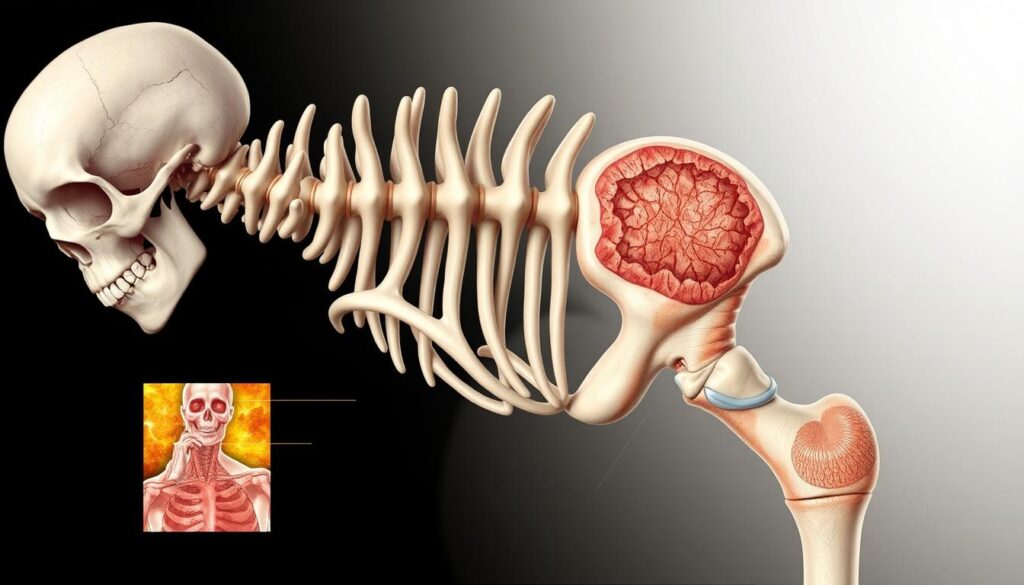
Paget’s Disease of Bone disrupts normal bone remodeling. It can cause bone pain, deformities, and increased fracture risks1. This condition affects about 2-3% of people over 551.
Genetics play a big role in Paget’s disease. 25-40% of patients have a family history of the condition1. Men are more likely to get this bone disorder2.
The disease is common in the US, England, and Western Europe1. Osteoclasts, specialized bone cells, become overactive in Paget’s disease. This leads to abnormal bone remodeling.
Weakened bones and increased pain can result. Potential bone fractures may affect your daily life. Understanding these effects is crucial for managing the condition.
Key Takeaways
- Paget’s disease primarily affects individuals over 55
- Genetic factors contribute to disease development
- Bone pain and potential fractures are common symptoms
- Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications
- Bisphosphonate medications can effectively control the condition
What is Paget’s Disease of Bone
Paget’s disease of bone disrupts normal bone remodeling. It affects how bones grow, rebuild, and maintain structure. This condition creates challenges for skeletal health3.
The disease typically impacts specific areas of the skeleton. Some individuals experience changes in just one or a few bones4.
Understanding Bone Remodeling Process
Healthy bone remodeling balances osteoclasts and osteoblasts. Paget’s disease makes this process abnormal. Osteoclasts become overactive, breaking down bone faster than osteoblasts can rebuild it3.
This leads to larger, denser bones. However, these bones are paradoxically weaker.
Risk Factors and Causes
Genetic factors play a significant role in Paget’s disease. Your risk increases with close relatives who have the condition3.
The disease is more prevalent in:
- Individuals over 40 years old4
- People of northern European heritage3
- Those with a family history of bone disorders
Common Symptoms and Complications
Many people with Paget’s disease have no initial symptoms. When symptoms appear, they can include:
- Bone pain
- Bone fractures
- Bone deformities
- Potential nerve compression3
Complications might involve arthritis, hearing loss, and rarely, bone tumors. Doctors often discover the condition through blood tests or X-rays3.
