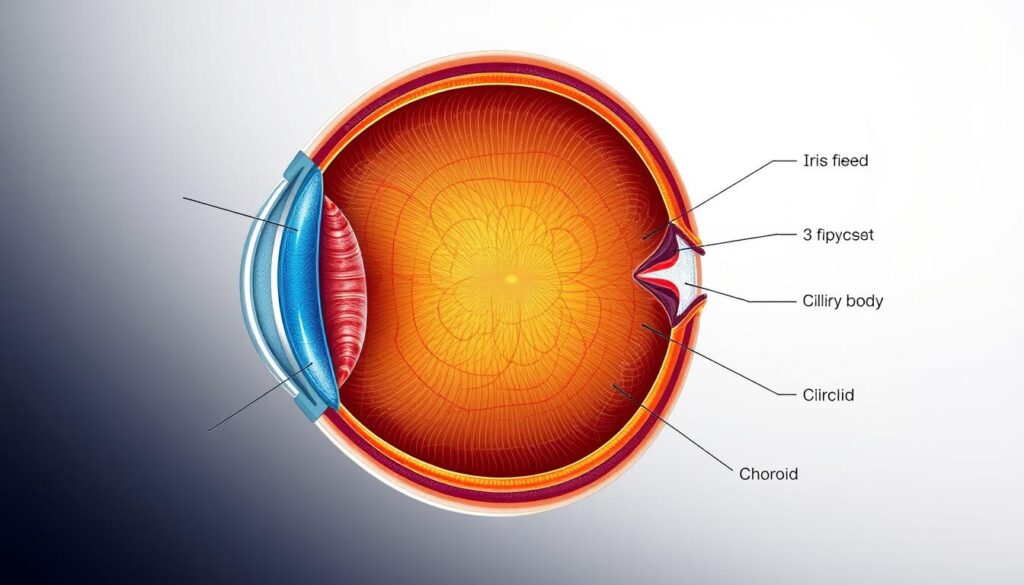
The uveal tract is a key part of your eye’s complex structure. It’s the middle layer that keeps your eyes healthy and working well. This tract has three main parts that team up for top-notch vision1.
The uveal tract sits between the white sclera and the retina. It feeds the eye with nutrients and helps various eye functions. This layer is crucial for keeping your vision sharp and healthy.
Regular eye check-ups are vital to spot uveal tract problems early. Some issues can grow without symptoms, so pro screenings are key. Uveal melanomas are the most common eye cancer1.
Key Takeaways
- The uveal tract is the middle layer of the eye with critical functions
- Consists of three main components: iris, ciliary body, and choroid
- Plays a vital role in nutrient delivery and eye protection
- Regular eye exams can help detect potential uveal tract issues
- Understanding eye anatomy supports better ocular health
What is the Uveal Tract and Its Location in Your Eye
The uveal tract is a vital middle layer in your eye. It connects essential structures that work together for vision. This specialized part maintains your eye’s health and functionality.
Beneath the eye’s white outer layer lies the uveal tract. This fascinating structure serves as a crucial intermediate layer. It supports numerous eye functions2.
Three Primary Components of the Uvea
Your eye’s uveal tract has three distinct components:
- Iris: Controls light entering the eye3
- Ciliary Body: Helps focus by adjusting lens thickness3
- Choroid: Provides nutritional support to inner eye structures3
Anatomical Positioning and Structure
The uveal tract sits between the retina and sclera. It forms a complex network of tissues2. This unique location allows for crucial functions.
- Nutrient delivery
- Gas exchange
- Light absorption
- Accommodation control
Relationship with Other Eye Structures
Your uveal tract houses special immune cells. These cells protect against potential eye inflammation4. Macrophages and lymphocytes play a key role in eye health.
The uveal tract is more than just a layer—it’s a dynamic system supporting your vision.
The uveal tract is a complex system enabling clear vision. Each part works together seamlessly. It supports your overall visual experience3.
Source: Statistical data on uveitis and uveal tract components2Source: Detailed anatomical description of uveal tract4Source: Immunological characteristics of uveal tract
Eye with Uvea: Essential Functions and Importance
Your eye’s uvea is vital for maintaining optimal eye health. It performs crucial tasks that keep your vision sharp and responsive5.
The uvea has three key parts working together for your vision. These are the iris, ciliary body, and choroid.
