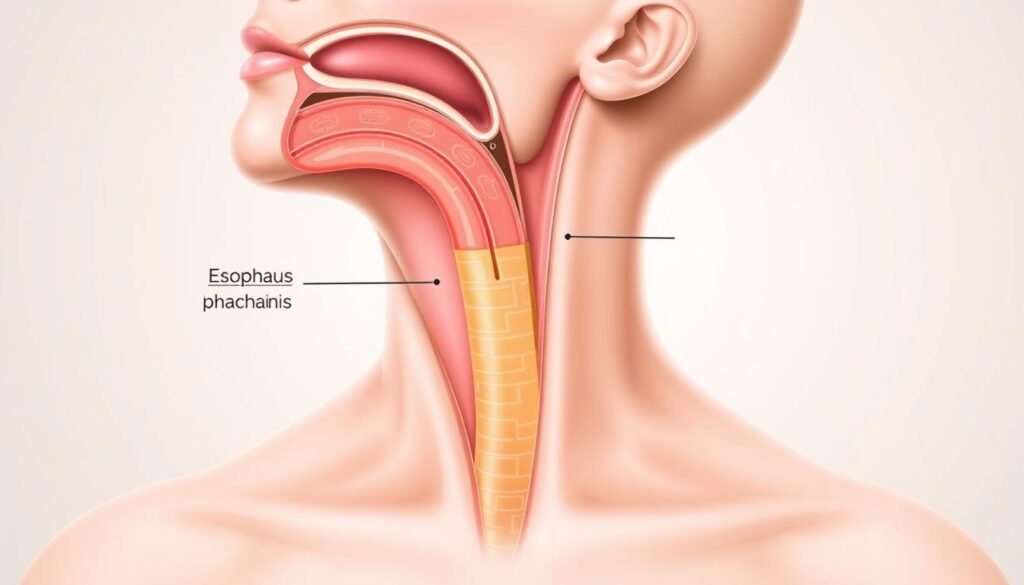
Dysphagia affects your ability to swallow food and drinks safely. It can cause mild discomfort or serious health issues. This complex condition impacts how you move food from mouth to stomach12.
Several factors can trigger swallowing disorders. These include neurological problems, weak muscles, and structural issues1. Older adults often face this challenge, but it affects people with various conditions too.
Cerebral palsy, Parkinson’s disease, and head injuries can lead to dysphagia1. Knowing these details helps spot potential risks and get proper medical help2.
Swallowing difficulties can cause serious health problems. These include malnutrition, dehydration, and aspiration pneumonia2. Spotting symptoms early and seeing a doctor can prevent complications1.
Key Takeaways
- Dysphagia impacts safe food and liquid consumption
- Multiple medical conditions can cause swallowing disorders
- Early detection prevents serious health complications
- Treatment options vary based on underlying causes
- Professional medical evaluation is crucial
What is Dysphagia and Its Impact on Daily Life
Dysphagia is a complex swallowing disorder that disrupts eating3. It affects how you consume food and liquids. This condition creates challenges beyond simple meal times.
The Stages of Normal Swallowing
The swallowing process involves three critical stages:
- Oral Stage: Food preparation in the mouth
- Pharyngeal Stage: Transporting food through the throat
- Esophageal Stage: Moving food into the stomach
Common Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing oropharyngeal dysphagia symptoms is crucial for early intervention. Patients might experience:
- Pain while swallowing
- Sensation of food stuck in throat
- Unexpected weight loss
- Persistent drooling
Impact on Quality of Life
Dysphagia can change your relationship with eating3. It may cause malnutrition, dehydration, and social isolation4.
Patients often enjoy meals less. They may avoid eating with others outside their close family.
Understanding dysphagia is the first step toward managing its challenges effectively.
Managing dysphagia often requires modified diet textures and special eating strategies4. Patients adapt by eating slowly and taking smaller bites.
They also adjust food consistencies to make swallowing easier. These changes help them cope with daily challenges.
| Dysphagia Type | Primary Affected Area | Common Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Oropharyngeal Dysphagia | Mouth and Throat | Difficulty initiating swallow |
| Esophageal Dysphagia | Esophagus | Feeling of food stuck in chest |
Seeking professional medical guidance is essential for proper diagnosis and personalized treatment of dysphagia.
Types and Causes of Dysphagia
Swallowing difficulties can greatly affect your daily life. They impact nutrition, communication, and overall well-being. Knowing the types and causes of dysphagia helps with diagnosis and treatment.
