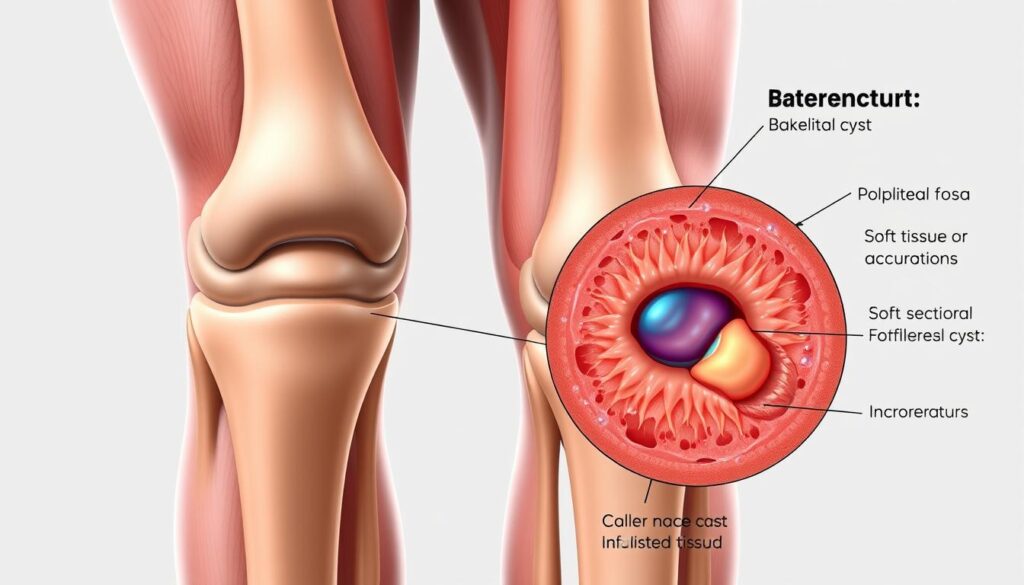
A Baker cyst is a fluid-filled swelling behind your knee joint. It can cause discomfort and affect your mobility. This happens when the knee joint is inflamed or damaged1.
Baker’s cysts form when extra fluid builds up behind the knee. This creates a bulge that can lead to pain and stiffness2.
Knowing about this condition helps you manage symptoms better. Most people with Baker’s cysts feel knee swelling and pain. These issues often link to other knee problems like cartilage tears or arthritis2.
Taking care of your knee joint health is key. It can help prevent and manage these cysts1.
Key Takeaways
- Baker cysts are fluid-filled swellings behind the knee
- Most common in adults between 35 and 70 years old
- Can be caused by various knee joint conditions
- Often treatable with non-surgical methods
- Rarely lead to long-term complications
Understanding Baker Cyst and Its Causes
A Baker cyst is a fluid-filled growth behind the knee. It can cause significant pain and discomfort. This condition impacts joint mobility and overall comfort3.
What Defines a Baker Cyst?
A Baker cyst is a fluid-filled sac in the back of your knee. It’s usually connected to the synovial membrane. Excess synovial fluid creates a bulge, causing tightness and limited movement4.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to Baker cyst development:
- Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis3
- Meniscus or ACL tear
- Cartilage damage
- Chronic knee joint inflammation
Some people may have Baker cysts without knowing the exact cause. This is especially true for younger patients3.
Synovial Fluid and Cyst Formation
The synovial membrane is key in cyst development. Knee joint problems can make this membrane produce excess fluid. This excess fluid leads to Baker cyst formation4.
| Characteristic | Details |
|---|---|
| Prevalence | Common in individuals with underlying knee conditions3 |
| Symptom Variation | Can be asymptomatic or cause significant discomfort4 |
| Treatment Approach | Typically managed with nonsurgical methods3 |
Understanding the nuanced nature of Baker cysts can help you recognize potential symptoms and seek appropriate medical guidance.
Signs, Symptoms and Complications
Baker cysts can cause knee discomfort and limit mobility. Knowing the signs helps manage this condition better.
The primary symptoms of a Baker cyst typically include:
- Pain behind the knee5
- Knee stiffness and reduced flexibility6
- Swelling in the knee and calf area7
- Discomfort during prolonged standing or physical activity5
Severe Baker cysts can cause intense symptoms. In rare cases, the cyst may rupture, leading to sharp pain and significant swelling7.
Some people feel fluid running down their calf. This can be quite alarming5.
| Symptom Severity | Potential Complications |
|---|---|
| Mild | Slight knee discomfort |
| Moderate | Increased calf pain and knee stiffness |
| Severe | Potential cyst rupture, nerve trapping, or artery blockage5 |
“Early recognition of symptoms can prevent potential complications and improve treatment outcomes.”
If you have ongoing knee swelling or calf pain, see an orthopedic specialist. They can find the cause and create a treatment plan7.
Conclusion
Managing a Baker cyst requires a tailored approach to your knee health. Treatment depends on factors like swelling severity and joint conditions8. Your doctor can help create a plan that addresses the cyst’s root cause, which medical research links to meniscal issues or inflammation8.
Most patients find relief through conservative methods. Younger patients may see the cyst resolve on its own9. Ultrasonography helps doctors assess the cyst and determine the best treatment9.
Surgery might be needed for larger cysts or persistent knee problems. Careful monitoring is essential to prevent recurrence9.
Your Baker cyst experience can be manageable. Work closely with your healthcare team to understand your condition. Follow recommended treatments to effectively manage symptoms and maintain knee function.
Remember, each case is unique. What works for one person may not work exactly the same for another.
FAQ
What exactly is a Baker cyst?
What are the main symptoms of a Baker cyst?
Who is most at risk of developing a Baker cyst?
How is a Baker cyst typically treated?
Can a Baker cyst be dangerous?
How long does a Baker cyst typically last?
Can I prevent a Baker cyst from developing?
Source Links
- Baker’s cyst – https://patient.info/bones-joints-muscles/knee-pain-patellofemoral-pain/bakers-cyst
- Bakers Cyst Removal in Los Angeles: Symptoms & Treatment | Meier Orthopedic Sports Medicine – https://www.mosm.com/bakers-cyst/
- Baker’s Cyst (Popliteal Cyst) – OrthoInfo – AAOS – https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/bakers-cyst-popliteal-cyst/
- Baker cyst – Symptoms and causes – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/bakers-cyst/symptoms-causes/syc-20369950
- No title found – https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content?contenttypeid=134&contentid=510
- Baker’s cysts – https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/bakers-cysts
- Baker’s Cyst (Popliteal Cyst) – https://www.webmd.com/arthritis/what-is-bakers-cysts
- Determination of the Factors Influencing Rupture of Baker’s Cysts in the Knee on Plain Radiographs and MRI – https://i-mri.org/DOIx.php?id=10.13104/jksmrm.2012.16.3.217
- Baker’s cyst in children: conservative management versus surgical excision according to clinical and imaging criteria – Annals of Pediatric Surgery – https://aops.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s43159-021-00071-1