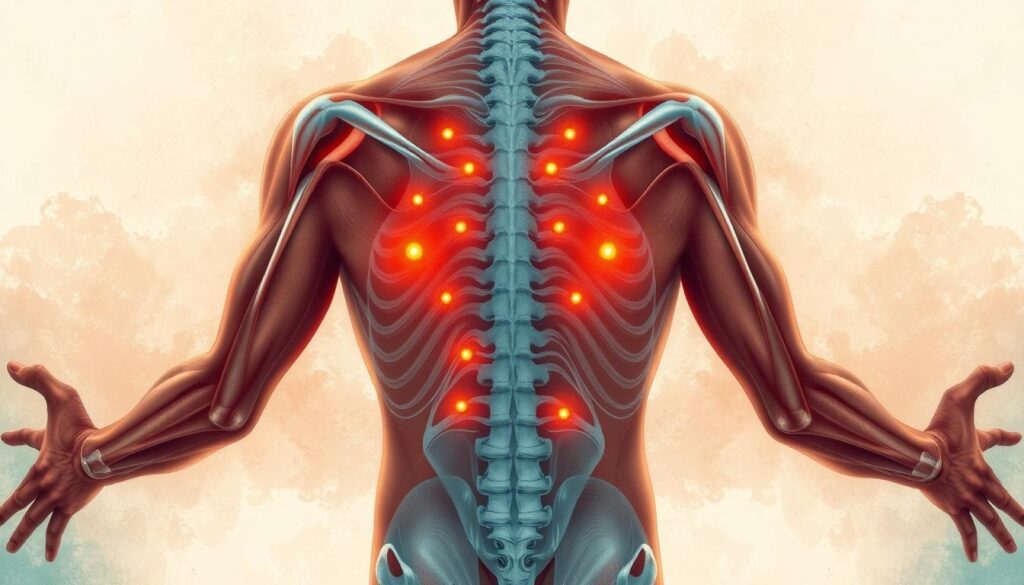
Myofascial pain syndrome (MPS) is a complex condition affecting millions. It causes muscle pain and discomfort that can greatly impact daily life1. Your muscles might feel tender with specific trigger points creating intense sensations when pressed1.
MPS involves tight muscle fibers causing referred pain and discomfort2. Repetitive motions, poor posture, and stress can lead to these painful trigger points2.
The pain can feel like burning, aching, or stabbing sensations. These symptoms often worsen with activity or stress1. Chronic pain from MPS can also cause sleep issues, headaches, and fatigue1.
Key Takeaways
- Myofascial pain syndrome is a complex chronic pain condition
- Trigger points can cause localized and referred pain
- Stress and repetitive motions can worsen symptoms
- Mental health can be impacted by persistent muscle pain
- Early recognition and management are crucial
What Is Myofascial Pain Syndrome and Its Causes
Myofascial pain syndrome affects muscles and soft tissues. It causes ongoing discomfort and may limit daily activities3. Knowing its causes can help you manage this tough condition better.
Common Triggers and Risk Factors
Muscle knots and soft tissue pain can come from many sources. Here are key triggers for myofascial pain syndrome:
- Repetitive work activities4
- Poor ergonomic postures4
- Sustained muscle tension4
- Emotional stress and anxiety4
How Trigger Points Develop
Trigger points are specific areas of muscle tension. They can cause pain in different body parts4. These points often form in tight, ropey muscle bands.
Trigger points can be active or latent. Active points hurt at rest, while latent ones hurt when pressed5.
The Role of Muscle Tension and Stress
Stress greatly affects muscle tension and myofascial pain syndrome. Long-term emotional strain can lead to unconscious muscle clenching. This creates lasting muscle knots and soft tissue discomfort3.
“Effective management requires understanding the complex interplay between physical and psychological factors”3
| Risk Factors | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Repetitive Motion | High muscle strain |
| Emotional Stress | Increased muscle tension |
| Poor Posture | Muscle imbalance |
| Nutritional Deficiencies | Reduced muscle recovery |
Knowing these factors helps you take action. You can manage and possibly prevent muscle tension and related pain4.
Key Symptoms and Warning Signs
Myofascial pain syndrome can greatly affect your daily life. It causes ongoing muscle discomfort and specific warning signs. Knowing these symptoms helps you spot and tackle the condition early6.
Key symptoms of chronic pain in this syndrome include:
- Deep, aching muscle pain that persists or intensifies over time7
- Presence of tender knots called trigger points in muscles6
- Difficulty sleeping due to persistent pain7
- General fatigue and muscle weakness7
Muscle pain can show up in unique ways. It may spread to different body areas. Unlike other conditions, it doesn’t cause burning or tingling feelings7.