Oropharyngeal Dysphagia: Understanding Neural and Muscular Challenges
Oropharyngeal dysphagia starts in the throat and mouth. It often stems from neurological or muscular conditions. Patients may struggle to start swallowing due to weak muscles or neural control issues5.
Common causes include:
- Stroke
- Parkinson’s disease
- Multiple sclerosis
- Neurological disorders
Esophageal Dysphagia and Its Complex Origins
Esophageal dysphagia makes moving food through the esophagus difficult. It can result from various medical conditions, including acid reflux and structural abnormalities5.
Potential causes include:
- Achalasia
- Esophageal spasms
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
Medical Conditions Leading to Swallowing Difficulties
Many medical conditions can cause dysphagia. About one in 25 adults face swallowing problems each year6. The risk grows with age and links to various health issues7.
| Condition Category | Potential Impact on Swallowing |
|---|---|
| Neurological Disorders | Muscle weakness, nerve damage |
| Head and Neck Cancers | Structural changes, treatment side effects |
| Respiratory Conditions | Inflammation, muscle dysfunction |
Diagnostic tools are key in assessing swallowing disorders. These include videofluoroscopic swallow study and fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation7.
“Early detection and appropriate swallowing therapy can significantly improve patient outcomes and quality of life.”
Modern Treatment Approaches for Swallowing Disorders
Dysphagia management requires a tailored approach. Swallowing therapy offers techniques to boost muscle strength and coordination. It helps you tackle eating and drinking challenges8.
Your doctor may suggest various strategies to reduce aspiration risk. These aim to improve your overall swallowing function9.
Therapeutic interventions often include:
- Speech and language therapy exercises9
- Modified diet textures to ensure safe eating9
- Electrical stimulation techniques9
- Specialized swallowing techniques
For complex cases, doctors might explore advanced options. Surgical interventions can fix structural issues affecting safe swallowing10. These may include esophageal dilation or techniques to enhance muscle function10.
Dietary changes are key in managing dysphagia. Your nutritionist might suggest:
| Strategy | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Thickened liquids | Reduce aspiration risk |
| Pureed foods | Easier swallowing |
| Smaller food portions | Improve swallowing control |
Successful dysphagia management requires a personalized approach that combines medical expertise, therapeutic techniques, and patient commitment.
Remember, early intervention and consistent therapy can significantly improve your swallowing function and quality of life. Team up with your healthcare providers to create an effective treatment plan9.
Conclusion
Swallowing disorders affect many people, especially older adults. Up to 50% of seniors may experience dysphagia. With the right knowledge and support, managing this condition becomes easier.
Detecting dysphagia early is key. Half of patients don’t report their symptoms to doctors. This can lead to complications. If you have trouble swallowing, talk to your doctor right away.
New diagnostic methods offer more accurate ways to understand and treat dysphagia. Medical professionals are developing innovative techniques to help those with swallowing difficulties.
Working with speech-language pathologists and specialists can improve your quality of life. They can help you create personalized strategies to manage dysphagia effectively.
Dysphagia isn’t an unavoidable part of aging. Proper care and medical help can make a big difference. Stay informed and seek professional guidance to address your swallowing challenges successfully1112.
FAQ
What is dysphagia?
What are the main symptoms of dysphagia?
What causes dysphagia?
How is dysphagia diagnosed?
What treatment options are available for dysphagia?
Can dysphagia be prevented?
How does dysphagia affect quality of life?
Are there different types of dysphagia?
Source Links
- Dysphagia – https://www.nidcd.nih.gov/health/dysphagia
- Dysphagia – Symptoms and causes – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/dysphagia/symptoms-causes/syc-20372028
- Dysphagia (swallowing problems) – https://www.nhsinform.scot/illnesses-and-conditions/stomach-liver-and-gastrointestinal-tract/dysphagia-swallowing-problems/
- Social importance of dysphagia: its impact on diagnosis and therapy – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2640007/
- Dysphagia (swallowing problems) – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/swallowing-problems-dysphagia/
- Dysphagia Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options – https://www.tgh.org/institutes-and-services/conditions/dysphagia
- Types – https://stanfordhealthcare.org/medical-conditions/digestion-and-metabolic-health/dysphagia/types.html
- Advances in the Treatment of Dysphagia in Neurological Disorders: A Review of Current Evidence and Future Considerations – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9578488/
- Effective Clinical Strategies for Managing Swallowing Disorders – https://www.beckerentandallergy.com/blog/strategies-for-swallowing-disorders
- Dysphagia – Diagnosis and treatment – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/dysphagia/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20372033
- Dysphagia – PMC – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6140149/
- Dysphagia – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559174/