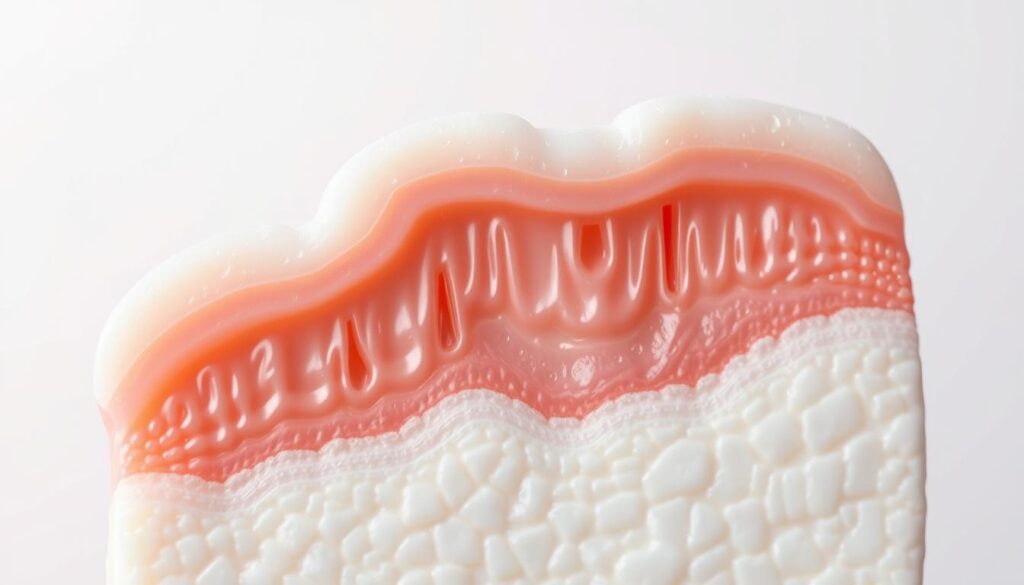
Your dental enamel is a tough shield that protects your teeth’s inner structures. This hard outer layer is crucial for your oral health. It’s the hardest tissue in the human body, guarding your teeth against daily challenges.
Dental enamel has an amazing makeup. It’s 95% inorganic substances, mainly hydroxyapatite. Key minerals like sodium, magnesium, phosphorus, and calcium are also present1.
Your enamel can be up to 2.5 millimeters thick. This offers strong protection for your teeth1.
Tooth enamel’s strength is what makes it special. It’s even harder than iron, with a Mohs hardness of 5.01. Its tiny crystal structure forms an invisible shield.
This network protects your teeth from daily wear and possible damage.
Key Takeaways
- Tooth enamel is the hardest tissue in the human body
- Enamel consists of 95% inorganic substances
- It can be up to 2.5 millimeters thick
- Enamel provides critical protection for tooth structure
- The unique crystal structure contributes to its exceptional strength
Understanding Tooth Enamel: The Basics
Your teeth have an incredible protective layer called tooth enamel. It’s a powerful guardian that shields your smile from daily challenges. This remarkable substance is your dental health’s first line of defense.
What is Tooth Enamel?
Tooth enamel is the hard, see-through outer layer of your teeth. It’s made mostly of calcium hydroxyapatite and organic proteins. Enamel is the hardest substance in the human body2.
Special enamel rods form an incredible protective barrier. This shield safeguards the sensitive inner parts of your teeth2.
Importance of Tooth Enamel
Your tooth enamel performs several crucial functions:
- Protects against temperature sensitivity
- Guards against bacterial invasion
- Enables comfortable chewing and eating
- Maintains overall dental structural integrity
Common Myths about Tooth Enamel
“Not all white teeth mean healthy enamel!”
People often misunderstand what tooth enamel can do. Here are some common myths:
- Myth: Enamel can fully regenerate
- Myth: Whiteness equals perfect enamel health
- Myth: Enamel damage is always reversible
Knowing about your tooth enamel structure helps you make smart choices. You can better protect your teeth when you understand enamel’s unique properties3.
The Composition of Tooth Enamel
Tooth enamel is a tough shield for your teeth. It’s a complex structure with a unique composition. Let’s explore why this tissue is so strong and resilient.
Tooth enamel is mostly made of minerals. It contains 95% minerals by weight. The rest is organic material and water4.
The enamel’s crystals are incredibly tiny. They’re about 1,000 times thinner than a human hair5. This small size contributes to enamel’s strength.
