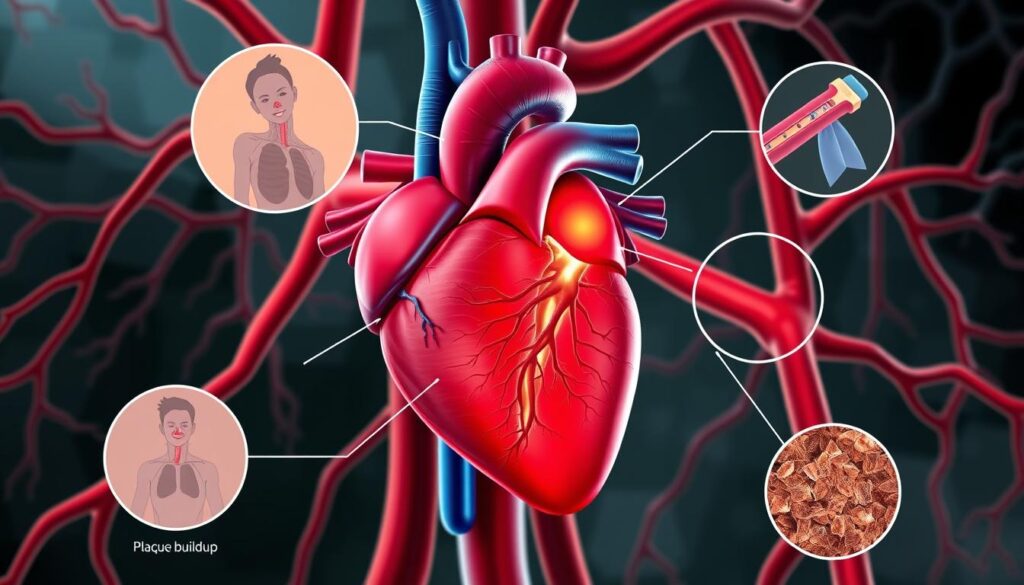
Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) is a critical heart emergency that needs quick action1. It happens when blood flow to your heart suddenly stops2. Knowing the warning signs and risks can save your life3.
Your heart needs steady blood flow to work well. A blood clot or plaque break in your arteries can block this flow2. Chest pain often signals that something’s wrong1.
Spotting symptoms early is crucial. These may include trouble breathing, feeling dizzy, sick, or sweaty1.
Several factors can raise your ACS risk. Smoking, high blood pressure, diabetes, and family history are key ones3.
Key Takeaways
- ACS is a serious medical emergency requiring immediate attention
- Chest pain is the most common warning sign
- Multiple risk factors contribute to heart disease
- Early recognition can prevent severe heart damage
- Lifestyle changes can help reduce ACS risk
What is Acute Coronary Syndrome: Definition and Types
Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) is a critical heart condition. It includes various heart emergencies. Knowing these conditions helps spot heart risks early4.
ACS has three main types of coronary artery disease. These affect how the heart works:
- ST-segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI)
- Non-ST-segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction (NSTEMI)
- Unstable Angina
Understanding STEMI and NSTEMI
STEMI is a full blockage of a heart artery. It shows up on ECG tests. Doctors do ECGs within 10 minutes to diagnose it4.
NSTEMI is a partial artery blockage. It doesn’t show ST-segment elevation on ECGs.
Unstable Angina vs. Heart Attack
Unstable angina differs from a heart attack. It causes chest pain at rest or with little effort. It doesn’t cause permanent heart muscle damage.
The key difference is that it doesn’t harm heart tissue much5.
The Role of Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is the main cause of acute coronary syndrome. It’s when plaque builds up in heart arteries. This plaque can break and form blood clots.
These clots can block blood flow. This can lead to serious heart problems5.
Early recognition and swift medical response can significantly improve outcomes in acute coronary syndrome cases.
Cardiac-specific troponin tests help diagnose these conditions. They show how severe the problem is. These tests can find tiny signs of heart damage.
This helps doctors make better choices for treatment45.
Recognizing Warning Signs and Risk Factors
Knowing the warning signs of coronary artery disease is vital for early detection. Your heart’s well-being depends on spotting potential symptoms quickly. Recognizing these signs can help prevent serious cardiovascular conditions.
Chest pain is the most important warning sign to watch for. It may feel like pressure, tightness, or burning in your chest. This pain can spread to your neck, jaw, shoulders, arms, or back6.
Some people experience shortness of breath without chest pain. This can be just as serious6. Don’t ignore these symptoms if they occur.
