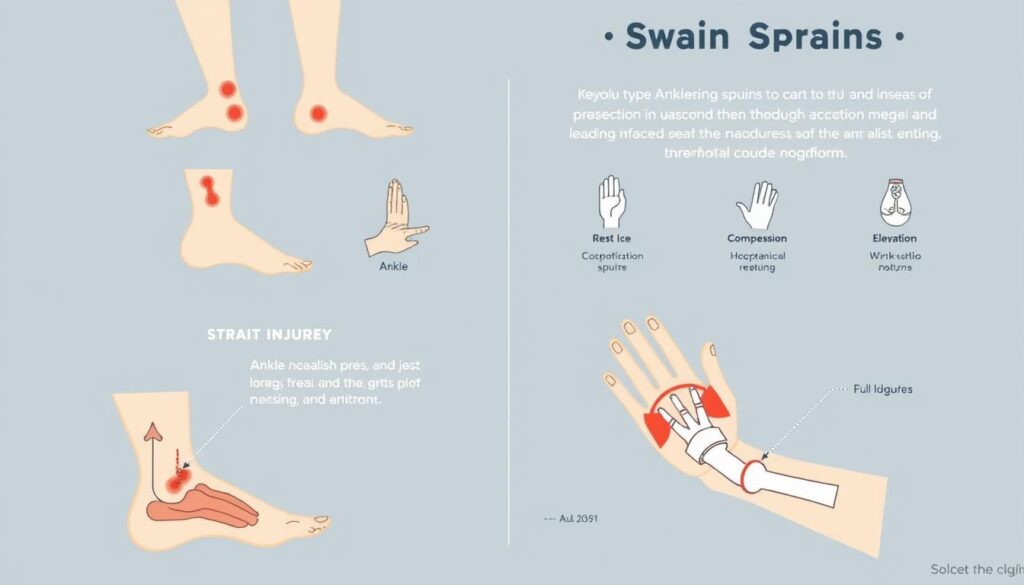
Sprains can strike anyone, anytime. These painful ligament injuries happen when joints are overstretched or torn. They often occur during sports or everyday activities.
Sprains range from mild to severe. Symptoms include swelling, pain, and limited joint movement. Some heal quickly, while others need professional care.
Knowing sprain basics helps you act fast. Quick first aid can make a big difference. It’s vital to know when to seek medical help.
Key Takeaways
- Sprains are common ligament injuries that affect joints
- Different severity levels require varying treatment approaches
- Immediate first aid can help minimize long-term damage
- Professional medical assessment is crucial for severe sprains
- Recovery time varies depending on injury severity1
What Are Sprains and Their Common Causes
Sprains are painful injuries that occur when ligaments stretch or tear during unexpected movements. These injuries can affect your body’s performance and recovery. Learning about sprains helps you protect yourself and heal faster2.
Athletes often experience ankle, wrist, and knee sprains. These injuries can greatly impact their physical performance3.
Types of Ligament Injuries
Ligament injuries are classified into three distinct grades:
- Grade 1: Mild stretching with minimal damage3
- Grade 2: Moderate ligament tears with partial disruption3
- Grade 3: Severe complete ligament tears3
Most Affected Body Parts
Certain body parts are more susceptible to sprains:
| Body Part | Frequency of Sprains |
|---|---|
| Ankle | Most common sprain location2 |
| Knee | Second most frequent injury site3 |
| Wrist | Common in sports and falls3 |
Risk Factors and Common Scenarios
Your risk of experiencing ligament tears increases with certain factors:
- Participation in high-intensity sports3
- Walking on uneven surfaces2
- Sudden directional changes3
- Improper footwear3
- Muscle weakness or poor balance2
“Prevention is always better than cure when it comes to sprains and ligament injuries.” – Sports Medicine Expert
Knowing these risk factors helps you protect yourself. You can take steps to avoid ankle, wrist, and knee sprains23.
The RICE Method: Immediate Treatment for Sprains
The RICE method is crucial for managing acute soft tissue injuries. Dr. Gabe Mirkin introduced this technique in 1978. It has since evolved to help people manage pain and promote healing.
