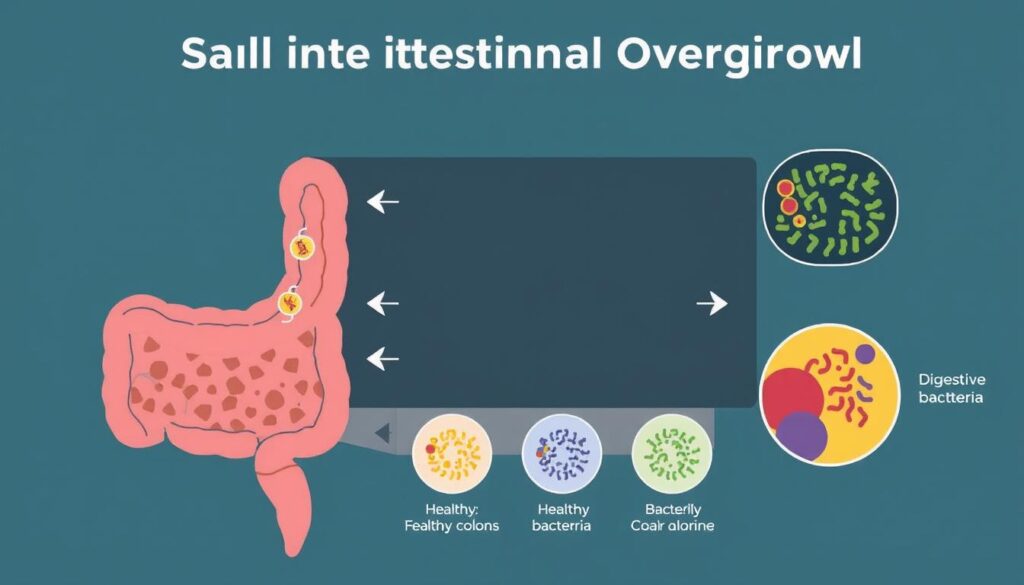
Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO) disrupts your gut’s delicate bacterial balance. It happens when bacteria multiply too much in your small intestine. This can lead to significant health issues12.
SIBO can result from various medical conditions and lifestyle factors. Surgical procedures like gastric bypass can trigger it. These events can compromise your digestive system’s normal bacterial balance12.
Gut dysbiosis occurs when bacteria overtake your small intestine. They compete for nutrients, causing malabsorption and diarrhea. This can lead to nutritional deficiencies1.
These complications may result in unexpected weight loss. They can also have broader impacts on your overall health2.
Key Takeaways
- SIBO disrupts normal gut bacterial balance
- Surgical procedures can increase SIBO risk
- Bacterial overgrowth impacts nutrient absorption
- Multiple factors contribute to intestinal bacterial overgrowth
- Early detection helps prevent serious complications
What is Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO) and Its Impact on Gut Health
SIBO is a complex digestive disorder that can disrupt your gut health. It’s crucial to recognize potential symptoms and seek medical guidance. Understanding SIBO helps you take control of your digestive well-being.
Understanding Bacterial Balance in Your Digestive System
Your small intestine usually maintains a delicate bacterial balance. When disrupted, bacterial overgrowth can occur, causing uncomfortable digestive symptoms.
About 5.9% of younger adults have SIBO. The prevalence increases in older populations3.
How SIBO Impacts Digestive Functions
SIBO can significantly disrupt your digestive process. It may lead to malabsorption syndrome, impaired nutrient absorption, and compromised intestinal function.
- Malabsorption syndrome
- Impaired nutrient absorption
- Compromised intestinal function
Common Signs and Symptoms
SIBO patients often experience a range of uncomfortable symptoms4:
| Physical Symptoms | Digestive Disturbances |
|---|---|
| Abdominal pain | Bloating |
| Flatulence | Diarrhea |
| Weight loss | Foul-smelling stools |
“Your gut health is a window to your overall wellness”
Several medical conditions can increase your risk of developing SIBO. These include diabetes, cirrhosis, Crohn’s disease, and gastroparesis.
Knowing these potential triggers helps you work with healthcare professionals. Together, you can manage your digestive health effectively4.
Risk Factors and Common Causes of SIBO Development
Gut dysbiosis occurs when the delicate balance of your digestive system is disrupted. Multiple complex mechanisms can lead to this challenging gastrointestinal disorder. Knowing these causes helps identify potential risks for SIBO.
