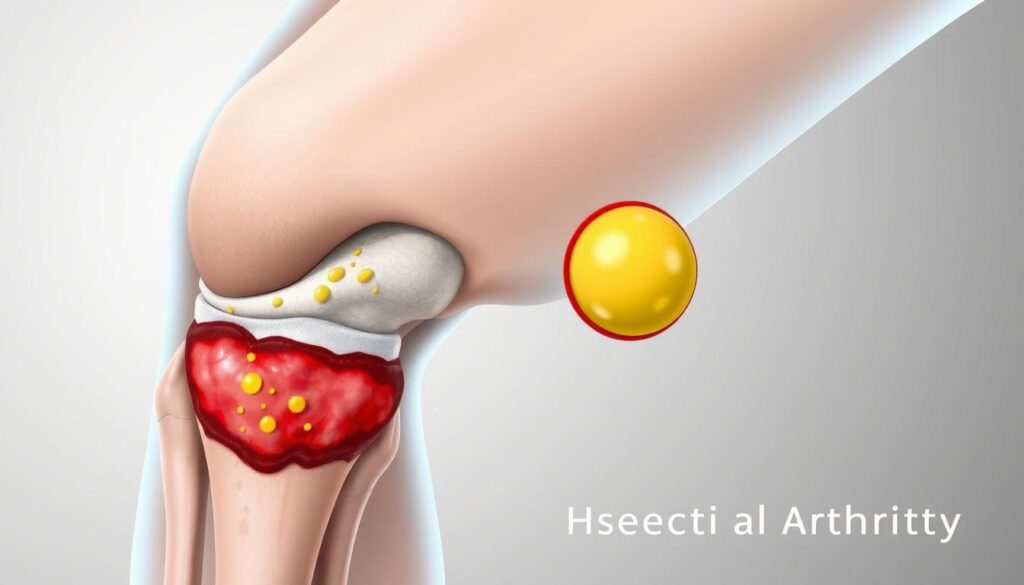
Joint infections can make everyday movements painful. Septic arthritis is a severe bacterial condition that needs quick action. It happens when harmful germs enter your joints, causing swelling and possible lasting damage1.
Anyone can get septic arthritis, but some people are at higher risk. These include babies, older adults, and those with artificial joints2. The knees are most often affected, but hips and shoulders can also be targets2.
Knowing about pyogenic arthritis helps spot it early. It’s not very common, affecting 2 to 6 people out of 100,000 each year1. The main culprit is usually Staphylococcus aureus bacteria2.
Key Takeaways
- Septic arthritis is a serious bacterial joint infection
- Knees are most commonly affected by the condition
- Prompt medical intervention is critical
- Certain groups have higher risk factors
- Staphylococcus aureus is the leading bacterial cause
Understanding Septic Arthritis and Its Impact on Joint Health
Septic arthritis is a serious joint infection that affects health and mobility. It occurs when germs invade joints, causing inflammation and potential long-term damage. This condition can severely impact your ability to move freely.
Joint infections can affect various groups of people. Young adults who are sexually active face higher risks. Those with weak immune systems are also more likely to get septic arthritis3.
Infections can spread through the bloodstream or direct joint injury. These pathways make it easy for harmful bacteria to reach your joints.
What is Septic Arthritis?
Septic arthritis causes inflammation in joint fluid and surrounding tissues. Doctors can identify the specific germ causing the infection through fluid tests4. However, about 30% of cases show no germs in tests, making diagnosis tricky4.
Common Types of Joint Infections
- Staphylococcus infections
- Streptococcus infections
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae in sexually active adults3
- Polymicrobial infections affecting around 7% of cases4
Most Affected Joints
Doctors use joint fluid tests to find infected areas. Large joints like knees, hips, and shoulders are often affected. In children, hip joints are most at risk.
Adults usually get infections in their knees3. Different age groups face varying risks for specific joint infections.
| Patient Group | Most Affected Joints | Infection Probability |
|---|---|---|
| Children | Hip | High |
| Adults | Knee | Moderate |
| Injection Drug Users | Sacroiliac and Sternoclavicular | Variable |
Antibiotics are the main treatment for septic arthritis. Treatment usually lasts four to six weeks to fully remove the infection3. Quick diagnosis and treatment are key to avoiding long-term joint damage.
Prompt medical intervention can significantly reduce the risk of permanent joint complications.
Recognizing Signs and Risk Factors of Joint Infection
Protecting your joint health requires understanding septic arthritis signs and risk factors. Osteomyelitis and other joint infections can quickly worsen, especially in immunocompromised patients. These individuals are more vulnerable to serious complications.
Septic arthritis has distinctive symptoms that need immediate attention. Rapid onset of severe joint pain, swelling, and redness are key warning signs5. Without treatment, the infection can cause immobility within hours.
Key Risk Factors
- Existing joint problems
- Artificial joint replacements6
- Chronic medical conditions
- Weakened immune system
Certain medical conditions increase your risk of joint infections. Diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and recent joint surgeries can raise your chances significantly7.
Diagnostic Insights
| Diagnostic Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Blood Cultures | Detect potential bacteremia |
| Synovial Fluid Analysis | Identify infection type and severity |
| Inflammatory Marker Tests | Assess infection progression |
Early detection is your best defense against permanent joint damage.
Staphylococcus aureus is the main cause of septic arthritis in all age groups6. Watch for persistent joint pain, fever, or reduced mobility.
Quick medical evaluation can prevent long-term complications. It’s crucial for preserving your joint health.
Conclusion
Septic arthritis is a serious bacterial joint infection that affects people of all ages. It can strike unexpectedly, with varying risk levels. The infection rate is 4-12 cases per 100,000 person-years in the general population8.
Medical treatments offer promising results. About 81% of medically-managed patients and 82% of surgically-managed patients fully recover within a year8. However, the risk remains high. Mortality rates for native joint infections range from 4-13%, potentially reaching 20% in prosthetic joints8.
Early detection and quick medical help are your best defense against joint infections. Knowing the symptoms and risk factors can greatly improve your chances. Bacterial arthritis is serious and requires professional medical care.
Stay alert to your body’s signals. Don’t wait to see a doctor if you have ongoing joint pain. Your quick action can protect your joint health and overall wellness.
FAQ
What is septic arthritis?
What are the main symptoms of septic arthritis?
Which joints are most commonly affected?
What causes septic arthritis?
Who is at highest risk for septic arthritis?
How is septic arthritis treated?
Can septic arthritis be prevented?
Is septic arthritis dangerous?
Source Links
- Septic Arthritis: What Is It, Symptoms, Treatment & Causes – https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22418-septic-arthritis
- Septic arthritis: Infection can severely damage the joint-Septic arthritis – Symptoms & causes – Mayo Clinic – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/bone-and-joint-infections/symptoms-causes/syc-20350755
- An Overview of Septic Arthritis – https://www.webmd.com/arthritis/septic-arthritis-symptoms-diagnosis-and-treatment
- Background, Etiology and Pathophysiology, Prognosis – https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/236299-overview
- Septic Arthritis – https://www.chop.edu/conditions-diseases/septic-arthritis
- Septic arthritis – https://patient.info/doctor/septic-arthritis-pro
- Septic Arthritis: Diagnosis and Treatment – https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2021/1200/p589.html
- Medical Versus Surgical Management Of Native Joint Septic Arthritis In Adults: A Retrospective Comparison Of Outcomes Within The Va Ct Medical System – https://elischolar.library.yale.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=2154&context=ymtdl