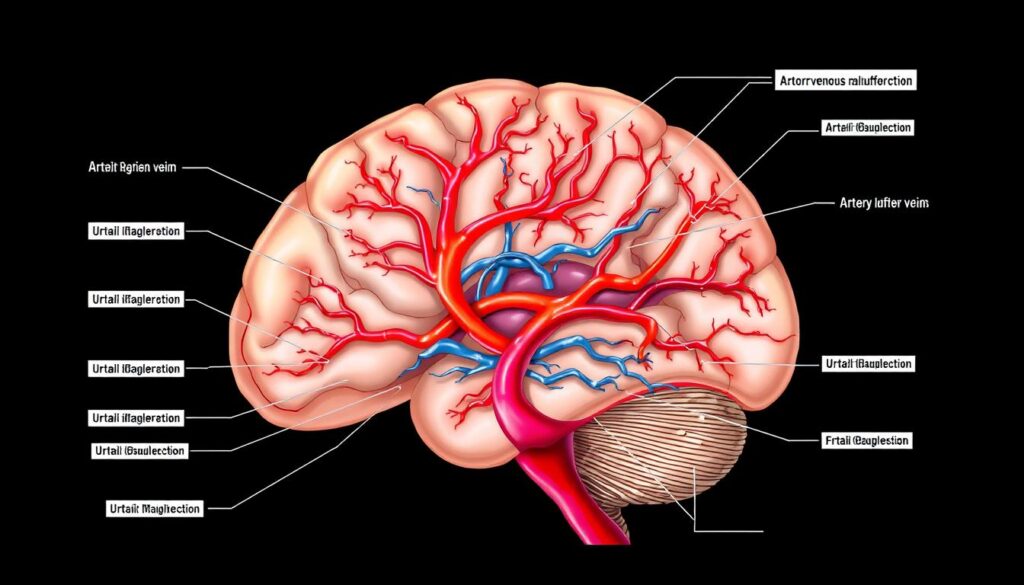
Arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is a complex vascular condition that affects your health. It creates abnormal connections between arteries and veins, disrupting normal blood flow. These tangles can cause serious complications1.
AVMs can occur in various body parts, with brain AVMs being the most well-known. Nearly 12% of people with AVMs experience noticeable symptoms2. These can range from mild to severe.
Symptoms might include cognitive issues, headaches, seizures, and vision problems1. These cerebrovascular disorders can emerge unexpectedly, often surprising patients.
Most AVMs are present from birth but may not cause immediate problems. Genetic factors might contribute to their development. However, they are typically not hereditary1.
Less than 4% of AVMs lead to hemorrhage2. Understanding your specific condition is crucial for proper management.
Key Takeaways
- AVMs are complex vascular abnormalities affecting blood flow
- Symptoms can range from mild cognitive issues to severe neurological complications
- Genetic factors may contribute to AVM development
- Most AVMs are congenital but may not cause immediate symptoms
- Professional medical evaluation is critical for proper management
What is Arteriovenous Malformation and Its Impact on Blood Flow
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are complex neurovascular abnormalities that disrupt normal blood flow. These congenital vascular defects create unique challenges for your circulatory system. They are particularly troublesome in intracranial AVM locations3.
AVMs differ from normal blood vessels, posing potential risks. In a typical system, blood flows through arteries, capillaries, and veins. AVMs interrupt this pathway, creating direct connections between arteries and veins3.
Unique Characteristics of AVM Blood Flow
- Direct arterial to venous connection without capillary network
- High-pressure blood flow
- Potential oxygen deprivation in surrounding tissues
- Increased risk of bleeding4
Common AVM Locations
AVMs can develop in various body parts. However, they most frequently occur in critical areas:
| Location | Prevalence | Potential Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Brain | Most Common | Headaches, seizures, muscle weakness3 |
| Spinal Cord | Secondary Location | Numbness, potential motor function issues |
AVM Development and Progression
These neurovascular abnormalities typically develop before birth or early in life. They can grow and change over time. Significant developments may occur during puberty or pregnancy4.
AVMs are like unexpected roadblocks in your body’s circulatory highway, redirecting blood flow in unpredictable ways.
Some key insights about AVM progression include:
- 2-4% chance of bleeding per year for unruptured AVMs4
- 17% of previously ruptured AVMs may burst annually4
- Symptoms often appear between ages 10 and 403
Knowing about these complex vascular formations can help you manage potential risks. It’s important to seek appropriate medical guidance for proper care.
Common Signs and Symptoms of AVM
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are complex neurovascular abnormalities. They can be silent or cause significant challenges. Some people may have an AVM without realizing it5.
