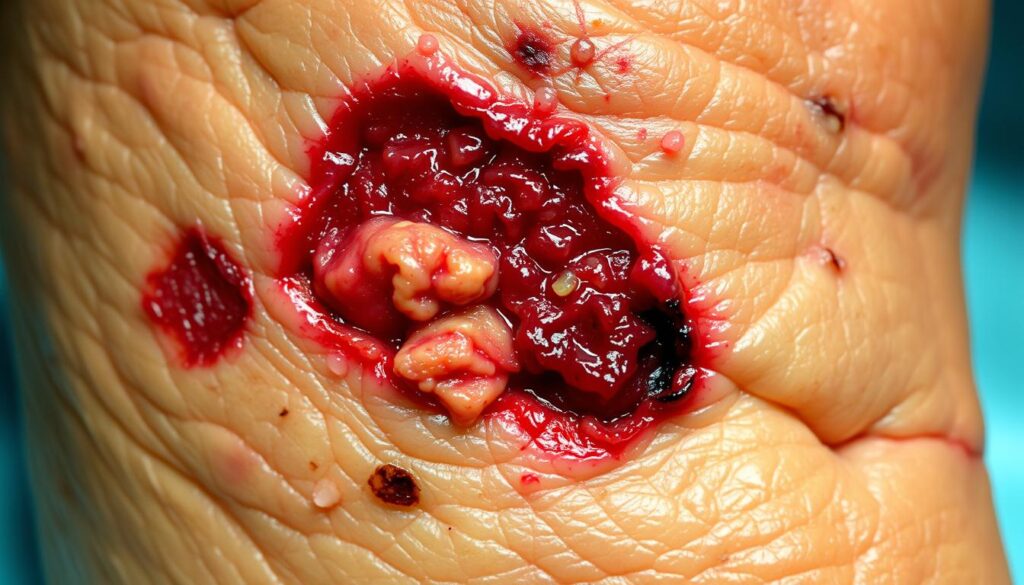
Gangrene is a serious condition where body tissue dies due to poor blood supply or severe infection. It can affect various body parts and lead to life-threatening complications1. Early detection is crucial, especially for internal organs.
Certain health conditions increase your risk of gangrene. Diabetes damages blood vessels, contributing to tissue death2. Atherosclerosis and peripheral artery disease slow blood circulation, raising gangrene risk2.
Smoking also harms blood flow throughout your body2. Trauma or serious injuries might create conditions leading to infection2. Gas gangrene, though rare, can be deadly within 48 hours if untreated3.
About 1,000 people in the United States develop gas gangrene each year3. Knowing gangrene triggers helps you take preventive steps. Quick action is key to successful treatment.
Key Takeaways
- Gangrene is a serious condition involving tissue death
- Diabetes and circulation issues increase gangrene risk
- Early detection is critical for successful treatment
- Gas gangrene can be fatal if not promptly addressed
- Various body parts can be affected by gangrene
What is Gangrene and How Does It Develop?
Gangrene is a severe medical issue where body tissue dies. It happens when blood supply stops or a bad bacterial infection occurs4. Your tissues need constant blood flow to live.
When this flow stops, the results can be awful. This problem often affects arms, legs, toes, and fingers4.
Understanding the Basics of Gangrene
Many factors can trigger gangrene. It’s vital to know its types and possible risks. Recognizing these can help prevent serious problems.
Types of Gangrene
- Dry Gangrene: Develops slowly, often linked to diabetes or blood vessel diseases4
- Wet Gangrene: Fast bacterial infection that spreads quickly5
- Gas Gangrene: Affects deep muscle tissue, caused by specific bacteria4
- Internal Gangrene: Impacts internal organs and can be very dangerous4
Symptoms to Watch For
Spotting gangrene early can save your life. Look out for these warning signs:
- Skin discoloration
- Swelling and pain
- Numbness in affected areas
- Foul-smelling discharge
- Persistent fever
Early identification and treatment significantly improve your chances of recovery4.
Risk factors include diabetes, blood vessel disease, and severe injuries. Smoking, obesity, and weak immune systems also increase risk5.
Knowing these risks helps you protect your health. Take action to prevent this serious condition.
Common Causes and Risk Factors of Gangrene
Gangrene prevention requires understanding its causes. Healthy tissue depends on good blood flow and a strong immune system. Your body needs these to fight off gangrene.
Infection and Its Role in Tissue Damage
Bacterial infections are a major cause of gangrene. People with weak immune systems are more likely to get this serious condition6.
Skin infections, dog bites, and injuries can let harmful bacteria in. These bacteria can quickly destroy tissue7.
Reduced Blood Flow and Circulation Challenges
Some health issues can harm your blood vessels. This can raise your risk of gangrene:
- Diabetes impacts blood circulation, especially in extremities6
- Atherosclerosis narrows blood vessels7
- Peripheral artery disease reduces blood flow8
Key Risk Factors to Understand
| Risk Category | Specific Risks |
|---|---|
| Medical Conditions | Diabetes, Raynaud’s syndrome |
| Lifestyle Factors | Smoking, obesity |
| Age-Related Risks | Over 60 years old6 |
Smoking harms blood vessels and greatly increases gangrene risk8. Your age, health, and lifestyle choices affect your chances of getting gangrene7.
Prevention is always better than treatment when it comes to gangrene.
Manage chronic conditions to lower your risk. Keep good circulation and stay healthy. Talk to your doctor about your specific health concerns.
Treatment Options for Gangrene
Your medical team will create a tailored treatment plan for gangrene. Surgical interventions are crucial in managing this serious health issue. Debridement removes dead tissue and stops its spread9.
Depending on severity, your doctor might suggest vascular surgery or amputation9. Antibiotics are vital in fighting gangrene, especially when infections occur. Your doctor may prescribe injections or tablets to combat bacterial infections9.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is an innovative treatment for certain gangrene types9. It exposes the affected area to high-pressure oxygen, helping your body fight harmful bacteria10. This therapy can speed up healing and prevent infection spread.
In advanced cases, reconstructive procedures like skin grafting might be necessary10. However, this depends on having adequate blood supply to the affected area. Your medical team will monitor your progress closely.
Quick treatment improves your chances of recovery and prevents complications10. Your active participation in treatment and follow-up care is essential. Work closely with your healthcare providers and maintain open communication about your recovery.
FAQ
What exactly is gangrene?
What are the different types of gangrene?
What are the primary symptoms of gangrene?
What causes gangrene?
Who is at higher risk of developing gangrene?
How is gangrene treated?
When should I seek emergency medical care?
Can gangrene be prevented?
Source Links
- Gangrene – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/gangrene/
- Gangrene: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments – https://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/gangrene-causes-symptoms-treatments
- Gangrene: Types, Symptoms, Risk Factors, and Diagnosis – https://www.healthline.com/health/gangrene
- Sore, shiny and swollen skin: Is it gangrene?-Gangrene – Symptoms & causes – Mayo Clinic – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gangrene/symptoms-causes/syc-20352567
- Gangrene – https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/gangrene
- Gangrene – Causes – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/gangrene/causes/
- No title found – https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content?contenttypeid=134&contentid=151
- Gangrene: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment and Prevention – https://westcoastwound.com/gangrene-treatment-and-prevention/
- Gangrene – Treatment – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/gangrene/treatment/
- Sore, shiny and swollen skin: Is it gangrene?-Gangrene – Diagnosis & treatment – Mayo Clinic – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gangrene/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20352573