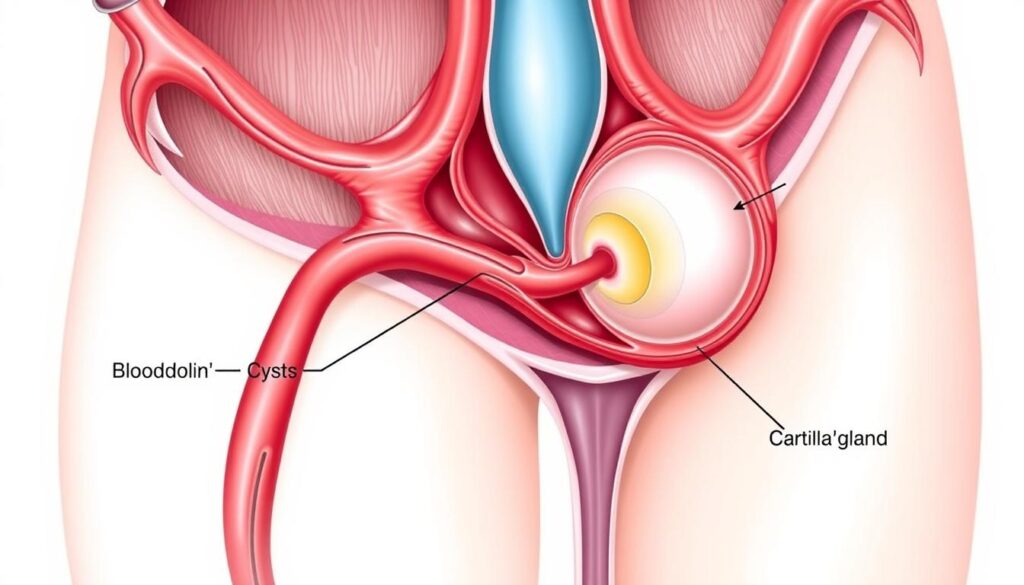
Bartholin’s cysts are common vaginal issues. They form when Bartholin’s glands near the vaginal opening get blocked. This blockage causes fluid buildup1.
Small, uninfected cysts may go unnoticed. However, they can quickly become painful vulvar abscesses1. These cysts usually appear on one side of the vaginal opening.
Pelvic pain from Bartholin’s cysts can be worrisome. They often develop rapidly within days1. Understanding their nature helps in managing them effectively.
Prevention is key in dealing with Bartholin’s cysts. Safe sex and good hygiene reduce infection risks. These practices also help prevent abscess formation1.
Be aware of potential complications. Seek medical advice if you notice ongoing symptoms. Proper care is essential for effective treatment.
Key Takeaways
- Bartholin’s cysts are fluid-filled sacs near the vaginal opening
- They can develop quickly and cause significant discomfort
- Good hygiene and safe sex practices can help prevent infections
- Most cysts heal naturally with proper care2
- Professional medical advice is crucial for proper treatment
What is a Bartholin’s Cyst?
Bartholin’s glands are vital for women’s reproductive health. These tiny glands play a key role in vaginal lubrication. They’re crucial for overall intimate wellness.
Anatomy and Location
Bartholin’s glands sit on each side of the vaginal opening. These pea-sized structures become active during puberty. They typically shrink after menopause3.
These glands are critical for vaginal comfort. They also play a big part in sexual health.
Function of Bartholin’s Glands
Bartholin’s glands mainly provide vaginal lubrication. When working properly, they secrete fluid that helps:
- Reduce friction during sexual activity
- Maintain vaginal moisture
- Support overall reproductive health
Potential Complications
Bartholin’s glands can develop issues like cysts or vulvar swelling3. A Bartholin’s cyst forms when the gland’s duct gets blocked. This prevents normal fluid drainage3.
These cysts can form due to various factors:
- Sexual activity
- Sexually transmitted infections
- Direct injury to the area
- Surgical complications
“Knowledge about your body is the first step to maintaining reproductive health.”
Women of reproductive age are more likely to experience Bartholin’s gland complications3. If you notice unusual swelling or discomfort, consult a healthcare professional. They can provide proper diagnosis and treatment.