Let’s explore the key components of the RICE method:
- Rest: Avoid activities that cause pain or discomfort to prevent further injury
- Ice: Apply cold packs for 10-20 minutes at least three times daily4
- Compression: Use an elastic bandage to limit swelling5
- Elevation: Keep the injured area above heart level to reduce fluid buildup
Recent research suggests applying RICE for the first 1-3 days after an injury6. Be careful with prolonged rest or icing. These can interfere with your body’s natural healing process6.
| RICE Component | Key Recommendation | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Rest | Avoid painful movements | 1-3 days |
| Ice | Apply cold pack with cloth barrier | 10-20 minutes, 3x daily |
| Compression | Use elastic bandage | Until swelling reduces |
| Elevation | Raise above heart level | When possible, especially at night |
Pro tip: If pain and swelling persist beyond 5-7 days, consult a healthcare professional to prevent further complications6.
PEACE and MICE offer alternative perspectives on injury management6. Over-the-counter pain medications can complement the RICE method. These can provide additional relief for your injury6.
Professional Treatment Options and Recovery Timeline
Treating sprains effectively requires the right approach. A personalized strategy is key for optimal healing. Your specific needs guide the treatment plan.
Professional medical assessment is crucial when you sprain something. Doctors perform thorough exams to evaluate your injury’s extent. This step is vital for proper treatment.
Medical Diagnosis Methods
Healthcare pros use various techniques to assess sprain severity:
- Physical examination to assess swelling and tenderness
- X-rays to rule out fractures
- MRI or ultrasound for detailed ligament damage assessment7
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Physical therapy is crucial for rehabilitation. Your treatment plan may include:
- Targeted strength exercises
- Balance training
- Gradual range of motion activities
“Proper rehabilitation is key to preventing future injuries and restoring full functionality.”
Expected Recovery Periods
Recovery times vary based on injury severity. Minor sprains may heal within a week. Complex injuries might need months of rehab8.
Most ankle sprain patients recover in six weeks with non-operative treatment9. Your recovery depends on injury type, affected body part, and therapy commitment.
Listen to your body and follow expert advice. This approach ensures the best possible outcome for your recovery7.
Conclusion
Protecting your body during physical activities is key to effective injury management. Wear properly fitting footwear and stretch regularly to reduce soft-tissue injury risks10. These strategies help maintain an active lifestyle while minimizing sprain risks11.
Sprain recovery requires patience and strategic care. Most sprains heal within two weeks, but severe injuries may take months12. Include balance exercises, strength training, and supportive gear in your sprain prevention routine.
X-rays and MRIs can help assess injury severity and guide treatment plans11. Pay attention to your body’s signals. Seek medical advice for severe pain, significant swelling, or restricted movement.
Your dedication to proper injury management will help maintain mobility. It allows you to keep enjoying your favorite physical activities. With the right knowledge, you can effectively handle sprains and stay active.
FAQ
What exactly is a sprain?
How do I know if I have a sprain or something more serious?
What is the RICE method, and how does it help with sprains?
How long does it take to recover from a sprain?
When should I see a doctor about a sprain?
Can I prevent sprains from happening?
What pain medications can I take for a sprain?
Do I need physical therapy for a sprain?
Source Links
- Sprains – Diagnosis and treatment – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/sprains/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20377943
- Sprains – Symptoms and causes – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/sprains/symptoms-causes/syc-20377938
- Sprains and Strains Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments – https://www.upmc.com/services/orthopaedics/conditions/sprains-strains
- Treating injuries using the RICE method – https://www.salinememorial.org/news/rice
- The RICE Method for Strains, Sprains and Other Injuries – http://www.union.health/the-rice-method-for-strains-sprains-and-other-injuries
- What Is the RICE Method for Injuries? – https://www.webmd.com/first-aid/rice-method-injuries
- Sprain: First aid – https://www.mayoclinic.org/first-aid/first-aid-sprain/basics/art-20056622
- Recovery Timelines for Common Sports Injuries: Bluetail Medical Group: Alternative Medicine – https://www.bluetailmedicalgroup.com/blog/recovery-timelines-for-common-sports-injuries
- Treatment for Ankle Injuries for Fast Recovery | The Bone & Joint Center – https://www.bone-joint.com/sprained-or-broken-ankle-treatment-options-for-fast-recovery/
- Overview – https://www.haleonhealthpartner.com/en-us/pain-relief/conditions/sprains-strains/overview/
- Heal Faster: Treat Sprains and Strains – https://www.truhealthnow.com/what-we-treat-uc/sprains-and-strains
- Sprain vs Strain: What You Need To Know | Portland Urgent Care – Portland Urgent Care Blog – https://www.portlandurgentcare.com/blog/sprain-vs-strain