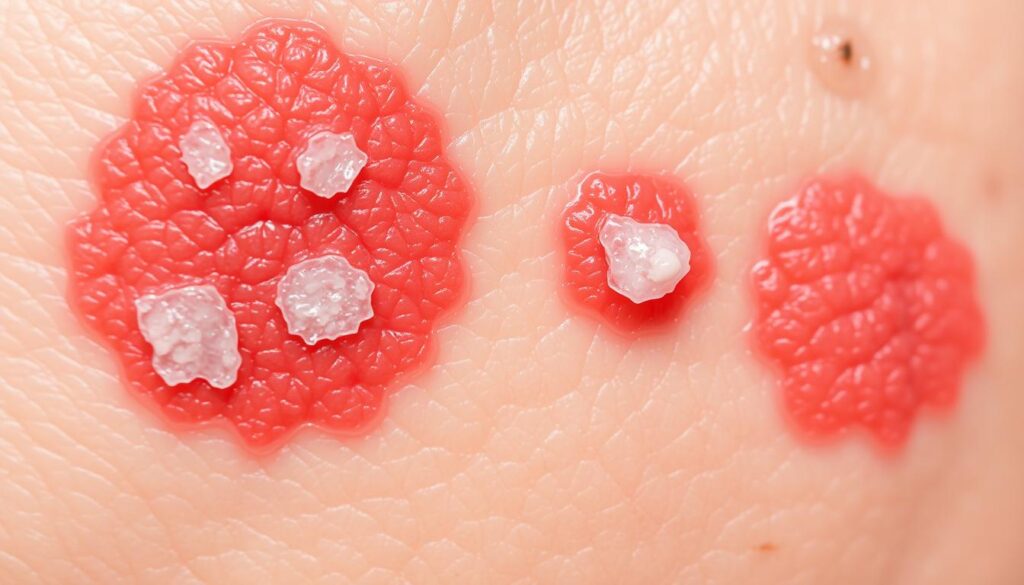
Skin yeast infections, or cutaneous candidiasis, are surprisingly common. They happen when Candida fungi grow too much on your skin1. Candida albicans is usually the cause, thriving in warm, moist body areas1.
Some health issues raise your risk of Candida skin rash. Diabetes, obesity, and weak immune systems make you more likely to get infected1. Antibiotics and chemotherapy can also increase your chances1.
Knowing about these infections helps catch them early. Most skin yeast infections can be treated well with good hygiene and medicine1.
Key Takeaways
- Cutaneous candidiasis is a common fungal skin infection
- Warm, moist body areas are most susceptible to infection
- Diabetes and obesity increase infection risk
- Proper hygiene is essential for prevention
- Antifungal treatments are typically effective
What is Cutaneous Candidiasis and Its Causes
Cutaneous fungal infection happens when Candida yeast grows out of control on your skin. This overgrowth can cause Candidal dermatitis, leading to uncomfortable skin symptoms2. These symptoms can affect various areas of your body.
Understanding Candida’s Impact on Skin
Skin yeast overgrowth thrives in warm, moist environments2. These areas include:
- Armpits
- Groin
- Skin folds
- Diaper areas in infants
Common Risk Factors for Infection
Several conditions can increase your chances of getting a Candida skin infection2. These include:
- Diabetes (31% incidence rate)3
- Obesity
- Prolonged antibiotic use
- Steroid therapy
- Weakened immune system
Medical Conditions and Candida Risks
Some medical conditions greatly increase your risk of cutaneous candidiasis. Diabetic patients have a 68% higher chance of Candida sp. infections3.
People with weak immune systems are more likely to get widespread skin infections2.
Managing underlying health conditions and maintaining proper hygiene can help prevent Candida skin infections.
Recognizing Signs and Symptoms of Skin Yeast Infections
Yeast infections on skin can be tricky to identify. Understanding their key characteristics helps you recognize them quickly. Candida skin symptoms vary depending on the affected body area and individual health conditions4.
