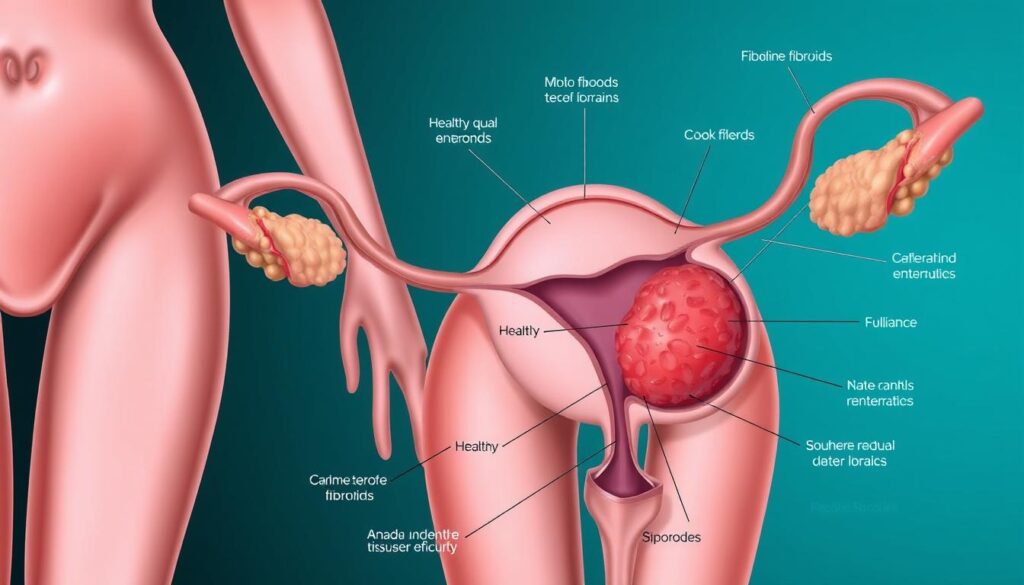
Uterine fibroids are common non-cancerous growths affecting many women. These myomas or leiomyomas develop in and around the uterus1. Up to 77% of women experience these growths during their childbearing years1.
Fibroids can vary greatly in size and number. They range from tiny, undetectable masses to growths as big as a grapefruit2. Some women have no symptoms, while others face serious health issues2.
Your risk of fibroids depends on several factors. Black women often develop fibroids earlier and have worse symptoms2. Other risk factors include family history, obesity, diet, and lifestyle choices2.
Key Takeaways
- Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths affecting up to 77% of women
- Fibroids can range from tiny to grapefruit-sized
- Some women experience no symptoms, while others may have significant health impacts
- Black women are at higher risk of developing fibroids
- Lifestyle and genetic factors play a role in fibroid development
What Are Uterine Fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are common growths in women’s reproductive organs. These benign tumors develop in the uterus. They can greatly affect a woman’s daily life3.
Understanding Leiomyomas
Leiomyomas are non-cancerous tumors in the uterus muscle tissues. They are incredibly prevalent. One in five women may have fibroids during their childbearing years3.
Types of Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroids come in different types. Each type has its own features:
- Intramural fibroids: Located within the uterine wall
- Subserosal fibroids: Projecting outside the uterus
- Submucosal fibroids: Bulging into the uterine cavity
Risk Factors and Prevalence
Some groups are more likely to get fibroids. African-American women and overweight individuals face higher risks4.
About 20 to 80 percent of women develop fibroids by age 505.
| Age Group | Fibroid Prevalence |
|---|---|
| 40-50 years | Highest risk |
| Under 20 years | Rare occurrence |
“Most women with fibroids may not even know they have them” – Women’s Health Experts
Knowing about these growths is key for good reproductive health. Fibroids are usually harmless. However, they can cause symptoms that affect daily life5.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroids can cause various symptoms that affect your daily life. Knowing these signs helps you get timely medical care. It also aids in managing your health effectively6.
Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
Heavy menstrual bleeding often signals uterine fibroids. You might have long periods or abnormal bleeding between cycles. Extremely heavy flow can disrupt your routine6.
Some women with fibroids notice:
- Periods lasting longer than a week
- Soaking through multiple sanitary products in hours
- Severe cramping during menstruation
Pelvic Pain and Pressure
Pelvic pain can be tough to deal with for fibroid sufferers. You might feel ongoing pressure in your lower belly. Some women experience discomfort during sex.
Sharp or dull aching in the pelvic area is also common. These feelings can change based on your fibroids’ size and location7.
