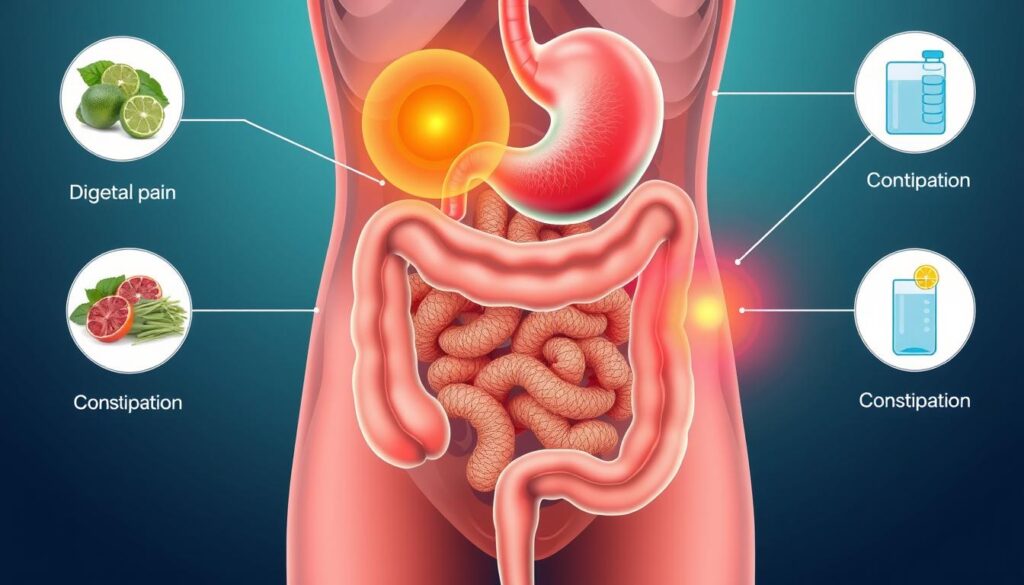
Digestive issues can turn your daily life upside down. Abdominal pain and constipation are common problems that cause discomfort and disruption1. In the U.S., about 16% of adults deal with constipation symptoms1.
Knowing these issues helps manage your health better. Constipation means having less than three bowel movements weekly. This can lead to stomach cramps and bloating2.
Abdominal pain and constipation can stem from various causes. These include lifestyle choices, medications, and underlying medical conditions2.
Your gut health depends on many factors. Stress, diet, hydration, and physical activity all play a role. Not eating enough fiber, drinking too little water, and being inactive can upset your digestion2.
Key Takeaways
- Constipation affects a significant portion of adults in the United States
- Digestive issues can result from lifestyle, medication, and medical conditions
- Fewer than three bowel movements per week indicates potential constipation
- Stress and diet play crucial roles in digestive health
- Understanding your symptoms is key to effective management
Common Signs and Symptoms of Digestive Distress
Digestive health is vital for your overall well-being. Knowing the signs of digestive issues can help you spot problems early. These issues can affect your daily life in various ways3.
Physical Manifestations and Pain Patterns
Intestinal discomfort shows through key signs. You might have ongoing belly pain or cramping. Unexpected bloating or feeling too full are also common.
- Persistent abdominal pain or cramping
- Unexpected bloating that disrupts daily activities
- Reduced appetite or feeling of fullness
Gut problems can really mess up your daily routine3. The pain can be all over or just in one spot4.
Bowel Movement Changes
Your poop can tell you a lot about your gut health. Watch for these changes:
- Infrequent bowel movements (less than three per week)
- Hard or lumpy stools
- Difficulty passing stools
These signs might point to gut issues that need attention3.
Associated Digestive Symptoms
You might have other signs of digestive trouble too. These can include too much gas, feeling sick, or constant bloating.
| Symptom | Potential Indication |
|---|---|
| Excessive gas | Potential digestive system imbalance |
| Nausea | Possible digestive tract irritation |
| Persistent bloating | Potential food sensitivity or gut issues |
Remember, persistent or severe symptoms should always be evaluated by a healthcare professional. Many gut problems can be managed with the right diagnosis and care4.