“Recognizing trigger points is crucial in managing myofascial pain syndrome”
Stress and ongoing muscle tension can raise your risk of trigger points. People with repeated muscle stress or injuries are more likely to get this condition6.
If left untreated, myofascial pain syndrome can cause more problems:
- Potential development of fibromyalgia6
- Sleep disturbances7
- Mental health challenges like depression7
Early recognition and professional medical consultation are essential for effective management of myofascial pain syndrome.
Treatment Options for Myofascial Pain Syndrome
Myofascial pain syndrome requires a comprehensive approach tailored to your unique symptoms. Your treatment plan will likely include multiple strategies for relief. These aim to improve your quality of life through targeted medical interventions.
Medical Interventions and Medications
Carefully chosen medications often kickstart myofascial pain management. Prescription drugs can effectively control your symptoms8:
- Pain relievers
- Muscle relaxers
- Anti-depressants
- Tranquilizers
Physical Therapy and Exercise
Physical therapy is key to managing your pain. Trigger point therapy and specific exercises can ease muscle tension and boost mobility9.
Your treatment might include:
- Myofascial release therapy
- Gentle stretching techniques
- Manipulation therapy
- Dry needling
Alternative Treatment Methods
Alternative treatments provide extra pain management options10. These may include:
- Acupuncture
- Massage therapy
- Biofeedback
- Ultrasound therapy
“Effective treatment is about finding the right combination of therapies that work for your specific condition.” – Pain Management Specialist
Lifestyle changes can greatly impact your recovery. Regular exercise and stress reduction are vital for pain management. Maintaining a healthy diet also plays a crucial role10.
Conclusion
Myofascial pain syndrome needs a complete approach to treat chronic pain. This condition is treatable, even though it’s challenging. Early action is key to prevent long-term issues and improve life quality11.
Effective pain management goes beyond medical treatments. Lifestyle changes are crucial in addressing trigger points and easing muscle tension12. You can take action by maintaining good posture and reducing stress.
Incorporating targeted therapeutic approaches recommended by health experts can also help11. Recovery may seem tough, but the right mix of treatments can manage symptoms effectively.
Myofascial pain syndrome affects many people. In fact, musculoskeletal pain impacts 33 percent of adults12. Stay positive and stick to your treatment plan. Many successfully deal with this condition and regain mobility.
FAQ
What is Myofascial Pain Syndrome?
What causes Myofascial Pain Syndrome?
What are the main symptoms of Myofascial Pain Syndrome?
How is Myofascial Pain Syndrome diagnosed?
What are the most effective treatments?
Can Myofascial Pain Syndrome be prevented?
Is Myofascial Pain Syndrome a permanent condition?
How does Myofascial Pain Syndrome differ from Fibromyalgia?
Source Links
- Muscle Pain (Myofascial Pain Syndrome) – https://www.webmd.com/pain-management/myofascial-pain-syndrome
- Myofascial Pain Syndrome | National Spine Health Foundation – https://spinehealth.org/article/myofascial-pain-syndrome/
- Myofascial pain syndrome – PubMed – https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2657382/
- Myofascial Pain: Treatment, Symptoms, Causes, and More – https://www.healthline.com/health/myofascial-pain
- Myofascial Pain – Causes & Treatment | Made for This Moment – https://madeforthismoment.asahq.org/pain-management/types-of-pain/myofascial-pain-syndrome/
- Myofascial pain syndrome – Symptoms and causes – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/myofascial-pain-syndrome/symptoms-causes/syc-20375444
- Myofascial Pain Syndrome – https://www.columbiadoctors.org/health-library/condition/myofascial-pain-syndrome/
- Treatment of Myofascial Pain Syndrome – London Pain Clinic – https://www.londonpainclinic.com/conditions/treatment-of-myofascial-pain-syndrome-23/
- Myofascial Pain Syndrome | Houston Methodist – https://www.houstonmethodist.org/neurology/conditions-treatments/pain/myofascial-pain/
- Myofascial Pain Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms and Treatments – https://www.apollohospitals.com/diseases-and-conditions/myofascial-pain-syndrome-causes-symptoms-and-treatments/
- Myofascial Pain Syndrome: Tips and Techniques for Relief – Southeast Pain & Spine Care – https://www.sepainandspinecare.com/myofascial-pain-syndrome-tips-and-techniques-for-relief/
- Myofascial pain syndrome – https://www.pathos-journal.com/2020_3_214.html