ongoing research efforts for PKD?
How does PKD affect different age groups?
What lifestyle changes can help manage PKD?
Source Links
- Polycystic Kidney Disease – https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/polycystic-kidney-disease
- Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) symptoms, treatments & causes – https://www.kidneyfund.org/all-about-kidneys/types-kidney-diseases/polycystic-kidney-disease
- Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/autosomal-dominant-polycystic-kidney-disease-adpkd/
- Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD): Treatment – https://www.uptodate.com/contents/autosomal-dominant-polycystic-kidney-disease-adpkd-treatment
- Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease – Symptoms – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/autosomal-dominant-polycystic-kidney-disease-adpkd/symptoms/
- Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD): Pain syndromes – https://www.uptodate.com/contents/autosomal-dominant-polycystic-kidney-disease-adpkd-pain-syndromes
- Polycystic kidney disease: MedlinePlus Genetics – https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/polycystic-kidney-disease/
- Prevalence, risk factors and disease knowledge of polycystic kidney disease in Pakistan – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7607775/
- Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease – Diagnosis – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/autosomal-dominant-polycystic-kidney-disease-adpkd/diagnosis/
- Approach Considerations, Blood Pressure Control, Infectious and Other Disorders – https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/244907-treatment
- Scientists discover potential treatment approaches for polycystic kidney disease – https://www.nih.gov/news-events/news-releases/scientists-discover-potential-treatment-approaches-polycystic-kidney-disease
- Practical Issues in the Management of Polycystic Kidney Disease: Blood Pressure and Water Balance – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9685325/
- Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease – NIDDK – https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/kidney-disease/polycystic-kidney-disease/autosomal-dominant-pkd
- Complications of Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) – https://www.news-medical.net/health/Complications-of-Polycystic-Kidney-Disease-(PKD).aspx
- Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease – Complications – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/autosomal-dominant-polycystic-kidney-disease-adpkd/complications/
- How to Live Your Best Life With ADPKD – https://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/ss/slideshow-living-with-adpkd
- Lifestyle – https://pkdcure.org/living-with-pkd/lifestyle/
- Advances in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: A Clinical Review – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7380379/
- Home – https://pkdcure.org/
- What Is Polycystic Kidney Disease? – NIDDK – https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/kidney-disease/polycystic-kidney-disease/what-is-pkd