Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths that affect many women worldwide. These common health issues can impact reproductive health significantly. About 80 percent of females will experience fibroids during their lifetime.
Fibroid symptoms can vary widely between individuals. You might have heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pressure, or unexpected pain. These symptoms can range from mild to severe, affecting your daily life.
Fibroids come in different sizes. They can be microscopic or as large as a grapefruit. Most remain small and don’t cause symptoms1.
Treatment options for uterine fibroids have greatly improved. Modern medical approaches offer hope and relief. From medication to minimally invasive procedures, there are many choices available2.
Key Takeaways
- Fibroids are extremely common, affecting up to 80% of women
- Symptoms can vary from mild to severe
- Multiple treatment options are available
- Early diagnosis can help manage fibroid progression
- Personalized treatment plans are crucial for effective management
Understanding Uterine Fibroids and Their Impact
Uterine fibroids are common growths that affect many women’s health. These benign tumors grow in the uterus and can vary in size and location3.
They can impact a woman’s reproductive health and overall well-being. Understanding fibroids is crucial for managing their effects.
What Are Uterine Fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous tumors that grow in the uterine walls. They come in different types, each with unique features:
- Subserosal fibroids: Grow outside the uterine wall
- Intramural fibroids: Develop within the uterine muscle
- Submucosal fibroids: Grow into the uterine cavity
Risk Factors and Causes
Knowing fibroid risk factors can help you assess your chances of developing them. Key risk factors include:
| Risk Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| African-American Descent | Higher likelihood of fibroid development4 |
| Age | More common in women over 40 |
| Obesity | Increased risk of fibroid growth |
| Family History | Genetic predisposition |
Common Symptoms and Complications
Uterine fibroid symptoms can greatly affect your daily life. Women may experience:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Pelvic pressure or pain
- Frequent urination
- Reproductive challenges4
“Up to 77% of women will develop fibroids during their childbearing years, making awareness crucial”
Fibroids can cause pregnancy complications, including increased risks of cesarean delivery and preterm labor3. The chance of malignancy is very low, at less than 1%.
Knowing about fibroids helps you spot potential symptoms and seek medical help4. Early detection can lead to better management and treatment options.
Diagnosis and Testing Methods
Uterine fibroid identification requires a thorough diagnostic approach. Your doctor will start with a pelvic exam and review your medical history. This helps understand your specific symptoms5.
Ultrasound is the main tool for detecting fibroids. Transvaginal ultrasound offers high accuracy in revealing fibroid details5. This safe method shows the size, number, and location of fibroids clearly6.
- Pelvic examination
- Transvaginal ultrasound
- Saline sonogram
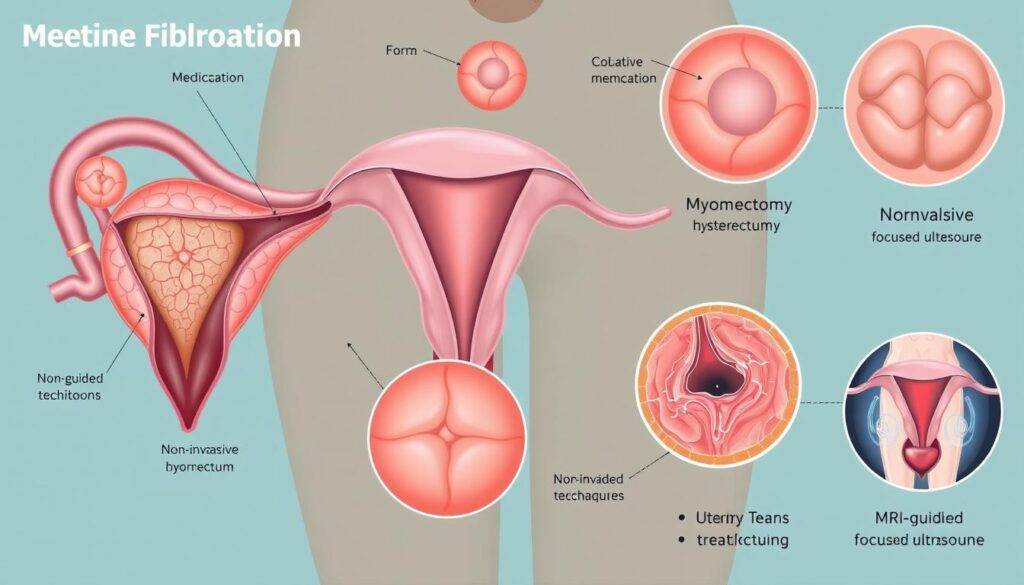
- MRI for Fibroids
MRI for Fibroids provides in-depth imaging when needed. It offers detailed views of fibroid structures. MRI helps distinguish between benign growths and possible cancers6.
