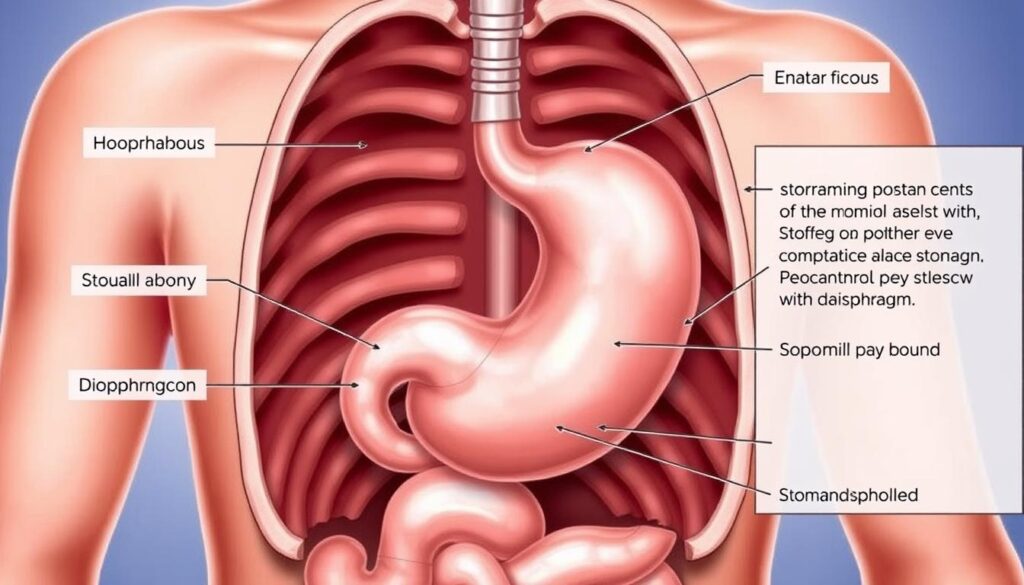
A Hiatal Hernia happens when your stomach pushes through the diaphragm into your chest. This can affect your digestion and life quality1. People over 50 are more likely to have this issue due to age-related diaphragm changes1.
Small hiatal hernias often cause no symptoms. However, larger ones can lead to discomfort. Acid reflux, heartburn, and chest pain may signal a diaphragmatic hernia2.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) often occurs with this condition. This creates extra challenges for patients.
Several factors can raise your chances of getting a hiatal hernia. These include obesity, chronic coughing, and frequent heavy lifting2. Knowing these risks can help you care for your digestive health.
Key Takeaways
- Hiatal hernias are more common in people over 50
- Not all hiatal hernias cause noticeable symptoms
- Obesity and physical strain can increase hernia risk
- Acid reflux is a potential complication
- Regular medical check-ups can help detect hiatal hernias early
What is a Hiatal Hernia?
A hiatal hernia happens when your stomach pushes through the diaphragm. This creates an unusual opening between your chest and abdomen. Knowing about this condition can help you manage potential health issues better.
Types of Hiatal Hernias
There are two main types of hiatal hernias:
- Sliding Hiatal Hernia: The most common type, where the stomach and esophagus slide up into the chest through the hiatus3. More than 1 in 4 adults develop this type by age 404.
- Paraesophageal Hernia: Less common but potentially more serious, where part of the stomach squeezes next to the esophagus3.
Classification of Hiatal Hernias
Doctors use a detailed system to classify hiatal hernias:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Type 1 (Sliding) | Most common type, involving minimal displacement |
| Type 2 (Paraesophageal) | Stomach protrudes through diaphragm opening |
| Type 3 (Mixed) | Combination of sliding and paraesophageal characteristics |
Causes and Risk Factors
Several things can lead to a hiatal hernia:
- Age: More prevalent in individuals over 505
- Obesity: Increases pressure on abdominal muscles
- Chronic coughing or sneezing
- Pregnancy
- Intense physical activities
Understanding your risk factors can help you take proactive steps in managing potential hiatal hernia development.
Most hiatal hernias aren’t immediately dangerous. However, some paraesophageal hernias can get worse and need medical help4.
If you have ongoing symptoms, it’s best to see a doctor5. They can provide proper diagnosis and treatment options.
Recognizing Hiatal Hernia Symptoms
Hiatal hernias can cause unexpected discomfort. Knowing these signs helps you manage your health better. Understanding symptoms allows for early action and improved care.
Common Symptoms You May Experience
Hiatal hernias often come with distinct signs. Spotting these early can greatly impact your treatment’s success.
- Persistent acid reflux and heartburn
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Difficulty swallowing
- Regurgitation of food or liquids
Women and those over 50 face higher risks of hiatal hernias67. Pain usually occurs in the chest or stomach area. This can make daily tasks quite uncomfortable.