Primary Visual and Physical Symptoms
When identifying a fungal rash, look for these distinctive signs:
- Red or discolored patches on the skin5
- Itchy and burning sensations
- Potential white flaky substance or skin shedding5
- Possible pustules or lesions
Different Manifestations in Various Body Areas
Candida skin symptoms can appear differently across body regions:
- Skin Folds: Moist, red rash with potential breakdown4
- Genital Area: White or yellow discharge, redness4
- Mouth: White patches resembling cottage cheese (oral thrush)4
- Nails: Discolored, thickened nail beds4
When to Seek Medical Attention
“Persistent symptoms require professional evaluation to prevent potential complications.”
You should consult a healthcare provider if you experience:
- Symptoms persist despite over-the-counter treatments
- Infection spreads or worsens rapidly
- You develop a fever
- You have compromised immune system4
People with diabetes, recurrent infections, or weakened immunity need prompt medical guidance. These conditions can make yeast infections more serious5.
Treatment Options and Prevention Strategies
Cutaneous candidiasis has several effective treatment options. Topical antifungal treatments are key in managing symptoms and eliminating Candida overgrowth6. For mild infections, over-the-counter creams with clotrimazole or miconazole can help target specific skin irritations.
Your yeast infection management should be comprehensive. It includes maintaining excellent hygiene and keeping affected areas clean and dry. Wear loose, breathable clothes and change out of damp ones quickly.
- Maintain excellent personal hygiene
- Keep affected skin areas clean and dry
- Wear loose-fitting, breathable clothing
- Change out of damp clothes promptly
- Manage underlying health conditions
Severe cases may need prescription antifungal medications7. Healthcare providers might suggest different treatments based on the infection’s extent.
| Infection Type | Treatment Option |
|---|---|
| Mild Skin Infection | Topical antifungal creams |
| Widespread Infection | Oral antifungal medications |
| Chronic Condition | Comprehensive treatment plan |
Candida prevention needs consistent care. For infants, change diapers often and let skin air dry6. Always talk to a healthcare professional about the best treatment for your situation.
Conclusion
Grasping cutaneous candidiasis is key for managing skin yeast infections. Your fungal skin care journey starts with understanding Candida infections8. Most cases can be handled with proper treatment and prevention, as clinical research shows9.
Candida infections affect over a billion people worldwide. About 95.78% of cases occur in adults9. Knowing your risk factors helps develop a proactive approach to skin health.
Most Candida species are harmless under normal conditions8. Early treatment is crucial for effective management. Men have a higher rate of cutaneous candidiasis cases9.
Seeking medical advice helps address potential complications. It also aids in creating a personalized management plan. Everyone can benefit from careful skin care practices.
You’re not alone in dealing with Candida. Good hygiene and medical guidance can help control these infections8. Stay informed and attentive to your body’s signals.
Don’t hesitate to seek professional help when needed. With the right approach, you can effectively manage and prevent fungal skin issues.
FAQ
What is Cutaneous Candidiasis?
What are the Common Symptoms of Cutaneous Candidiasis?
Who is Most at Risk for Developing Cutaneous Candidiasis?
How Can I Treat Cutaneous Candidiasis?
Can Cutaneous Candidiasis Be Prevented?
Is Cutaneous Candidiasis Contagious?
When Should I See a Healthcare Provider?
Can Cutaneous Candidiasis Affect Different Body Parts?
Source Links
- Candida infection of the skin – https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/diseases-conditions/candida-infection-of-the-skin
- Candida infection of the skin: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia – https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000880.htm
- Cutaneous Candidiasis: Practice Essentials, Pathophysiology, Etiology – https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1090632-overview
- Yeast Infection – https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/candidiasis-yeast-infection
- Candida Fungus Skin Infection: Causes, Symptoms & Diagnosis – https://www.healthline.com/health/skin/candida-fungus
- Cutaneous Candidiasis: Symptoms and Treatment | The Skin Surgery Center – https://www.skinsurgerycenter.net/conditions/cutaneous-candidiasis
- Medical Care, Surgical Care, Consultations – https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/213853-treatment
- Candida Infections: Clinical Features, Diagnosis and Treatment – https://www.idcmjournal.org/candida-infections
- Frontiers | Antifungal susceptibility pattern of Candida isolated from cutaneous candidiasis patients in eastern Guangdong region: A retrospective study of the past 10 years – https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/microbiology/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2022.981181/full