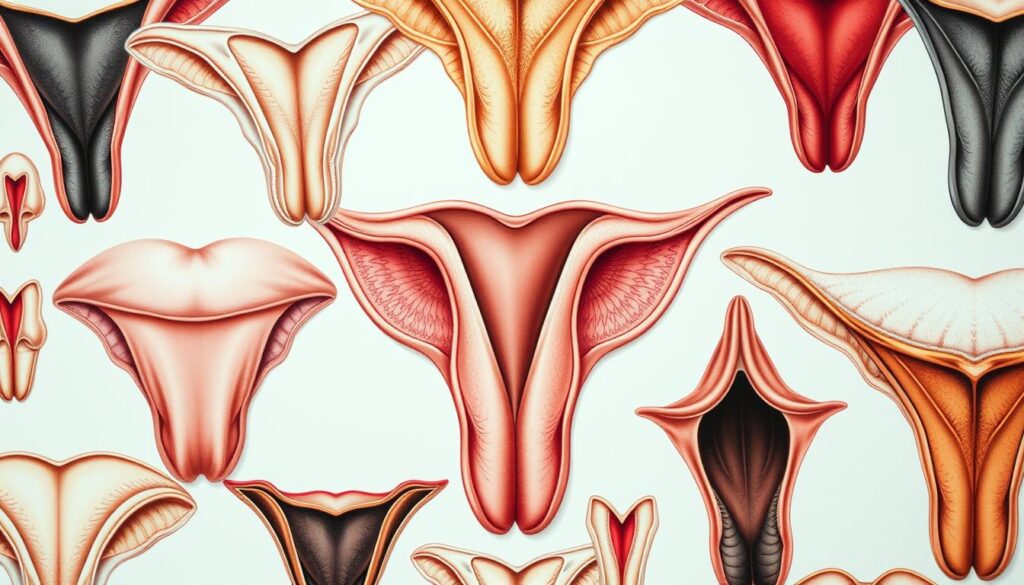
Vulva anatomy showcases a stunning variety that defies traditional beauty norms. Your body is unique, especially when it comes to female genitals. The labia variations you have are natural and beautiful1.
Research reveals remarkable differences in labial shapes among women. A study of 400 adult women found interesting labia minora patterns. 34.25% had prominent anterior labia, 46.75% showed prominent midpoint labia, and 19% displayed posterior protrusion1.
There’s no single “normal” vulva appearance. Your labia are as unique as your fingerprint. Genetics, hormones, and development all play a role in shaping them.
Body positivity celebrates this natural variation. It encourages self-acceptance and understanding of our bodies. Age and childbirth can also affect labial characteristics.
The study showed age distribution trends. 55% of participants were between 18-30 years old. This highlights the diversity across different life stages1.
Key Takeaways
- Vulva anatomy is incredibly diverse and unique to each individual
- Labia variations are completely natural and normal
- No single appearance represents the “ideal” vulva
- Genetic and hormonal factors influence labial characteristics
- Body positivity celebrates genital diversity
Understanding Labial Morphology and Natural Variation
The human vulva shows incredible diversity. Each person has unique labial features reflecting their genetics and physiology. Your intimate anatomy showcases the beautiful complexity of human genital diversity.
Labial appearance varies widely in size, color, and structure. Understanding this natural range is important. Labia can look very different from person to person.
Different Types and Shapes of Labia
Labia come in numerous configurations, including:
- Asymmetrical inner lips
- Curved outer lips
- Prominent inner or outer lips
- Long dangling inner or outer lips
- Small open or closed outer lips
Typical Size Ranges and Measurements
Research reveals fascinating variations in labial measurements across different age groups. Here are some average measurements2:
| Labial Region | Length (mm) | Width (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| Right Labia Majora | 79.71 | – |
| Left Labia Majora | 79.99 | – |
| Right Labia Minora | 42.1 | 13.4 |
| Left Labia Minora | 42.97 | 14.15 |
Factors Influencing Labial Appearance
Your labial appearance can change due to various factors:
- Genetic predisposition
- Hormonal shifts during puberty
- Pregnancy and childbirth
- Aging processes
- Potential medical conditions
Labial changes are normal and can happen throughout your life. Labial hypertrophy might cause discomfort. Learning about these natural variations can help ease worries about your body.