Key Minerals in Enamel
Hydroxylapatite is the main mineral in tooth enamel. It forms a super hard protective layer. The enamel also contains other important minerals.
- Calcium
- Phosphorus
- Magnesium
- Sodium
- Fluoride
Organic Matrix in Enamel Structure
Enamel has a unique structure of tightly packed crystal rods. Each rod contains thousands of tiny crystallites5. These rods form a complex grid-like pattern.
“Enamel is the hardest substance in the human body, designed to withstand decades of chewing and resist tooth decay.”5
Scientists use advanced imaging to study enamel’s structure. They’ve found interesting details about its atomic-level makeup5. For example, the crystal cores are more prone to acid erosion than the outer shell5.
Tooth Enamel vs. Other Dental Tissues
Your teeth are made of special tissues. Each tissue has its own job and features. Together, they keep your teeth healthy6.
Tooth enamel is the top layer of your teeth. It’s unique and very protective. Enamel is different from other parts of your teeth7.
Comparing Dental Tissue Characteristics
Let’s explore the unique properties of different dental tissues:
- Enamel: The hardest tissue in the human body6
- Dentin: Softer and more flexible6
- Pulp: Contains nerves and blood vessels6
| Tissue | Composition | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Enamel | 96% inorganic matrix6 | Protection and tooth structure |
| Dentin | 70% mineral, 20% organic matrix6 | Supporting tooth structure |
| Pulp | Soft tissue with blood vessels | Nerve supply and nutrition |
The Role of Cementum
Cementum covers the tooth root. It helps anchor the tooth to your jawbone6. Its structure is like bone, supporting your dental health.
Teeth are not just simple structures, but complex systems of specialized tissues working in harmony.
Your teeth are amazing examples of natural design. Each part works together to make your teeth strong7.
The Formation of Tooth Enamel
Tooth enamel forms before birth through a fascinating process. Learning about teeth development reveals the complexity of dental health. This knowledge can help you care for your teeth better.
Amelogenesis is the complex process of enamel formation during tooth development. Specialized cells called ameloblasts create the hardest substance in your body8. These cells produce proteins that mineralize to form tooth enamel structure9.
The Science of Enamel Development
Your tooth enamel is truly remarkable. It contains 96% minerals, the highest percentage in the human body8. Enamel forms slowly, growing about 4 micrometers per day8.
- Enamel formation begins around the third or fourth month of pregnancy8
- Thickness varies across different tooth surfaces8
- Cusp areas can reach up to 2.5 mm in thickness8
Key Characteristics of Enamel Formation
Tooth enamel development involves fascinating molecular mechanisms. Amelogenin proteins play a crucial role in creating the mineral scaffold9. These proteins form unique ribbons that help calcium phosphate crystals grow9.
| Enamel Formation Characteristic | Details |
|---|---|
| Mineral Composition | Hydroxyapatite (calcium phosphate) |
| Hardness Scale | Ranked 5 on Mohs scale |
| Young’s Modulus | 83 GPa |
“Enamel formation is a testament to the incredible precision of human biological processes.” – Dental Research Journal
Tooth enamel forms before teeth erupt and remains in its final state. Unlike other tissues, mature enamel can’t regenerate or repair itself8. Protecting your enamel through good dental hygiene is vital for long-term oral health.
Factors Affecting Tooth Enamel Health
Tooth enamel is a remarkable protective shield that needs careful attention. Knowing what impacts dental enamel care can help you protect this vital layer of your teeth10.
Dietary Influences on Enamel Integrity
Your diet greatly affects enamel health. Certain foods and drinks can significantly impact your tooth’s protective layer.
Acidic substances pose a challenge to dental enamel care10:
- Citrus fruits like lemons and grapefruit
- Sugary and sticky food items
- Carbonated beverages
“Your diet is a powerful tool in maintaining or damaging tooth enamel” – Dental Health Experts
Protecting Your Enamel Through Oral Hygiene
Maintaining strong enamel health requires a thorough approach to oral care11. Your daily routine can help preserve your dental enamel.
- Use fluoride toothpaste regularly
- Brush gently with soft-bristled toothbrushes
- Limit consumption of acidic foods
- Stay hydrated to promote saliva production
Some lifestyle factors can speed up enamel damage. Teeth grinding, tobacco use, and certain medications can harm your enamel’s integrity10.
