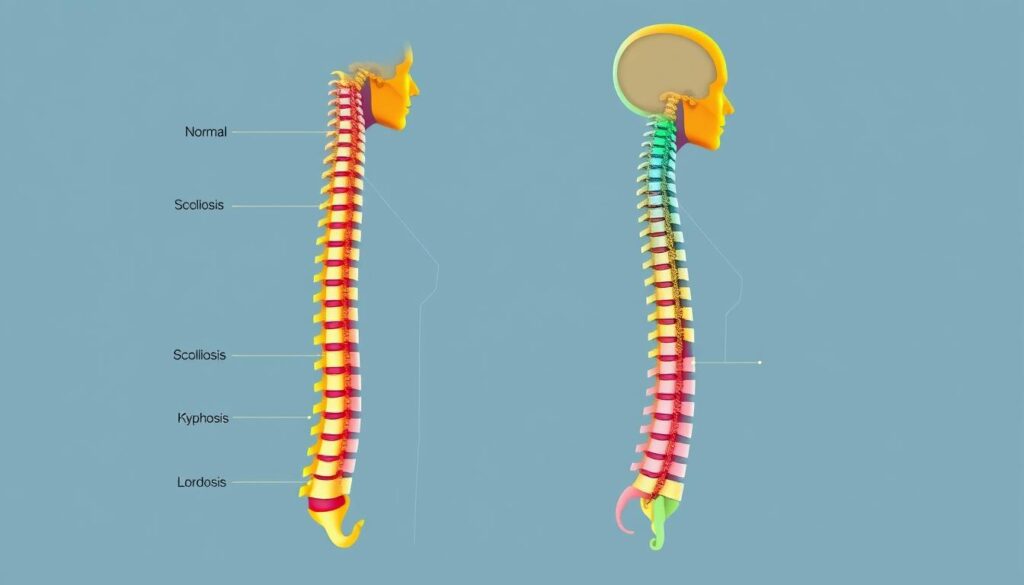
Your spine is an amazing support system that can face unexpected challenges. Scoliosis is a unique condition causing abnormal sideways spinal curvature. It affects many people worldwide and is often spotted during teenage years1.
Doctors use special methods to measure the spine’s curve. The Cobb angle helps determine how severe the curve is2. Mild scoliosis has a curve of 10 to 24 degrees.
Moderate curves measure between 25 to 39 degrees12. It’s vital to understand your spine’s structure. Girls have a higher risk of the curve getting worse.
They might need more intensive treatment than boys3. While the exact cause is unknown, genes likely play a big role in scoliosis3.
Key Takeaways
- Scoliosis is an abnormal sideways spinal curvature
- Most diagnoses occur during adolescence
- Severity ranges from mild to severe curvatures
- Genetic factors may contribute to development
- Early detection is important for effective management
What is Scoliosis and How Does It Develop?
Scoliosis is a complex spinal condition that impacts lives unexpectedly. Early detection and management are crucial for those affected by this condition4.
The Anatomy of the Spine
A healthy spine is straight, but scoliosis causes an abnormal sideways curve. This three-dimensional deformity creates unique challenges for individuals5.
Common Causes of Scoliosis
Scoliosis comes in several types, each with distinct characteristics:
- Idiopathic scoliosis: The most common type, with no known cause. It affects approximately 8 out of 10 cases4.
- Congenital scoliosis: Caused by vertebrae malformation during fetal development5.
- Neuromuscular scoliosis: Associated with conditions like cerebral palsy and muscular dystrophy5.
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
Spotting scoliosis early helps manage it better. Look out for these signs:
- Uneven shoulders or shoulder blades
- Asymmetrical waistline
- One hip appearing higher than the other
- Clothes hanging unevenly
Scoliosis typically emerges during adolescence, around age 10 to 15, but can affect people of all ages4.
| Scoliosis Type | Key Characteristics | Age of Onset |
|---|---|---|
| Idiopathic | Unknown cause | 10-15 years |
| Congenital | Vertebrae malformation | Birth |
| Neuromuscular | Associated with neurological conditions | Varies |
Most people with scoliosis can lead normal, active lives. Proper management is key to maintaining a good quality of life4.