“Every vulva is unique, just like a fingerprint.” – Dr. Elizabeth Smithson, Gynecological Researcher
Celebrate your body’s natural diversity. Remember, variation isn’t just normal—it’s beautiful. Your unique features make you who you are.
The Role of Genetics and Hormones in Vulvar Diversity
Your vulva’s appearance is a unique genetic blueprint. Genetic factors determine the size, shape, and characteristics of your external genitalia3. Like eye color or hair texture, your labial morphology is shaped by inherited genetic information.
Hormones greatly impact vulva development throughout life. During puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, hormonal changes can alter your labia’s appearance and elasticity4. Estrogen is key in maintaining skin color, texture, and overall vulvar health.
- Genetic inheritance determines initial labial characteristics
- Hormonal fluctuations modify vulvar appearance over time
- Ethnic background contributes to natural labial variations
Research has revealed fascinating insights into genital development’s genetic mechanisms. Specific gene transcripts can differ between normal and atypical genital development3. Scientists have identified key genes like HOXA13, TBX3, and BMP4 that influence external genitalia formation.
Every vulva tells a unique story of genetic inheritance and hormonal journey.
Hormonal shifts can cause changes in labial appearance as you age. Post-menopausal women may experience changes in genital tissue, including skin elasticity and sensitivity4. Understanding these natural variations can help promote body acceptance.
| Life Stage | Hormonal Impact | Vulvar Changes |
|---|---|---|
| Puberty | Increasing Estrogen | Initial Development |
| Pregnancy | Hormonal Fluctuations | Increased Tissue Elasticity |
| Menopause | Decreasing Hormones | Potential Tissue Changes |
A scientific study showed that the vaginal introitus is highly sensitive to hormonal changes. However, the labia remain relatively stable across different hormonal conditions4.
Conclusion
Vulva diversity teaches us a powerful lesson in body positivity. Every vulva is unique, with natural variations in size, shape, and appearance. Understanding this diversity promotes labia health awareness and challenges unrealistic beauty standards5.
If you’re worried about your labia, talk to a healthcare provider. They can offer personalized advice. Labiaplasty is an option for physical discomfort, but consider it carefully.
Online communities supporting vulva acceptance show a shift towards inclusive body image views6. Education is crucial for promoting body positivity and self-acceptance. Learning about vulvar anatomy helps build a healthier relationship with your body.
Embracing your unique physiology celebrates your individual beauty and worth. Vulva acceptance is a journey of self-love and understanding. Your body is remarkable and deserves respect, regardless of its appearance.
Keep seeking knowledge, support, and compassion as you explore body positivity. Remember, your body is unique and valuable just as it is.
FAQ
Are all vulvas and labia different?
What are the common variations in labial appearance?
How do hormones affect vulvar appearance?
Is it normal for labia to change with age?
Can genetics influence labial appearance?
When should I be concerned about my labial appearance?
What is labial hypertrophy?
How common are variations in vulvar appearance?
Are there resources to help me understand vulvar diversity?
Should I consider labiaplasty?
Source Links
- Frontiers | Quantitative analysis of the labia minora morphology in 400 Chinese women: A new method for assessing the shape of the labia minora – https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/surgery/articles/10.3389/fsurg.2022.961247/full
- Quantitative analysis of the labia minora morphology in 400 Chinese women: A new method for assessing the shape of the labia minora – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9852508/
- Differential gene-expression patterns in genital fibroblasts of normal males and 46,XY females with androgen insensitivity syndrome: evidence for early programming involving the androgen receptor – Genome Biology – https://genomebiology.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/gb-2003-4-6-r37
- Histological and Gene Expression Analysis of the Effects of Menopause Status and Hormone Therapy on the Vaginal Introitus and Labia Majora | Binder – https://www.jocmr.org/index.php/JOCMR/article/view/4006/25893020
- Morphological variations of the labial frenum, type of attachment and presence of diastemas: integrative review – https://www.scielo.br/j/rgo/a/njvLRNKy5mHwS6sKNHt8JhD/?format=html&lang=en
- Assessment and Management of Maxillary Labial Frenum—A Scoping Review – https://www.mdpi.com/2075-4418/14/16/1710