When to Consult a Doctor
Not all symptoms need immediate medical care. However, some signs require professional attention:
| Warning Signs | Recommended Action |
|---|---|
| Persistent chest pain | Seek medical evaluation |
| Difficulty swallowing | Immediate doctor consultation |
| Chronic acid reflux | Schedule a comprehensive check-up |
GERD symptoms can greatly affect your daily life. Over-the-counter meds might help temporarily6. But ongoing symptoms need a doctor’s assessment.
Your body communicates through symptoms—listen carefully and seek expert guidance when needed.
Obesity, pregnancy, and chronic straining raise hiatal hernia risks7. Prevent issues by adopting healthy habits. Stay in touch with your doctor to manage potential problems.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
Diagnosing a hiatal hernia involves various tests. These help doctors understand your condition’s specifics. Healthcare providers use multiple methods to identify and assess diaphragmatic hernias8.
Diagnostic Tests for Hiatal Hernia
Your medical evaluation may include several key procedures:
- Upper Endoscopy: A tiny camera examines your esophagus and stomach
- X-ray Imaging: Helps visualize the upper digestive system
- Esophageal Manometry: Measures muscle contractions in the esophagus
An upper endoscopy allows doctors to view the digestive tract directly. This helps identify potential hernia repair surgery needs9.
Understanding Your Doctor’s Findings
Test results reveal the type and severity of your hiatal hernia. Sliding hiatal hernias are most common, making up about 95% of cases8.
Your doctor will decide if anti-reflux surgery is needed based on these findings10.
Early detection and proper evaluation are crucial in managing hiatal hernia effectively.
The diagnostic process guides your medical team. It helps create a personalized treatment plan for your specific condition8.
Treatment Options for Hiatal Hernia
Hiatal hernia treatment varies based on severity. Your doctor will create a personalized plan for you. This may include lifestyle changes, medications, or surgery11.
Lifestyle changes can greatly improve your condition. Eat smaller meals and avoid trigger foods. Maintaining a healthy weight is also crucial12.
Over-the-counter medications like antacids can help manage acid reflux. For severe cases, doctors may prescribe omeprazole or esomeprazole11.
Surgery becomes necessary when other treatments fail. Nissen fundoplication is the most common anti-reflux surgery. It wraps the upper stomach around the lower esophagus11.
This surgery has shown great results. It boasts an 89.5% success rate over 10 years13. Large hernias or persistent symptoms may require surgical intervention12.
Surgeons can use open surgery or minimally invasive techniques. Your treatment plan is unique to you. Work closely with your doctor for effective management12.
FAQ
What exactly is a hiatal hernia?
What are the main types of hiatal hernias?
What causes a hiatal hernia?
What are the most common symptoms of a hiatal hernia?
How is a hiatal hernia diagnosed?
What treatment options are available for a hiatal hernia?
When should I see a doctor about a possible hiatal hernia?
Can a hiatal hernia be prevented?
Source Links
- Hiatal hernia – Symptoms and causes – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hiatal-hernia/symptoms-causes/syc-20373379
- Hiatal Hernia: A Hidden Cause of Acid Reflux – https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/8098-hiatal-hernia
- Find Out the Differences by Types of Hiatal Hernia! – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6955185/
- Paraesophageal Hernia (Hiatal Hernia) | Minimally Invasive and Gastrointestinal Surgery – https://www.mcw.edu/departments/surgery/divisions/minimally-invasive-and-gastrointestinal-surgery/patient-care/gerd-and-gastrointestinal-surgery-program/paraesophageal-hernia-hiatal-hernia
- Hiatal hernia – https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/diseases-conditions/hiatal-hernia
- Hiatal Hernia – https://www.pennstatehealth.org/services-treatments/hiatal-hernia
- Hiatal Hernia Symptoms & Treatment | Aurora Health Care – https://www.aurorahealthcare.org/services/gastroenterology-colorectal-surgery/hiatus-hernia-hiatal-hernia
- An Overview of Hiatal Hernia – https://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/hiatal-hernia
- Approaches to the Diagnosis and Grading of Hiatal Hernia – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2548324/
- Approach Considerations, Imaging Studies, Procedures – https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/178393-workup
- You Don’t Always Need Surgery To Treat a Hiatal Hernia: 13 Other Ways To Find Relief – https://www.health.com/hiatal-hernia-treatment-8302968
- Hiatal Hernia: Symptoms, Surgery, Treatment, and More – https://www.healthline.com/health/hiatal-hernia
- Treatment Options for Hiatal Hernia – https://www.verywellhealth.com/treating-hiatal-hernias-1742603