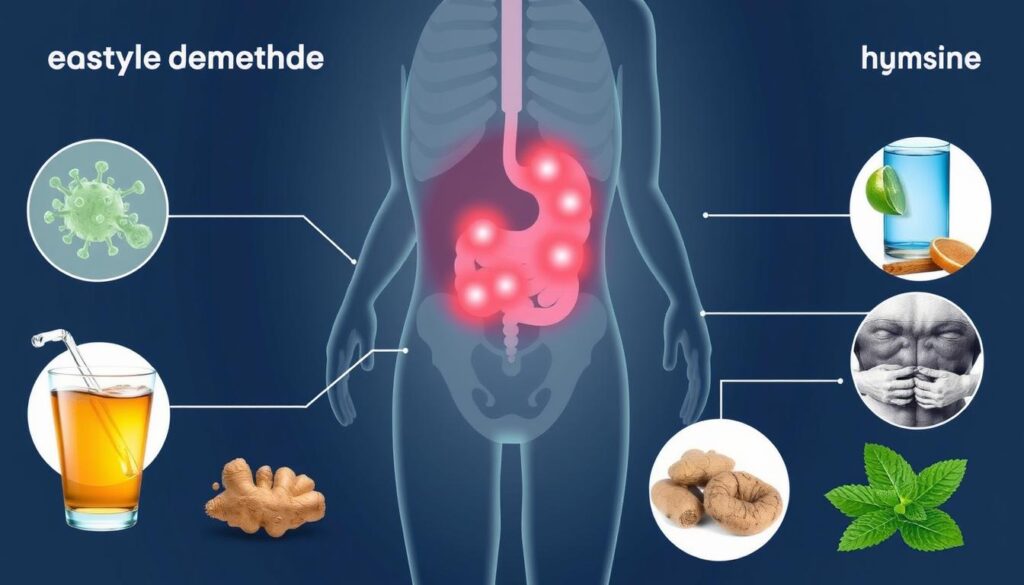
Diarrhea can disrupt your daily life, causing discomfort and health risks. It’s crucial to understand this common digestive issue. The National Institute defines diarrhea as passing three or more loose stools daily1.
Your body signals something’s wrong when you have diarrhea. Various factors can trigger it, from viral infections to food choices. Acute diarrhea is most common, typically lasting up to 2 days1.
Persistent cases need more attention to avoid dehydration and electrolyte imbalance2. Recognizing early signs helps manage gastroenteritis effectively. Consult a doctor if symptoms last over two days for adults or 24 hours for kids1.
Be alert for warning signs like frequent vomiting, fever, or severe stomach pain1. These symptoms may indicate a more serious condition requiring immediate medical care.
Key Takeaways
- Diarrhea is defined as three or more loose stools per day
- Acute diarrhea typically resolves within 2 days
- Persistent symptoms require medical attention
- Hydration is critical during diarrhea episodes
- Multiple factors can trigger digestive issues
Understanding Diarrhea: Definition and Types
Diarrhea can disrupt your daily life. It’s a common digestive issue that affects many people. Learning about diarrhea helps you manage it better and recover faster.
Diarrhea means having loose, watery stools multiple times a day. It can be mild or serious. Adults in the U.S. usually get acute diarrhea once yearly.
Young children may experience it twice a year3. This condition ranges from a minor bother to a major health concern4.
What Exactly is Diarrhea?
Diarrhea is your body’s way of getting rid of harmful substances quickly. Various factors can trigger it.
- Viral infections
- Bacterial contamination
- Food intolerances
- Digestive tract problems
Different Types of Diarrhea
Knowing the types of diarrhea helps you manage symptoms better. There are three main classifications:
| Type | Duration | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Acute Diarrhea | 1-2 days | Most common type, often resolves quickly |
| Persistent Diarrhea | 2-4 weeks | Requires closer monitoring |
| Chronic Diarrhea | 4+ weeks | May indicate underlying health issues |
Acute vs. Chronic Diarrhea
Acute diarrhea is short-lived, often caused by food poisoning or quick viral infections3. Chronic diarrhea lasts at least four weeks.
It might signal a serious condition like irritable bowel syndrome3. If symptoms persist, consult a healthcare professional.
“Prevention is always better than cure when it comes to digestive health.”
Some groups are more likely to get diarrhea. These include people working in hospitals, nursing homes, or daycare facilities4.
Common Causes of Diarrhea You Should Know
Diarrhea can strike unexpectedly, causing discomfort and disrupting your daily routine. Knowing its root causes helps you manage and prevent this challenging condition.
Foodborne Illnesses and Infections
Your digestive system is vulnerable to various pathogens that trigger diarrhea. Bacterial infections like E. coli and viral infections such as rotavirus are common culprits5.