“Understanding your bone health is the first step in managing Paget’s disease effectively.”
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Healthcare providers use X-rays and blood tests to diagnose Paget’s disease of bone. Specialized bone scans help assess the extent of bone involvement. These tools are crucial for confirming the condition56.
Blood tests measure alkaline phosphatase levels. High levels of this enzyme can indicate active bone remodeling. This is a key feature of Paget’s disease5.
Treatment Approaches
Bisphosphonates are the main treatment for managing bone growth and reducing symptoms. Doctors often prescribe zoledronic acid, pamidronate, or alendronate. These drugs slow down bone turnover5.
Patients can take these medications orally or through intravenous infusion. Zoledronate provides pain relief for several years7.
- Zoledronate: Provides pain relief for several years7
- Risedronate: Oral medication with potential stomach-related side effects7
Calcitonin is an option for those who can’t take bisphosphonates. It’s given by injection or nasal spray. Calcitonin treatments usually last up to three months57.
| Treatment Option | Administration | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Bisphosphonates | Oral/Intravenous | Ongoing management |
| Calcitonin | Injection/Nasal Spray | Up to 3 months |
Supportive therapies can boost quality of life. Physiotherapy and occupational therapy help manage pain and improve mobility. Walking sticks and other devices can also be helpful7.
Vitamin D supplements and calcium-rich diets support overall bone health. Regular monitoring and a complete treatment plan help manage Paget’s disease effectively7.
In rare cases, surgery might be needed for fractures, bone deformities, or severe joint problems5.
With proper care, patients can maintain their quality of life. This approach helps minimize potential complications of Paget’s disease.
Conclusion
Paget’s Disease of Bone requires a proactive approach to bone health. Working with healthcare professionals is key to developing an effective treatment strategy8. With proper medical care, you can improve your life quality and reduce potential complications. Research backs comprehensive management.
Genetic factors are important in Paget’s Disease of Bone. Up to 40% of cases show familial predisposition8. The disease is more common in people of European ancestry9.
Modern treatments offer hope. Antiresorptive agents like bisphosphonates help manage bone remodeling and slow disease progression8.
Your treatment plan should be tailored to your needs. Regular check-ups and following prescribed medications are crucial. Lifestyle changes can also help manage this chronic condition.
Stay informed about new research and treatments. Medical understanding of Paget’s Disease of Bone is always improving. Early diagnosis and active management can help maintain your bone health8.
Teaming up with your doctor is vital for managing Paget’s Disease of Bone. Stay engaged and follow recommended treatments. A positive outlook can help you navigate this challenging but manageable condition.
FAQ
What is Paget’s Disease of Bone?
What are the main symptoms of Paget’s Disease?
Who is most at risk for developing Paget’s Disease?
How is Paget’s Disease diagnosed?
What are the primary treatment options?
Can Paget’s Disease be cured?
How can I manage Paget’s Disease at home?
Source Links
- Paget’s Disease of Bone – OrthoInfo – AAOS – https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/pagets-disease-of-bone
- Paget’s disease of bone: How to relieve the discomfort-Paget’s disease of bone – Symptoms & causes – Mayo Clinic – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pagets-disease-of-bone/symptoms-causes/syc-20350811
- Paget’s Disease of Bone | MedlinePlus – https://medlineplus.gov/pagetsdiseaseofbone.html
- Paget’s disease of bone – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/pagets-disease-bone/
- Paget’s disease of bone: How to relieve the discomfort-Paget’s disease of bone – Diagnosis & treatment – Mayo Clinic – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pagets-disease-of-bone/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20350816
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Paget’s Disease of Bone – https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2002/0515/p2069.html
- Paget’s disease of bone – Treatment – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/pagets-disease-bone/treatment/
- Diagnosis and treatment of Paget’s disease of bone: position paper from the Italian Society of Osteoporosis, Mineral Metabolism and Skeletal Diseases (SIOMMMS) – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11142991/
- Updates on Paget’s Disease of Bone – https://e-enm.org/journal/view.php?number=2339