Advanced imaging techniques offer precise visualization of uterine fibroids, enabling targeted treatment strategies.
Your doctor may use special tests to rule out other conditions:
- Hysteroscopy to examine uterine cavity
- Endometrial biopsy
- Complete blood count to check for anemia
| Diagnostic Method | Purpose | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Ultrasound | Initial fibroid detection | 90-99% sensitive |
| MRI | Detailed imaging | Comprehensive structural analysis |
| Hysteroscopy | Internal uterine examination | Direct visualization |
Remember, early and accurate diagnosis is key to effective fibroid management.
Uterine Fibroids Treatment Options
Choosing the right uterine fibroid treatment can be daunting. Understanding your options helps you make informed decisions. Your treatment depends on fibroid size, symptoms, and health goals.
Medication and Hormone Therapy
Fibroid medications offer various ways to manage your symptoms. Hormonal treatments can control bleeding and potentially shrink fibroids7.
Your doctor might suggest these options:
- Levonorgestrel intrauterine system (LNG-IUS)7
- Oral progestogen tablets7
- Anti-inflammatory medicines like ibuprofen7
- Tranexamic acid tablets7
Minimally Invasive Fibroid Treatments
These treatments offer effective alternatives to traditional surgery. They can manage fibroids with less recovery time8.
Options include:
- Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE)
- High-intensity focused ultrasound
- Radiofrequency ablation
Surgical Treatment Options
Fibroid surgery might be recommended if other treatments aren’t effective. Surgical options vary based on your specific needs8.
| Procedure | Description | Fertility Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Myomectomy | Removes fibroids while preserving the uterus | Fertility preserved |
| Hysterectomy | Removes the entire uterus | Ends fertility |
| Hysteroscopic Resection | Removes fibroids through the vagina | Minimal impact |
Your healthcare provider will guide you through these options. They’ll consider your health needs and future fertility plans9.
Remember, each treatment approach is unique, and what works best depends on your specific situation.
Conclusion
Uterine fibroid management is a unique journey for each woman. With expert medical guidance, you can create an effective care plan. Remember, 80% of women develop fibroids, making your experience common10.
Fibroid Management includes various treatment options. Your doctor can help choose the best approach for your symptoms and goals. Some women may benefit from medication, while others might need surgery11.
For 53.7% of women, fibroid symptoms greatly affect their lives. This fact highlights the importance of personalized treatment11.
Fibroid Treatment Outcomes are improving with ongoing research. New medical tech and clinical trials offer hope for better, less invasive treatments12. Not all fibroids need immediate action, and many women manage well with proper guidance12.
Your fibroid journey is one-of-a-kind. Stay informed and keep talking with your healthcare team. Regular check-ups and a proactive attitude can help manage your fibroid health effectively.
FAQ
What are uterine fibroids?
What are the common symptoms of uterine fibroids?
Who is at higher risk of developing uterine fibroids?
How are uterine fibroids diagnosed?
What treatment options are available for uterine fibroids?
Can uterine fibroids affect pregnancy?
What is the risk of fibroids becoming cancerous?
How can I manage uterine fibroids naturally?
Source Links
- Patient education: Uterine fibroids (Beyond the Basics) – https://www.uptodate.com/contents/uterine-fibroids-beyond-the-basics/print
- Uterine fibroids – Diagnosis and treatment – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/uterine-fibroids/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20354294
- Uterine Fibroids – Understanding Fibroids & Your Treatment Options – https://fibroids.com/blog/fibroids-101-understanding-uterine-fibroids-treatment-options/
- Fibroids – https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/uterine-fibroids
- Fibroid Diagnostic Tests – https://www.fibroid.com/about-fibroids/fibroid-diagnostic-tests/
- Diagnosing Fibroids – https://nyulangone.org/conditions/fibroids/diagnosis
- Fibroids – Treatment – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/fibroids/treatment/
- Uterine Fibroid Treatment Options – UChicago Medicine – https://www.uchicagomedicine.org/conditions-services/obgyn/uterine-fibroids/treatments-procedures
- Uterine fibroids – https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/uterine-fibroids
- Current medical treatment of uterine fibroids – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5854898/
- Prevalence, symptoms and management of uterine fibroids: an international internet-based survey of 21,746 women – BMC Women’s Health – https://bmcwomenshealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1472-6874-12-6
- Uterine Fibroids | Fibroids | MedlinePlus – https://medlineplus.gov/uterinefibroids.html