Professional dental sealants offer extra protection for those worried about enamel erosion11. Enamel is the hardest tissue in your body10.
Still, it needs consistent care to maintain its strength and protective abilities11.
Enamel Erosion: Causes and Consequences
Tooth enamel shields your smile, but it’s not invincible. Enamel erosion can quietly harm your teeth, weakening them over time. Knowing the causes helps you safeguard your dental health.
How Acidic Foods Affect Enamel
Your diet greatly impacts tooth enamel. High-sugar and acidic foods can slowly wear away your teeth’s protective layer12.
Citrus fruits, sodas, and fruit juices are major culprits in dental erosion13. They can quickly break down enamel if consumed often.
- Carbonated beverages
- Citrus fruits and juices
- Vinegar-based foods
- Alcoholic drinks
Signs of Enamel Erosion
Spotting early signs of enamel erosion helps prevent extensive damage. Look out for these warning signals:
- Tooth sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures
- Yellowish-brown discoloration
- Rounded or worn tooth edges
- Increased risk of tooth decay
Acid reflux, certain medications, and teeth grinding can speed up enamel erosion12. People with naturally thinner enamel face higher risks of dental wear12.
“Prevention is better than cure when it comes to protecting your tooth enamel.”
Regular dental visits and good oral habits can greatly reduce enamel erosion risk12. By addressing potential causes, you’ll keep your smile strong for years.
Protecting Your Tooth Enamel
Tooth enamel is crucial for dental health. Learn how to protect it and keep your smile bright. Good enamel care prevents dental problems and maintains oral health.
Best Practices for Enamel Preservation
Enamel protection involves using the right products and forming good habits. Smart techniques can greatly reduce enamel damage and erosion14.
- Use a soft-bristled toothbrush to minimize abrasion
- Choose dental care products with appropriate RDA values
- Limit consumption of acidic and sugary foods
- Practice gentle brushing techniques
Recommended Dental Care Products
Choosing the right dental products is key for enamel protection15. Fluoride toothpaste is a top choice for strengthening tooth enamel15.
| Product Type | Enamel Protection Benefits |
|---|---|
| Fluoride Toothpaste | Strengthens enamel, supports remineralization |
| Hydroxyapatite Toothpaste | Helps remineralize damaged enamel |
| Soft-Bristled Toothbrush | Reduces mechanical damage to enamel |
Protecting your tooth enamel is an investment in long-term dental health and overall well-being.
Regular dental check-ups help monitor enamel health. Try using a fluoride gel once a week for extra protection14.
These strategies will help keep your enamel strong. A healthy smile boosts confidence and overall well-being.
The Role of Fluoride in Enamel Health
Fluoride plays a vital role in protecting your tooth enamel. This powerful mineral strengthens and shields your teeth from decay16.
Dental experts hail fluoride as a tooth-saving hero. It attracts calcium and phosphate ions, creating a tougher tooth surface16.
Fluoride replaces hydroxyl ions, forming a denser crystal structure. This change greatly boosts enamel’s ability to resist acid attacks16.
How Fluoride Strengthens Enamel
Fluoride works in a remarkable way. It changes your tooth’s calcium hydroxyapatite into fluorapatite, a much stronger mineral17.
This transformation offers key benefits:
- Enhanced mineral density
- Increased resistance to bacterial acid
- Improved overall enamel durability
Sources of Fluoride
You can get fluoride from several sources17:
- Fluoridated water (recommended concentration: 0.7 mg/L)16
- Fluoride toothpaste
- Dental treatments and varnishes
- Some foods and beverages
“Fluoride is nature’s shield for your teeth” – Dental Research Institute
Pro tip: Regular fluoride exposure helps keep your enamel healthy and strong. It’s a key factor in preventing tooth decay17.
Enamel Repair: Myth or Reality?
Tooth enamel is the hardest substance in the human body. Yet, it can’t regenerate once damaged. This makes understanding enamel repair crucial for oral health.
Can Enamel Regenerate?
Enamel can’t naturally rebuild itself. It lacks living cells, making regeneration impossible18.
Remineralization offers a partial solution. It helps strengthen existing enamel through specific dental treatments.