Traveling to developing countries raises your risk of infectious diarrhea. Contaminated food and water are often the sources5.
Common Infection Types
- Viral infections (rotavirus)
- Bacterial infections (E. coli)
- Parasitic contaminations
Digestive Challenges and Medication Effects
Some conditions and medications can greatly impact your digestive health. Lactose intolerance often leads to digestive distress5.
Antibiotics can disrupt your gut’s natural bacterial balance. This disruption potentially causes diarrhea5.
| Cause Category | Specific Triggers |
|---|---|
| Food Intolerances | Lactose intolerance, artificial sweeteners |
| Medication Side Effects | Antibiotics, pain relievers |
| Digestive Disorders | IBS, Crohn’s disease, celiac disease |
Preventive Strategies
Protecting yourself from diarrhea involves several approaches. Frequent handwashing is crucial in defending against infectious diarrhea5.
Understanding your body’s signals and maintaining good hygiene can dramatically reduce your risk of experiencing diarrhea.
Effective Remedies to Stop Diarrhea Quickly
Diarrhea can be uncomfortable and disruptive. Learning how to manage it can help you recover fast. Here are some effective ways to treat this condition and get relief.
Over-the-Counter Solutions
Some over-the-counter medications can help with diarrhea. Loperamide (Imodium) slows digestion to firm up stools6. It’s good for frequent or severe cases.
Bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol) reduces gut inflammation. It also kills harmful organisms that cause diarrhea7.
Home Remedies and Nutritional Support
The BRAT diet is a gentle way to manage diarrhea. This diet includes:
- Bananas
- Rice
- Applesauce
- Toast
Probiotics can help restore gut balance6. Try eating fermented foods like kefir. You can also take probiotic supplements with Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium8.
Hydration and Recovery Strategies
Staying hydrated is key when you have diarrhea. Drink at least 8-10 glasses of water daily. Electrolyte drinks can replace lost fluids78.
Herbal teas like chamomile can also provide relief6.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Your health should always be the top priority.
Consult a doctor if you have:
- Diarrhea lasting more than two days
- Fever above 102°F
- Bloody stools
- Signs of severe dehydration
These remedies can help, but severe symptoms need medical attention. Always see a doctor if you’re unsure7.
Preventing Diarrhea: Tips for a Healthy Gut
Your daily habits can greatly affect your gut health. Good food safety and smart eating are key to protecting your digestive system. These steps help prevent diarrhea and boost overall wellness9.
Eating smaller meals more often can help your digestion. Try having 5-6 meals a day instead of three big ones. This can keep your system steady9.
Probiotic supplements with 10 billion CFU or more can be helpful. They add good bacteria to your gut and support your immune system9.
Choose foods with soluble fiber, like applesauce. Avoid fatty or spicy foods that might upset your stomach9.
Washing hands often is crucial for gut health. Do it before cooking and after using the bathroom. For families with kids, think about getting the rotavirus vaccine9.
Drink 8-10 cups of fluid daily to stay hydrated. This helps keep your gut working well9.
If you keep having digestive problems, talk to a doctor. They can make a plan just for you. They might suggest a special diet, like low FODMAP, for certain conditions9.
Taking care of your gut can help prevent diarrhea. It’s a smart way to support your long-term health.
FAQ
What exactly is diarrhea?
What are the most common causes of diarrhea?
How can I stop diarrhea quickly?
When should I see a doctor about diarrhea?
How can I prevent diarrhea?
Can certain foods trigger diarrhea?
Is traveler’s diarrhea different from regular diarrhea?
How important is hydration during diarrhea?
Source Links
- How to stop diarrhea fast: Methods and what to avoid – https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/how-to-stop-diarrhea-fast
- Diarrhea – https://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/digestive-diseases-diarrhea
- Diarrhea | MedlinePlus – https://medlineplus.gov/diarrhea.html
- Definition & Facts for Diarrhea – NIDDK – https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/diarrhea/definition-facts
- Diarrhea – Symptoms and causes – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diarrhea/symptoms-causes/syc-20352241
- How to Stop Diarrhea Fast – https://www.verywellhealth.com/how-to-make-diarrhea-go-away-1324506
- Dos and Don’ts for Quick Relief of Diarrhea – https://www.everydayhealth.com/diarrhea/treatment/dos-donts-treating-diarrhea-quick-relief/
- 7 Ways To Stop Diarrhea Fast Naturally – https://www.health.com/condition/digestive-health/diarrhea-home-remedies
- 10 Nutrition and Lifestyle Recommendations to Manage Diarrhea – https://badgut.org/information-centre/health-nutrition/diarrhea-and-diet/