Key Warning Signs
- Sudden chest discomfort
- Pain radiating to upper body areas
- Unexpected breathlessness
- Dizziness
- Unexplained sweating
Risk factors for coronary artery disease vary widely. Men over 45 and women over 55 face higher risks. These groups are more likely to develop heart-related issues7.
Primary Risk Factors
- Smoking and tobacco exposure7
- High blood pressure7
- Elevated cholesterol levels7
- Diabetes7
- Physical inactivity7
Stress and genetics can greatly impact your heart disease risk7. Metabolic syndrome, marked by obesity and metabolic issues, doubles your risk. It’s a serious condition to watch for7.
“Prevention is always better than cure when it comes to heart health.”
Not all heart problems show obvious signs. Older people and those with diabetes may have subtle symptoms6. If you notice anything unusual, see a doctor right away.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Facing a cardiac emergency? Quick action is key. Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) needs fast, precise care to protect your heart8.
Emergency Diagnostic Procedures
Your medical team will start with vital tests to check your heart health:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): A crucial test done within minutes of arrival8. It helps doctors quickly spot your heart issue.
- Cardiac Markers: Blood tests that find specific proteins showing heart muscle damage8.
- Coronary Angiogram: A special test to find blockages in heart arteries8.
Advanced Treatment Methods
ACS treatment depends on your specific diagnosis. The main goals? Restore blood flow and stop more heart damage9.
| Treatment Approach | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Primary PCI | Preferred method for STEMI patients, involves opening blocked arteries9 |
| Fibrinolytic Therapy | Alternative treatment when PCI is not immediately available9 |
Cardiac Catheterization and Stenting
Cardiac catheterization is vital for diagnosing and treating heart conditions. Doctors may do angioplasty to open blocked arteries.
“Early intervention can significantly improve patient outcomes in Acute Coronary Syndrome” – Cardiac Care Specialists
Your treatment plan might also include these medications:
- Antiplatelet drugs
- Beta blockers
- Statins
- Nitroglycerin
Remember, lifestyle changes are equally important in managing and preventing future cardiac events8.
Conclusion
Knowing about Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) is key for heart health. Your awareness can help detect and treat issues early. Cardiac diagnostic procedures are vital for comprehensive care10.
Your lifestyle choices can lower ACS risk. In the UK, over 80,000 patients are admitted yearly with acute coronary syndromes. Understanding your risk factors can boost your heart’s strength11.
ACS diagnosis keeps improving. High-sensitivity troponin tests help doctors identify different heart problems more accurately10. The UK’s 30-day mortality for STEMI patients is 8.1%11.
Your heart health journey is personal. Stay informed and work with your doctors. Take charge of your cardiac care to manage and prevent ACS.
Remember, knowledge is your best defense for heart health. Keep learning and making smart choices for your heart’s well-being.
FAQ
What exactly is Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS)?
What are the key warning signs of Acute Coronary Syndrome?
Who is most at risk for Acute Coronary Syndrome?
How is Acute Coronary Syndrome diagnosed?
What are the treatment options for Acute Coronary Syndrome?
Can Acute Coronary Syndrome be prevented?
What’s the difference between STEMI and NSTEMI?
Source Links
- Acute Coronary Syndrome – https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/heart-attack/about-heart-attacks/acute-coronary-syndrome
- Acute coronary syndrome – https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/diseases-conditions/acute-coronary-syndrome
- Acute coronary syndrome – Symptoms and causes – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/acute-coronary-syndrome/symptoms-causes/syc-20352136
- Overview of Acute Coronary Syndromes (ACS) – Cardiovascular Disorders – Merck Manual Professional Edition – https://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/cardiovascular-disorders/coronary-artery-disease/overview-of-acute-coronary-syndromes-acs
- Acute Coronary Syndrome: Practice Essentials, Background, Etiology – https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1910735-overview
- Symptomology, Outcomes and Risk Factors of Acute Coronary Syndrome Presentations without Cardiac Chest Pain: A Scoping Review – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11287626/
- Heart attack-Heart attack – Symptoms & causes – Mayo Clinic – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heart-attack/symptoms-causes/syc-20373106
- Acute coronary syndrome – Diagnosis and treatment – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/acute-coronary-syndrome/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20352140
- Acute Coronary Syndrome: Current Treatment – https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2017/0215/p232.html
- Acute coronary syndrome: Terminology and classification – https://www.uptodate.com/contents/acute-coronary-syndrome-terminology-and-classification
- Acute coronary syndromes – PMC – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6329574/