AVM symptoms require attention to various neurological signals. Most AVMs remain silent until a critical moment arrives. Common AVM symptoms include:
- Sudden severe headaches
- Seizures
- Vision problems
- Muscle weakness or paralysis
- Difficulty speaking
- Coordination challenges
Brain-related AVM symptoms can be unique. You might hear an abnormal ringing in your ears. Unexpected changes in perception or cognitive difficulties may occur6.
Spinal AVMs present differently. They can cause acute back pain and limb weakness6.
“Silent until dangerous” describes many AVM experiences.
Age affects when AVM symptoms appear. Most patients notice symptoms between ages 20 and 405. Nearly half of AVM patients stay symptom-free until a rupture happens5.
| AVM Location | Potential Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Brain | Headaches, seizures, speech problems |
| Spinal Cord | Back pain, movement difficulties |
| Nervous System | Numbness, cognitive changes |
The yearly rupture risk is between 2% and 4%. This can have serious consequences5. A brain AVM rupture can be deadly.
The mortality rate can reach 10%. Up to 50% of patients may face lasting neurological impacts5.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options for Arteriovenous Malformation
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) require precise diagnostic and treatment approaches. Sophisticated techniques are essential to identify and address these unique vascular abnormalities. Your medical team will guide you through this complex healthcare journey.
Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Techniques
Diagnostic imaging is crucial for identifying and evaluating AVMs. Your doctors will use multiple advanced imaging methods. These techniques provide a comprehensive understanding of the malformation.
- Cerebral angiography provides the most detailed visualization of brain AVMs, revealing intricate details about feeding arteries and draining veins7
- MRI scans offer sensitive insights into AVM location and blood circulation7
- CT scans help detect potential bleeding and structural abnormalities8
Treatment Approaches and Interventions
Your AVM treatment plan depends on factors like size, location, and potential risks. The main interventions include:
- AVM embolization: A minimally invasive procedure where special materials are injected to block abnormal blood vessels8
- AVM surgery: Complete surgical removal when the malformation poses significant risks8
- Stereotactic radiosurgery: Targeted radiation to damage and close abnormal blood vessels7
“Each AVM is unique, and treatment strategies must be tailored to individual patient needs and characteristics.” – Vascular Neurology Specialist
Risk Factors and Potential Complications
Understanding potential risks is crucial for effective AVM management. Key considerations include the potential for hemorrhage and neurological complications. Age and medical history also play a role in individual risk factors.
Your healthcare provider will use thorough diagnostic imaging to assess your situation. This assessment helps develop the most appropriate treatment strategy for your specific case7.
Conclusion
Arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is a complex cerebrovascular disorder. It needs a personalized medical approach. Most intracranial AVMs are silent, making regular check-ups crucial9.
Proper AVM management begins with a thorough medical assessment. The yearly bleeding risk varies from 2-4.5%, based on your AVM’s features910.
Working with specialists can greatly improve your outcomes. Ongoing research enhances our grasp of these intricate vascular conditions. Stay informed and attend regular doctor visits to manage your AVM effectively11.
Each AVM case is unique and requires a tailored treatment plan. Your active involvement with medical experts is vital. Stay positive and committed to your personalized care strategy.
FAQ
What is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)?
Are AVMs dangerous?
What symptoms might indicate an AVM?
How are AVMs diagnosed?
What treatment options are available for AVMs?
Can AVMs be prevented?
Are AVMs more common in certain age groups?
What complications can arise from untreated AVMs?
Source Links
- Arteriovenous malformation – Symptoms and causes – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/arteriovenous-malformation/symptoms-causes/syc-20350544
- Arteriovenous Malformations – https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/arteriovenous-malformations
- Brain AVM (arteriovenous malformation) – Symptoms and causes – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/brain-avm/symptoms-causes/syc-20350260
- Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM) – https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/16755-arteriovenous-malformation-avm
- Arteriovenous Malformation Symptoms – https://www.aaroncohen-gadol.com/en/patients/arteriovenous-malformation/types/symptoms
- Arteriovenous Malformations (AVM): Symptoms & Treatment | SSM Health – https://www.ssmhealth.com/services/neurosciences/av-malformation
- Brain AVM (arteriovenous malformation) – Diagnosis and treatment – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/brain-avm/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20350265
- Arteriovenous malformation – Diagnosis and treatment – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/arteriovenous-malformation/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20454895
- Arteriovenous Malformations of the Central Nervous System – StatPearls – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK531479/
- Updates in arteriovenous malformation management: the post-ARUBA era – https://svn.bmj.com/content/5/1/34
- Frontiers | Case Report: A Rare Abdominopelvic Arteriovenous Malformation: Originating From Splenic Artery and Draining Into Portal Vein – https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/cardiovascular-medicine/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2022.916096/full