Diagnosing Scoliosis: What You Need to Know
Knowing how scoliosis is diagnosed helps you understand treatment options. Early detection is key to managing spinal curvature well. Comprehensive screening methods play a vital role.
Scoliosis screening often starts in childhood or teen years. Doctors use specific techniques to spot potential spine issues6.
- Physical examination of spine alignment
- Forward bend test to assess curvature
- Comprehensive medical history review
Medical Imaging Procedures
Imaging is crucial for confirming scoliosis and its severity. X-rays are the main tool for measuring spinal curves using the Cobb angle method7.
A curve over 10 degrees is officially diagnosed as scoliosis7. Different imaging techniques help assess your condition.
- X-rays: Provide detailed bone structure visualization
- MRI scans: Examine soft tissue complications
- CT scans: Offer three-dimensional spine views
Evaluating Severity and Type of Scoliosis
Scoliosis severity is grouped based on the Cobb angle measurement. This helps determine the best treatment approach.
| Curve Classification | Cobb Angle Range | Recommended Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Minor Scoliosis | Less than 25 degrees | Regular observation |
| Moderate Scoliosis | 25-40 degrees | Bracing recommended |
| Severe Scoliosis | Over 40 degrees | Surgical intervention |
Doctors often use a scoliometer during initial screenings. This tool measures spinal rotation and asymmetry6.
Knowing your specific scoliosis type helps create an effective treatment plan7. This ensures you get the best care possible.
“Early detection and accurate diagnosis are key to managing scoliosis effectively.”
Treatment Options for Scoliosis Management
Scoliosis treatment is tailored to your specific condition. Options range from conservative methods to intensive interventions. Your curve’s severity and individual needs determine the best approach.
Physical therapy is crucial in scoliosis management. The Schroth Method, a specialized exercise technique, helps improve spinal alignment. It can benefit patients of all ages and reduce curve progression8.
Bracing is another key strategy, especially for adolescents. Wearing a brace for at least 16 hours daily can significantly reduce surgery needs9.
Severe cases may require spinal fusion surgery. This becomes an option when curves progress beyond 50 degrees8. Surgery can provide long-term stabilization but carries potential risks.
Pain management is important in treatment. NSAIDs are typically recommended as the first line of relief for scoliosis-related discomfort10.
Your treatment journey is unique. Work closely with healthcare professionals to develop an effective management strategy. Early intervention and consistent treatment can significantly improve your quality of life.
FAQ
What exactly is scoliosis?
How do I know if I have scoliosis?
What causes scoliosis?
At what age is scoliosis typically diagnosed?
What are the treatment options for scoliosis?
Can scoliosis be prevented?
Does scoliosis cause pain?
Is scoliosis a serious condition?
Source Links
- What Is Scoliosis? – https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15837-scoliosis
- Exploring The Scoliosis Degrees Of Curvature Chart – https://squareonehealth.com/a-guide-to-understanding-the-scoliosis-degrees-of-curvature-chart/
- Scoliosis – Symptoms and causes – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/scoliosis/symptoms-causes/syc-20350716
- Scoliosis – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/scoliosis/
- Scoliosis – https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/scoliosis
- Scoliosis – Detecting and Diagnosing – https://www.medtronic.com/en-us/l/patients/conditions/scoliosis/diagnosing.html
- Scoliosis in Adults: What to Know About Symptoms & Treatment – https://www.hss.edu/conditions_scoliosis-adults.asp
- Scoliosis Treatment Options for Kids and Adults | HSS – https://www.hss.edu/condition-list_scoliosis.asp
- Nonsurgical Treatment Options for Scoliosis – OrthoInfo – AAOS – https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/treatment/nonsurgical-treatment-options-for-scoliosis/
- Scoliosis – Treatment in adults – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/scoliosis/treatment-in-adults/