Several key risk factors contribute to small intestinal bacterial overgrowth:
- Aging and reduced stomach acid production5
- Chronic medical conditions affecting digestive function
- Structural abnormalities in the digestive tract
- Medication interactions
Specific medical conditions significantly increase your SIBO risk:
| Medical Condition | SIBO Prevalence |
|---|---|
| Diabetes | 75% occurrence rate5 |
| Scleroderma | 50% patients affected5 |
| Celiac Disease | Two-thirds of patients5 |
| Crohn’s Disease | Nearly double SIBO risk5 |
Your risk of SIBO increases with certain lifestyle and health factors. Age, medication use, and underlying health conditions all play crucial roles.
“Understanding your individual risk factors is the first step in managing potential gut health challenges.”
Do you have chronic digestive issues? A healthcare professional can help identify potential SIBO risks. They can also develop a suitable management strategy for you6.
Treatment Approaches and Management Strategies
SIBO management requires a comprehensive approach. It addresses root causes and provides targeted treatment. Your healthcare journey will involve multiple strategies to restore gut health.
Medical Interventions and Antibiotic Therapy
Antibiotic therapy is crucial in managing SIBO. Doctors prescribe specific antibiotics to reduce bacterial overgrowth in the small intestine7. Common medications include:
- Rifaximin
- Metronidazole
- Ciprofloxacin
- Amoxicillin/clavulanate
Dietary Modifications and Nutritional Support
Dietary changes are key in managing SIBO. They also address potential nutrient deficiencies7. Your diet plan might include:
- Limiting fermentable carbohydrates
- Reducing sugar and sweetener intake
- Avoiding problematic foods that trigger symptoms
- Supporting nutritional balance
“Nutrition is a critical component of SIBO management and recovery.”
Addressing Underlying Health Conditions
Successful SIBO treatment requires identifying underlying health issues. Some disorders have higher SIBO prevalence8:
- Up to 40% of systemic sclerosis patients
- 25% of Parkinson’s disease patients
- 33% of Crohn’s disease patients after ileocecal valve resection
Your doctor will create a personalized treatment plan. It will consider your medical history and nutritional needs7. Regular check-ups will help ensure effective SIBO management.
Conclusion
SIBO is a complex digestive challenge affecting overall wellness. It’s more common than once thought, with symptoms in 2.5% to 22% of healthy people9. Understanding SIBO is vital for effective gut health management through comprehensive research.
Tackling SIBO requires a multi-pronged approach. Breath tests help identify bacterial imbalances10. Treatment may include antibiotics, diet changes, and addressing underlying health issues. Probiotics can help restore bacterial balance in your gut10.
Early detection and personalized care prevent potential complications. SIBO prevalence varies, reaching 30% to 85% in irritable bowel syndrome patients9. Working with healthcare pros and adopting preventive strategies can improve your gut health.
FAQ
What exactly is Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO)?
What are the most common symptoms of SIBO?
What causes SIBO to develop?
How is SIBO typically treated?
Can SIBO be completely cured?
Who is most at risk for developing SIBO?
How is SIBO diagnosed?
Can diet help manage SIBO?
Source Links
- Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO)-Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) – Symptoms & causes – Mayo Clinic – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/small-intestinal-bacterial-overgrowth/symptoms-causes/syc-20370168
- SIBO: Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth – https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21820-small-intestinal-bacterial-overgrowth-sibo
- Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: A Comprehensive Review – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3099351/
- SIBO (Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth): Symptoms & Causes | NewYork-Presbyterian – https://www.nyp.org/digestive/small-intestinal-bacterial-overgrowth-sibo
- Risk Factors for Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth – https://www.news-medical.net/health/Risk-Factors-for-Small-Intestinal-Bacterial-Overgrowth.aspx
- Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO) – https://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/sibo-overview-what-is-it
- Diagnosis and management of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) – https://gastro.org/clinical-guidance/diagnosis-and-management-of-small-intestinal-bacterial-overgrowth-sibo/
- Aetiology, diagnosis and management of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9933597/
- Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth syndrome – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2890937/
- Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO) – https://www.metroatlantagastro.com/articles/general/956108-small-intestinal-bacterial-overgrowth-sibo