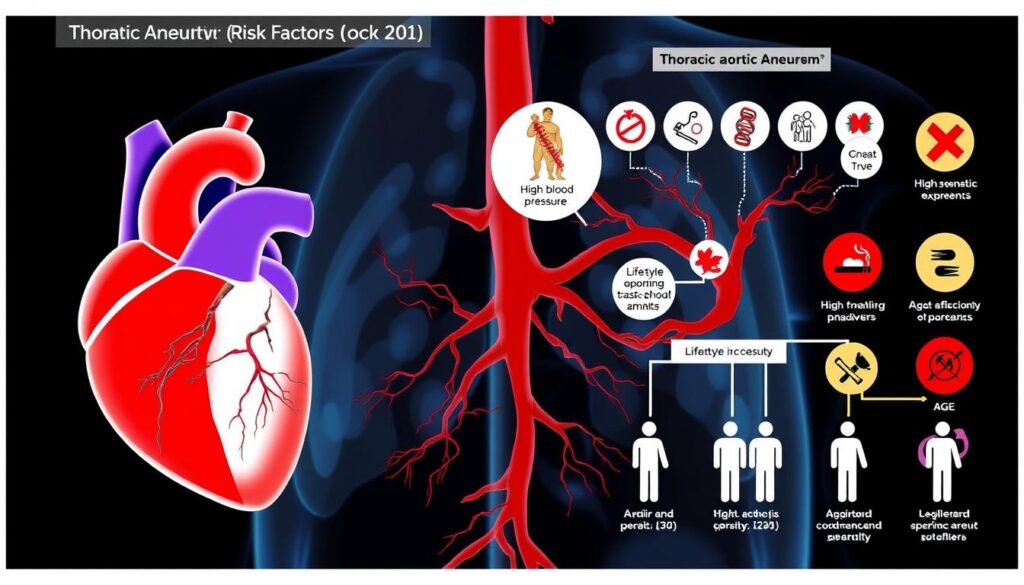
Thoracic aortic aneurysms are serious conditions affecting the body’s main blood vessel. They can develop silently, making early detection vital. Knowing your risk factors is key to prevention and timely treatment1.
Atherosclerosis weakens aorta walls, increasing aneurysm risk1. Your genes play a role too. Some mutations, like in the ACTA2 gene, raise your chances1.
These aneurysms often form in the ascending or descending aorta. Regular check-ups are crucial for catching them early1.
Lifestyle choices impact your risk too. High cholesterol, long-term high blood pressure, and smoking harden arteries2. The condition progresses slowly, often without obvious symptoms2.
Key Takeaways
- Atherosclerosis is the primary cause of thoracic aortic aneurysms
- Genetic factors can significantly increase your risk
- Most aneurysms form in the ascending or descending aorta
- Regular medical screenings are crucial for early detection
- Lifestyle changes can help manage your risk factors
Understanding Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm: A Life-Threatening Condition
Thoracic aortic aneurysms are serious medical conditions that silently develop in your body’s main blood vessel. These dangerous bulges create weak spots in the aorta’s wall. Such weaknesses can lead to life-threatening complications3.
What Defines a Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm
A thoracic aortic aneurysm occurs when the aorta’s wall weakens and expands. Most patients don’t know they have this condition. Doctors often find aneurysms during imaging tests for other medical issues4.
- Can occur near the heart
- Develops in the aortic arch
- Potentially forms in lower thoracic aorta
Common Symptoms and Warning Signs
Many thoracic aortic aneurysms don’t cause symptoms. However, some people might experience warning signs. Large aneurysms can cause back or chest discomfort4.
Possible symptoms include:
- Pain in jaw, neck, chest, or upper back
- Difficulty swallowing
- Hoarseness
- Persistent coughing
- Breathing difficulties
Emergency Symptoms Requiring Immediate Care
Some symptoms signal a potential aortic dissection or rupture. These require immediate medical help4. Critical warning signs include:
| Emergency Symptom | Potential Indication |
|---|---|
| Sudden severe chest pain | Possible aortic dissection |
| Dizziness | Potential blood flow disruption |
| Shortness of breath | Cardiovascular compromise |
| Rapid heart rate | Body’s stress response |
“Early recognition of symptoms can be life-saving in thoracic aortic aneurysm cases.”
Doctors use special imaging tests to find and monitor these serious vascular conditions. These include contrast-enhanced CT scans, MRIs, and echocardiograms4.
Critical Risk Factors and Prevention Strategies
Thoracic aortic aneurysms have various risk factors. Genes and lifestyle choices greatly impact your risk5. Knowing these can help you protect your health.
- Age: Higher risk for individuals over 505
- Genetic conditions: Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome5
- Family history of aortic diseases5
- Lifestyle threats: Smoking, high blood pressure, diabetes5
Prevention focuses on managing these risk factors. Your plan should include these key steps:
- Regular health screenings
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle
- Monitoring blood pressure and cholesterol
“Early detection and lifestyle management are key to preventing aortic aneurysm progression.”
Treatment options depend on aneurysm size and overall health5. Surgery might be needed when the aneurysm reaches about 6 cm5.
| Treatment Approach | Description |
|---|---|
| Observation | Regular CT scans to monitor aneurysm growth |
| Medication | Managing underlying risk factors |
| Surgical Repair | Open or endovascular procedures |
Post-operative care is vital for successful recovery. Your doctor will create a plan for your health. This plan helps prevent future problems.
Conclusion
Thoracic aortic aneurysms demand comprehensive knowledge and proactive healthcare management. Patient demographics significantly influence diagnosis, with specific patterns emerging in different populations6. Your medical journey may involve careful monitoring, strategic treatment options, and personalized post-operative care.
Aortic dissection risks increase when hypertension isn’t controlled7. Treatment depends on aneurysm size, growth rate, and individual health conditions. Males aged 60-70 are particularly vulnerable, with specific risk factors to consider67.
Your healthcare team will create a tailored approach to manage your condition. They may recommend surgical interventions based on precise measurements and potential complications. Regular screenings and lifestyle changes can improve your long-term outcomes.
Early detection and proactive management are crucial in dealing with thoracic aortic aneurysms. Work closely with your doctors to develop a personalized strategy. This approach will address your unique health profile and minimize potential life-threatening risks.
FAQ
What is a thoracic aortic aneurysm?
What are the common causes of thoracic aortic aneurysms?
What symptoms should I watch out for?
What are the emergency symptoms of a thoracic aortic aneurysm?
Who is at the highest risk for thoracic aortic aneurysms?
How can I prevent thoracic aortic aneurysms?
How are thoracic aortic aneurysms diagnosed?
What are the treatment options for thoracic aortic aneurysms?
Can thoracic aortic aneurysms be fatal?
Source Links
- Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm: What You Need To Know – https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17552-aorta-thoracic-aortic-aneurysm
- Thoracic aortic aneurysm – https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/diseases-conditions/thoracic-aortic-aneurysm
- Thoracic aortic aneurysm – Symptoms and causes – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/thoracic-aortic-aneurysm/symptoms-causes/syc-20350188
- Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm – https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/thoracic-aortic-aneurysm
- Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm – UChicago Medicine – https://www.uchicagomedicine.org/conditions-services/heart-vascular/aortic-disease/thoracic-aortic-aneurysm
- Decision-making algorithm for ascending aortic aneurysm: Effectiveness in clinical application? – https://www.jtcvs.org/article/S0022-5223(18)32927-1/fulltext
- Management of acute aortic dissection and thoracic aortic rupture – Journal of Intensive Care – https://jintensivecare.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40560-018-0287-7