- Iris: Controls light entering the eye
- Ciliary body: Manages lens accommodation
- Choroid: Provides blood supply to retinal layers
The uvea function is crucial for preventing eye diseases. The iris adjusts light levels, protecting your retina6.
Your ciliary body allows lens flexibility. This helps you focus on objects at different distances.
The choroid supplies vital nutrients and oxygen to your retina. Without it, your eye’s delicate tissues could suffer damage7.
Protecting your uvea means protecting your vision’s fundamental infrastructure.
| Uvea Component | Primary Function | Impact on Eye Health |
|---|---|---|
| Iris | Light regulation | Prevents retinal damage |
| Ciliary Body | Lens accommodation | Enables focus adjustment |
| Choroid | Blood supply | Nourishes retinal tissues |
Keeping your uvea healthy is an investment in your vision’s future. It helps prevent potential complications5.
Common Uveal Conditions and Eye Health
Eye health depends on recognizing signs of uveal conditions. The uvea is vital for eye function. Inflammatory processes can disrupt its balance.
Understanding Uveitis and Eye Inflammation
Uveitis is a complex eye condition causing uvea inflammation. It can appear suddenly and progress rapidly. It may affect one or both eyes8.
About 43,000 new uveitis cases occur in the United States every year9.
The primary symptoms of uveitis include:
- Eye redness
- Pain
- Blurred vision
- Light sensitivity
Risk Factors and Prevention Methods
Several factors can contribute to developing uveitis:
- Autoimmune disorders
- Genetic predispositions
- Infections
- Eye injuries
Smoking makes uveitis harder to manage8. A family history of inflammatory conditions can increase your risk9.
When to Consult a Uvea Specialist
See a uvea specialist for persistent eye inflammation or vision changes. The first visit usually takes 2-4 hours. It involves comprehensive testing9.
Early detection and treatment are critical to preventing potential permanent vision loss.
Untreated uveitis can cause serious problems. These include macular edema, retinal scarring, glaucoma, and potential blindness8.
Conclusion
Understanding the eye’s uvea is vital for maintaining good vision health. Uveitis, a condition affecting the uveal tract, can greatly impact eye function10. This rare inflammatory condition affects about one in a thousand people but can cause significant visual problems10.
Taking care of your eyes is important. Regular eye check-ups every 3 to 6 months help monitor potential uveal issues11. Knowing the risks and staying alert can help prevent serious eye problems.
The early detection of uveitis can make a big difference in keeping your vision healthy12. Many things can cause uveal inflammation, like autoimmune disorders, infections, and genetics11.
Some eye conditions can be managed well, but may not be fully cured11. If you notice any unusual eye symptoms, see an eye doctor right away. This can help protect your eye health and prevent long-term vision problems.
FAQ
What exactly is the uvea in my eye?
What are the primary functions of the uvea?
What is uveitis, and how does it affect my eye?
How can I protect the health of my uvea?
Can problems with the uvea affect my vision?
What are the warning signs of uveal conditions?
Are some people more at risk for uveal conditions?
Source Links
- Iris and Uvea of the Eye – Vital to Good Vision – https://www.allaboutvision.com/resources/uvea-iris-choroid.htm
- Uvea – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uvea
- Uveitis – Eye Disorders – Merck Manual Consumer Version – https://www.merckmanuals.com/home/eye-disorders/uveitis-and-related-disorders/uveitis
- The distribution of immune cells in the uveal tract of the normal eye – PubMed – https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9349410/
- Uvea Anatomy – Learn What Is Uvea & Diseases Affecting The Uvea – https://www.dragarwal.com/eye-anatomy/uvea/
- Importance of getting the proper treatment of Uvea – – https://shreeretinacare.com/importance-of-getting-the-proper-treatment-of-uvea/
- What is Uvea in Eye – https://www.theeyefoundation.com/eye/uvea-eye/
- Uveitis-Uveitis – Symptoms & causes – Mayo Clinic – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/uveitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20378734
- Uveitis and Ocular Inflammatory Disease – https://uthealthaustin.org/conditions/uveitis-and-ocular-inflammatory-disease
- The Eyes Have It: A Rheumatologist’s View of Uveitis – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6160350/
- Uveitis – Definition, Symptoms, Causes, and Signs – https://www.centreforsight.net/blog/uveitis
- Iritis – Symptoms and causes – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/iritis/symptoms-causes/syc-20354961