“Understanding your body’s signals is the first step towards better digestive health.”
Abdominal Pain and Constipation: Causes and Risk Factors
Abdominal pain and constipation have various root causes. One in five people faces chronic constipation. Your diet, lifestyle, and health conditions affect digestive wellness.
Key risk factors for gastrointestinal disorders include:
Lifestyle choices greatly impact digestive health. Poor fluid intake and low fiber can slow stool movement. Certain medications may also cause constipation.
| Risk Category | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Age | Higher risk in older adults6 |
| Gender | More common in women6 |
| Medical Conditions | Parkinson’s, Multiple Sclerosis6 |
Your digestive health is a complex interplay of multiple factors, requiring personalized attention and care.
Chronic constipation has various symptoms. These include fewer than three bowel movements per week. Spotting these signs early helps improve digestive wellness.
Warning signs that require professional medical consultation include persistent weight loss, bleeding, or unusual stool changes6.
Treatment Options and Management Strategies
Constipation can be managed with various approaches. These include lifestyle changes and medical treatments. Your strategy should be tailored to your specific symptoms7.
Dietary Modifications and Fiber Intake
Your diet is key in managing constipation. Experts suggest eating 22 to 34 grams of fiber daily7. This helps prevent and treat digestive issues.
- Whole grains
- Fresh fruits
- Leafy green vegetables
- Legumes
Hydration and Exercise Recommendations
Staying hydrated and active can boost your digestive health. Water helps soften stools, making them easier to pass. Exercise may not cure constipation, but it can improve your overall well-being8.
Medical Interventions and Medications
When lifestyle changes aren’t enough, medical treatments can help. Laxatives are often used to manage. These include:
- Fiber supplements
- Osmotic agents
- Stool softeners
- Lubricants
- Stimulant laxatives
“Stimulant laxatives should only be used for severe cases or after other treatments have failed” – Digestive Health Experts7
For ongoing issues, doctors may prescribe medications like lubiprostone or linaclotide7. In rare cases, biofeedback therapy or surgery might be needed7.
Conclusion
Digestive health is unique to each person. Your body reacts differently to abdominal pain and constipation. Medical research shows how complex digestive issues can be9.
Seeking medical advice is crucial for digestive problems. Some issues can be fixed with lifestyle changes. However, severe symptoms need a doctor’s help10.
Your digestive health journey is one-of-a-kind. There’s no single solution that works for everyone. Diet changes, drinking water, and exercise can often help11.
If you have ongoing discomfort or odd bowel changes, see a doctor. They can give you specific advice and relief.
Learn about your digestive health by listening to your body. Stay informed and take action when needed. Understanding abdominal pain and constipation can lead to better digestive wellness.
FAQ
What defines constipation?
What are common causes of abdominal pain and constipation?
How much fiber should I consume daily to help prevent constipation?
When should I see a healthcare professional about my symptoms?
What lifestyle changes can help manage abdominal pain and constipation?
Are there over-the-counter treatments for constipation?
Can medications cause constipation?
How does hydration impact digestive health?
Source Links
- Abdominal pain and constipation: Causes and when to see a doctor – https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/325741
- Abdominal Pain and Constipation: What Does It Mean and Causes – https://www.healthline.com/health/abdominal-pain-and-constipation
- Gastrointestinal Diseases: Symptoms, Treatment & Causes – https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/7040-gastrointestinal-diseases
- Irritable bowel syndrome – Symptoms and causes – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/irritable-bowel-syndrome/symptoms-causes/syc-20360016
- Constipation – Symptoms and causes – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/constipation/symptoms-causes/syc-20354253
- Constipation: Causes and Prevention Tips – https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/constipation-causes-and-prevention-tips
- Treatment for Constipation – NIDDK – https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/constipation/treatment
- Chronic constipation: Current treatment options – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3206558/
- The relationship between abdominal pain and emotional wellbeing in children and adolescents in the Raine Study – Scientific Reports – https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-58543-0
- PDF – https://www.facs.org/media/k3ddrpfx/abdominal_pain_content.pdf
- Constipation – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Constipation