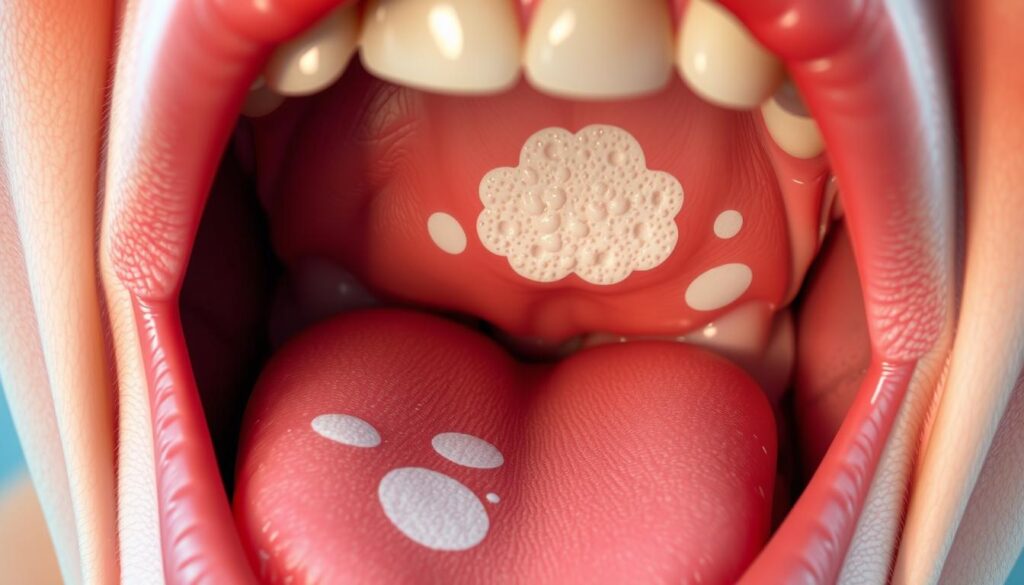
Oral thrush is a common fungal infection that can affect anyone. It occurs when Candida albicans fungus overgrows in your mouth. This creates uncomfortable white patches and potential health issues12.
Persistent mouth discomfort or white lesions might signal this fungal infection. Babies, older adults, and those with weak immune systems are often affected12.
Good oral health is key in preventing and managing oral thrush. Certain medications, health conditions, and lifestyle factors can raise your risk2.
Key Takeaways
- Oral thrush is a fungal infection caused by Candida albicans
- Babies and older adults are more susceptible to this condition
- Weakened immune systems significantly increase infection risk
- Good oral hygiene can help prevent and manage oral thrush
- Treatment options include antifungal medications and home remedies
What is Oral Thrush and What Causes It?
Oral candidiasis is a common fungal infection. It can affect anyone, but some people are more at risk. Knowing the causes and risk factors helps protect against this uncomfortable condition.
Understanding Candida Fungus
Candida fungus naturally exists in small amounts in your body. When balanced, it poses no threat3. A healthy immune system usually keeps this fungus in check4.
However, certain conditions can trigger an overgrowth. This overgrowth can lead to oral thrush.
Common Risk Factors
- Weakened immune system4
- Chronic medical conditions like diabetes4
- Prolonged antibiotic use
- Age-related vulnerabilities (infants and elderly)3
- Smoking
- Poor oral hygiene
Connection to Health Conditions
Oral thrush can be tough for people with compromised health. Those with HIV/AIDS, cancer, or diabetes face higher risks of severe infections4.
The key to managing oral thrush is understanding its underlying causes and maintaining a strong immune system.
In severe cases, Candida can spread beyond the mouth. It may affect the esophagus, lungs, and other body systems4. Early detection and proper treatment are crucial.
Prevention Strategies
- Maintain excellent oral hygiene3
- Visit your dentist regularly
- Manage underlying health conditions
- Practice good nutrition
Understanding risk factors helps prevent oral candidiasis. Taking proactive steps can greatly reduce your chances of developing this infection.
Symptoms of Oral Thrush
Spotting oral thrush early helps manage this uncomfortable condition. Knowing the key symptoms empowers you to seek proper treatment. This prevents complications and ensures quick relief.
Identifying the Signs and Symptoms
Oral thrush often shows up as white patches in your mouth. These creamy spots can appear on your tongue, inner cheeks, and throat5. They’re a telltale sign of oral thrush and can be tough to remove6.
- Creamy white lesions that may bleed when scraped
- Redness and soreness in the mouth
- Cottony feeling inside your mouth
- Potential loss of taste
Differences Between Oral Thrush and Other Conditions
It’s important to tell oral thrush apart from other mouth issues. Unlike regular mouth sores, thrush white patches cannot be easily wiped away. When removed, these patches leave red areas that might bleed6.
When to Seek Medical Attention
See a doctor if oral thrush symptoms don’t go away or get worse. Some groups need medical help right away:
- Infants experiencing feeding difficulties5
- Elderly individuals
- People with weakened immune systems
- Those with persistent symptoms after one week of treatment6
Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent more serious complications of oral thrush.
Certain factors can make you more likely to get oral thrush. These include diabetes, antibiotics use, and steroid medications7. Keep an eye on your oral health to lower potential risks.
Treatment Options for Oral Thrush
Oral thrush has several treatment strategies to manage and eliminate the infection. Antifungal medication is the main approach for this condition8. Your doctor may suggest different options based on your symptoms and health9.
Prescription treatments often include antifungal medications as tablets, lozenges, or liquid solutions9. These target the Candida albicans fungus causing the infection8. Treatment usually lasts 10 to 14 days, depending on age and health conditions9.
Home remedies can support medical treatment and improve oral hygiene. Saltwater rinses, coconut oil pulling, and apple cider vinegar rinses may help fight the infection9. You can also try prevention measures suggested by doctors.
These include good dental habits, less sugar, and managing chronic conditions like diabetes8. Regular teeth brushing and proper denture care are key to prevent recurrence. Seek medical help if symptoms persist or worsen9.
FAQ
What exactly is oral thrush?
Who is most at risk of developing oral thrush?
What are the common symptoms of oral thrush?
How is oral thrush treated?
Can oral thrush be prevented?
When should I see a doctor about oral thrush?
Is oral thrush contagious?
Can oral thrush indicate a more serious health condition?
Source Links
- Oral thrush – Symptoms and causes – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/oral-thrush/symptoms-causes/syc-20353533
- Do You Have Thrush? If So, Here Are Some Reasons Why – https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/what-is-thrush
- Oral thrush in adults – https://www.nhsinform.scot/illnesses-and-conditions/infections-and-poisoning/oral-thrush-in-adults/
- Thrush: What Is It and How To Get Rid of It – https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/10956-thrush
- Everything You Need to Know About Oral Thrush – https://www.healthline.com/health/thrush
- Oral thrush (mouth thrush) – https://www2.hse.ie/conditions/oral-thrush/
- Oral thrush: Symptoms, treatments, and more – https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/178864
- Oral thrush – https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/oral-thrush
- Remedies for Oral Thrush – https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/remedies-for-oral-thrush