Common Causes of Bartholin’s Cysts
Bartholin’s cysts form when gland ducts get blocked. This prevents normal fluid drainage. Understanding these causes helps manage and prevent cysts better.
Blockages in Bartholin’s Ducts
Cysts develop when gland ducts become obstructed. Blockages can occur due to multiple factors, leading to potential complications4.
Cyst sizes vary from tiny to golf ball-sized. The extent of the blockage determines their size4.
Infection and Inflammation Triggers
Several key factors contribute to Bartholin’s cyst formation:
- Bacterial infections, including E. coli and Staphylococcus aureus5
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like gonorrhea and chlamydia4
- Physical trauma to the vulvar area
- Reduced gland function with age
Women aged 20-30 who are sexually active face higher risks. These cysts can become serious if infected45.
Prevention is key: using barrier contraception can significantly reduce the risk of infection-related cyst development4.
About 2% of women experience Bartholin’s duct cysts or abscesses. Knowing early signs helps you seek timely medical help5.
Symptoms You Should Not Ignore
Bartholin’s cysts can be tricky to spot. These common growths affect about 2 out of 10 women of childbearing age. Small cysts may go unnoticed, but larger ones can cause discomfort.
Recognizing Painful Symptoms
Vulvar pain may signal a Bartholin’s cyst. You might feel pain during sex or while sitting and walking. These symptoms usually occur on one side of the vaginal opening6.
- Tender lump near vaginal opening
- Swelling in the labia
- Redness and warmth in affected area
Warning Signs of Potential Complications
An infected Bartholin’s cyst can lead to more severe symptoms. You might experience fever, increased swelling, and significant pain7.
Watch out for these red flags:
| Symptom | Potential Significance |
|---|---|
| Sudden onset of pain | Possible infection developing |
| High fever | Sign of spreading infection |
| Persistent swelling | Potential need for medical intervention |
“Early detection and proper care can prevent serious complications with Bartholin’s cysts.”
If you’re over 40 or have ongoing symptoms, see your doctor. Only a healthcare provider can confirm a Bartholin’s cyst through a thorough exam6.
Treatment Options for Relief
Bartholin’s cysts offer various treatment options based on severity. Sitz baths can provide initial relief. Soaking in warm water four times daily may help resolve infected cysts8.
If symptoms persist after three days, consult a healthcare professional8. Medical interventions are necessary for stubborn or infected cysts. Surgical drainage is common, with balloon catheter insertion showing promising results9.
Marsupialization creates a permanent drainage opening for deep or recurring cysts10. Antibiotics may be prescribed if an infection is present. For those over 40 or postmenopausal, a biopsy might be recommended8.
In rare cases, complete removal of the Bartholin’s gland may be required8. Follow post-treatment care instructions carefully. This may include avoiding sexual activity and tampons for up to 4 weeks9.
FAQ
What exactly is a Bartholin’s cyst?
Who is most likely to develop a Bartholin’s cyst?
What causes Bartholin’s cysts to form?
What symptoms should I watch out for?
How can I treat a Bartholin’s cyst at home?
When should I see a doctor about a Bartholin’s cyst?
What medical treatments are available?
Can Bartholin’s cysts be prevented?
Source Links
- Bartholin’s cyst: Treatment depends on size, pain, infection-Bartholin’s cyst – Symptoms & causes – Mayo Clinic – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/bartholin-cyst/symptoms-causes/syc-20369976
- What Is a Bartholin Cyst? – https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17737-bartholin-cyst
- Bartholin’s cysts – https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/bartholins-cysts
- Bartholin’s cyst: Causes, treatment, and symptoms – https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/185022
- Bartholin Duct Cyst and Gland Abscess: Office Management – https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2019/0615/p760.html
- What Is a Bartholin’s Gland Cyst? – https://www.webmd.com/women/bartholins-gland-cyst
- Bartholin cyst or abscess: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia – https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001489.htm
- Bartholin Cyst Home Treatment – https://www.healthline.com/health/bartholin-cyst-home-treatment
- Bartholin’s cyst – Treatment – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/bartholins-cyst/treatment/
- Management of Bartholin’s Duct Cyst and Gland Abscess – https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2003/0701/p135.html