Frequent Urination and Other Symptoms
Fibroids can cause unexpected issues beyond bleeding and pain. You might need to pee more often. Constipation and lower back pain are also possible.
Some women notice abdominal swelling. About 1 in 5 women of childbearing age develop these symptoms6.
“Understanding your body’s signals is the first step toward effective health management.”
Many women face these fibroid symptoms. However, not all fibroids need immediate treatment. Talk to a doctor to find the best way to manage your condition8.
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
Understanding uterine fibroid diagnosis is key for good reproductive health. A careful medical evaluation helps determine the best treatment plan. Your gynecologist will guide you through this process.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Schedule a doctor’s visit if you have ongoing symptoms of uterine fibroids. Watch out for these warning signs:
- Prolonged heavy menstrual bleeding
- Severe pelvic pain
- Frequent urination
- Unexplained abdominal discomfort
Diagnostic Imaging Options
Advanced imaging helps doctors diagnose fibroids accurately9. Here are some tools used to check your reproductive health:
| Imaging Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Ultrasound | Initial screening and fibroid detection |
| Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) | Detailed visualization of fibroid characteristics |
| Hysterosalpingography | Examining uterine and fallopian tube structure |
| Hysteroscopy | Direct internal examination of uterine cavity |
Importance of Comprehensive Evaluation
A thorough fibroid diagnosis involves more than just imaging. About 20% to 50% of women with fibroids need detailed medical assessment10.
Your doctor will look at these factors:
- Fibroid size and location
- Potential impact on fertility
- Overall reproductive health
Early detection and comprehensive evaluation are key to managing uterine fibroids effectively.
Team up with your gynecological specialist to create a plan for your fibroid condition11. This partnership ensures the best care for you.
Treatment Options for Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroid treatment offers various paths based on your health needs. Your doctor will consider symptom severity, fibroid size, and fertility goals. These factors guide the choice of Fibroid Treatment Options12.
Non-surgical approaches include pain medications and hormonal treatments. GnRH agonists can reduce uterine size by about 50% after three months. Hormonal birth control methods also help manage bleeding and discomfort1213.
Myomectomy removes fibroids while preserving your uterus. Uterine Artery Embolization (UAE) shrinks fibroids by 30 to 50%13. Minimally invasive techniques like laparoscopic or robotic surgeries are gaining popularity12.
Lifestyle changes can enhance medical treatments. A healthy weight, balanced diet, and physical activity may help manage symptoms. These habits might also reduce fibroid risks14.
FAQ
What exactly are uterine fibroids?
Who is most likely to develop uterine fibroids?
What are the most common symptoms of uterine fibroids?
How are uterine fibroids diagnosed?
What treatment options are available for uterine fibroids?
Can uterine fibroids affect pregnancy?
Are there ways to prevent uterine fibroids?
Do fibroids go away on their own?
Source Links
- Fibroids – https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/uterine-fibroids
- Uterine fibroids – Symptoms and causes – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/uterine-fibroids/symptoms-causes/syc-20354288
- Uterine fibroids – https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/diseases-conditions/uterine-fibroids
- Uterine Fibroids | Fibroids | MedlinePlus – https://medlineplus.gov/uterinefibroids.html
- Uterine fibroids | Office on Women’s Health – https://womenshealth.gov/a-z-topics/uterine-fibroids
- Uterine Fibroids – https://deprod.stanfordchildrens.org/en/topic/default?id=uterine-fibroids-85-P00560
- Uterine Fibroids Signs & Symptoms – https://www.rush.edu/conditions/uterine-fibroids
- Women’s Pelvic Surgery, LLC: Urogynecologists – https://www.womenspelvicsurgery.com/blog/signs-of-uterine-fibroids
- Uterine Fibroids: Diagnosis & Treatment | NewYork-Presbyterian – https://www.nyp.org/womens/fibroids/treatment
- Uterine Fibroids: Diagnosis and Treatment – https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2017/0115/p100.html
- Uterine Fibroids Diagnosis & Treatment » Medical & Surgical — A/Prof Alex Ades – https://www.advancedgynaecologymelbourne.com.au/fibroids/diagnosis-treatment
- Uterine Fibroid Treatment Options – UChicago Medicine – https://www.uchicagomedicine.org/conditions-services/obgyn/uterine-fibroids/treatments-procedures
- Fibroid Treatment Options – Brigham and Women’s Hospital – https://www.brighamandwomens.org/obgyn/infertility-reproductive-surgery/cysts-and-fibroids/non-surgical-fibroid-treatment
- Uterine fibroids and hysterectomy Information | Mount Sinai – https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/report/uterine-fibroids-and-hysterectomy