Dental Treatments for Enamel Loss
Modern dentistry offers several ways to address enamel loss:
- Fluoride varnishes to seal damaged enamel
- Synthetic materials to cover exposed areas
- Dental veneers for severe cases19
The FDA has approved multiple safe filling materials for dental restoration. These include:
| Material | Lifespan |
|---|---|
| Porcelain | 5-20 years |
| Composite Resin | 5-15 years |
| Gold | 10-20 years |
Dental treatments can improve appearance and reduce sensitivity. However, they can’t fully restore lost enamel19.
Researchers are exploring new solutions. This includes synthetic materials that mimic natural enamel18.
Protecting your existing enamel through proper oral hygiene remains the best defense against enamel loss.
Future of Tooth Enamel Research
Dental research is unveiling exciting possibilities for tooth health. Scientists are exploring new ways to understand and regenerate tooth enamel20. Advanced studies focus on single-cell investigations and tissue engineering techniques that could transform dental care20.
The genetic makeup of enamel structure is becoming clearer. Recent studies have uncovered complex molecular in enamel formation20. Data from 111 families has revealed insights into conditions like amelogenesis imperfecta.
Proteins like STIM1 and molecules such as ADAM10 are key to understanding enamel development20. These discoveries are shaping our knowledge of tooth enamel formation.
Synthetic enamel technologies are showing promising results. Researchers have created materials that may outperform natural enamel21. The University of Nottingham has developed a synthetic version for innovative dental treatments.
This new material could lead to “smart” teeth that detect health conditions21. While challenges remain, these advancements suggest an exciting future for personalized oral health solutions.
FAQ
What exactly is tooth enamel?
Can tooth enamel regenerate or repair itself?
What causes enamel erosion?
How can I protect my tooth enamel?
How thick is tooth enamel?
What role does fluoride play in enamel health?
What are the signs of enamel erosion?
Is all white tooth enamel healthy?
Source Links
- Build up and protect tooth enamel – https://curaprox.co.nz/blog/post/build-up-and-protect-tooth-enamel?srsltid=AfmBOorQj9CqTvYja5PvdU7WMpIZutQuiwwfsc5tjNmNoQLKdDoBNA6I
- Enamel – https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/enamel
- The Basics of Tooth Anatomy – Dentist in Ardmore, OK – https://www.stortsfamilydentistry.com/2024/05/29/the-basics-of-tooth-anatomy/
- Dental Enamel Formation and Implications for Oral Health and Disease – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6151498/
- Advanced imaging reveals structure of tooth enamel – https://www.nih.gov/news-events/nih-research-matters/advanced-imaging-reveals-structure-tooth-enamel
- Physicochemical Properties and Surface Characteristics of Ground Human Teeth – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9500924/
- What is Tooth Enamel? – https://www.news-medical.net/health/What-is-Tooth-Enamel.aspx
- Tooth enamel – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tooth_enamel
- How Proteins Form Tooth Enamel – https://www.pnnl.gov/publications/how-proteins-form-tooth-enamel
- 6 Things That Can Affect Your Tooth Enamel | Blog – https://asantedental.ca/blog/6-things-that-can-affect-your-tooth-enamel/
- Tooth Enamel | Structure, Function, and Health – https://www.kytdentalservices.com/tooth-anatomy/enamel
- Top 10 Causes of Tooth Enamel Erosion – McCarl Dental Group – https://www.mccarldental.com/blog/top-10-causes-of-tooth-enamel-erosion/
- Dental erosion – https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/dental-erosion
- Tooth Enamel in Birmingham, AL – Roberson Dental Care – https://robersondental.com/steps-you-can-take-to-protect-your-tooth-enamel/
- Build up and protect tooth enamel – https://curaprox.us/blog/post/build-up-and-protect-tooth-enamel?srsltid=AfmBOopZjlBsFFbLCfyVRfpGNKG3uOisp87Awe1VNU8vjOJEKru1seXK
- How Fluoride Protects Dental Enamel from Demineralization – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7339990/
- Role of Fluoride in Dentistry: A Narrative Review – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10799546/
- Synthetic Enamel Could Make Teeth Stronger and Smarter – https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/synthetic-enamel-could-make-teeth-stronger-and-smarter/
- 4 Myths About Dental Restorations – https://www.highlandsdentaldallas.com/blog/4-myths-about-dental-restorations-cip136/
- Editorial: Tooth enamel research: Enamel 10 and beyond – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10661229/
- Artificial Tooth Enamel: New Synthetic Material Could Impact Dental Care – https://www.todaysrdh.com/artificial-tooth-enamel-new-synthetic-material-could-impact-dental-care/